

Essential Safety Tips for Products Used During Disasters in Japan
Being Prepared for Disasters
Japan is a country frequently impacted by natural disasters such as earthquakes, typhoons, and heavy rainfall. Many citizens prepare for such events by stocking up on supplies, including emergency food, gas cylinders, portable stoves, and generators to use when utilities like gas and electricity are interrupted. However, these essential products can also pose risks, with reports of accidents leading to fatalities.
The National Institute of Technology and Evaluation (NITE), led by Director Fumihiko Hasegawa from Shibuya, Tokyo, has issued an advisory ahead of Disaster Prevention Day on September 1. The focus is on the important precautions to take when utilizing these life-saving products in times of crisis.
Key Precautions for Emergency Products
1. Gas Supply Substitute Products
- Gas Canisters: Be mindful of aging products. Check for proper attachment to devices and ensure there's no gas leakage. Never use canisters inappropriately in ways that cause them to overheat.
- Store canisters away from heat sources in a cool location below 40°C.
2. Electric Supply Substitute Products
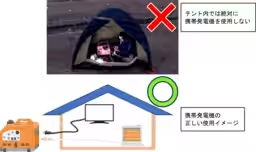
- Portable Generators: It's imperative to use generators outdoors in well-ventilated areas. Using them indoors can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning, a serious risk.
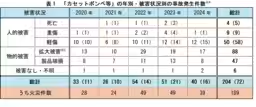
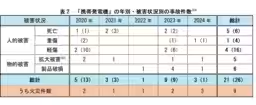
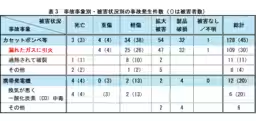
From 2020 to 2024, NITE compiled reports of 204 accidents involving gas canisters and 21 involving generators. Many of these accidents arose from improper usage or deterioration of the products over time, underscoring the need for regular checks and adherence to safety protocols.
Common Accident Scenarios
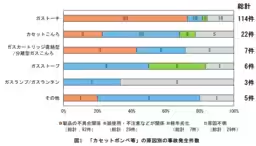
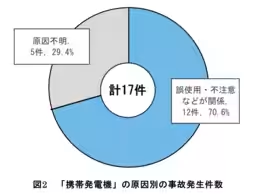
NITE's data reveals that significant numbers of incidents stemmed from mishandling. Gas-related accidents typically involved leaks leading to fires, while generator accidents frequently resulted from indoor use, exposing users to dangerous carbon monoxide. Always ensure that you are aware of product recalls and current safety information.
Understanding the Risks
- - Yearly Breakdown of Incidents: Accidents involving gas canisters often resulted in fires or injuries, while generator incidents led to multiple injuries from carbon monoxide intoxication, sometimes resulting in fatalities.
- - Causes of Accidents: Reports confirm that aging components, misuse, and negligence contributed prominently to these incidents. Specifically, older gas canisters may leak if not inspected regularly, and incorrect installation can lead to catastrophic consequences.
Guidelines for Using Gas Cylinders
1. Monitor for Aging: Gas cylinders can deteriorate over time, risking leakage. Consume old canisters first, and ensure you're regularly replacing your stock.
2. Correct Installation: Always follow the manufacturer's instructions when attaching gas canisters. Misinstallation can lead to serious risks.
3. Avoid Overheating: Do not expose canisters to excessive heat, which can expand the gas and cause explosions. Keep them away from any heat sources.
4. Safety in Storage: Store canisters in cool, shaded areas, ensuring they are capped tightly before storage.
Guidelines for Using Portable Generators
1. NO Indoor Use: Generators must only be used outside to prevent toxic gas accumulation which can lead to poisoning.
2. Ensure Ventilation: Pay attention to wind direction when setting up to avoid smoke entering living areas.
3. Electrical Safety: During wet weather, protect the generator from moisture to prevent electric shocks.
Utilizing NITE SAFE-Lite
NITE offers a web-based tool called NITE SAFE-Lite for consumers to check for safety recalls and incidents related to specific products. By entering the names of familiar products, users can access a wealth of safety information. This proactive approach aims to minimize risks and ensure public safety during emergencies.
For more details and to access the search tool, please visit: NITE SAFE-Lite
Conclusion
While preparation for emergencies is essential, using your prepared products safely is even more crucial. Familiarize yourself with handling emergency products and keep consistent checks on their condition for a safer experience during disasters. By adhering to these precautions, you can significantly reduce the risks associated with emergency preparedness.









Topics Policy & Public Interest)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.