

Exploring Strategies for Age-Friendly Societies in Asia: Insights from CAPS
Addressing Aging in Asia: Strategic Priorities
In response to the rapid aging of societies across Asia, the Centre for Asian Philanthropy and Society (CAPS) has unveiled a comprehensive report titled _Building Age-Friendly Societies in Asia: Philanthropy and Private Social Investment for the Elderly_, translated into Japanese as _アジアにおける高齢者に優しい社会の構築_. This report aims to identify effective strategies to harness philanthropic and private investments to support the elderly.
Overview of the Report
The report investigates the profound changes instigated by aging populations in various Asian nations, including China, Hong Kong, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, and Thailand. It identifies and recommends five strategic priorities to guide philanthropic and private investments towards sustainable, age-friendly environments. These strategies are tailored to optimize the use of limited private funds effectively.
The Japan NPO Center was instrumental as the Japanese partner for this research project, offering insights from Japan’s aging experiences. Their contribution enriches the understanding of how these experiences can inform broader regional solutions across Asia. The report serves as a crucial guide for philanthropists, business leaders, investors, policymakers, and NGOs in making impactful investments in the aging sector.
Key Findings of the Research
Among the critical insights outlined in the report:
1. Demographic Shift: Asia is experiencing a sharp transition into 'super-aged societies,' with increasing life expectancy and declining birth rates placing persistent pressure on pensions, finances, families, and communities.
2. Challenges in Care Systems: The public long-term care insurance system is under financial stress, struggling to meet the diverse needs of the demographic, particularly the 'missing middle.' This highlights that public systems alone cannot cater to all requirements.
3. Funding Landscape: Current funding sources—public budgets, philanthropy, business, and impact investing—are fragmented. Despite being adaptable, philanthropic efforts have not sufficiently focused on aging issues, and business investments often reflect short-term trends. Furthermore, impact investments in the aging sector remain largely unexplored.
4. Collaboration in Funding: Simply increasing the number of funding sources will not suffice. Genuine progress requires cooperative efforts between government, philanthropy, and private sectors, leveraging their respective strengths effectively to achieve common objectives.
5. Investment for the Future: The upcoming years will be pivotal in constructing systems, mindsets, and markets that empower elderly individuals to live with dignity, security, and purpose.
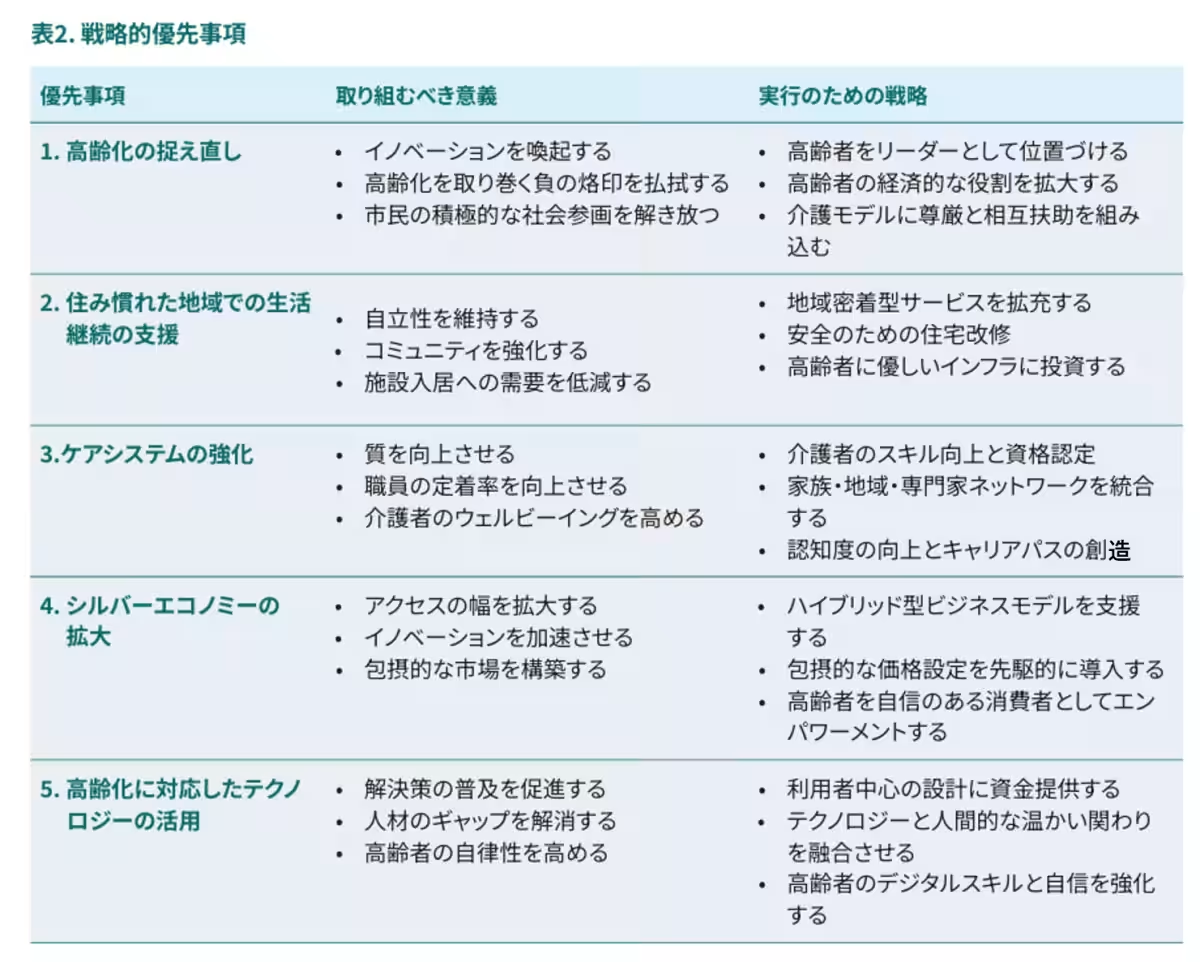
Five Strategic Priorities for Private Social Investments
The report identifies five strategic areas where private social investments can have an impactful influence:
- - Reframing Aging: Shift the perception of aging from a burden to a chance to tap into the leadership and economic contributions of older adults.
- - Supporting Local Living: Facilitate the continuation of life in familiar communities through local services, secure housing, and infrastructure development.
- - Fortifying Care Systems: Strengthen the care system by investing in caregiver skills, well-being, and career paths.
- - Expanding the Silver Economy: Grow the market in an inclusive manner to benefit a wide range of older adults.
- - Leveraging Technology: Utilize user-oriented technology designed to enhance autonomy combined with human support systems.
Insights for Japan from the Research
Through the lens of Asia, this investigation offers crucial insights for Japan. As a leading nation in aging, Japan serves as a vital model for how to address various challenges that other Asian countries may soon confront.
- - A Benchmark for Care Insurance: Japan's long-term care insurance is an international benchmark but also reflects the financial and human resource strains associated with aging demographics.
- - Regional Care Insights: The insights from Japan’s integrated community care models offer valuable lessons, emphasizing the need to address persistent issues such as elderly isolation and economic instability.
- - Contributions to Regional Best Practices: Japan's innovative approaches, such as community center establishment and sector collaborations, exemplify concrete cases of how actors can operate creatively within existing frameworks, contributing to best practices across Asia.
These reflections on Japan’s policies, funding strategies, and innovation pathways are essential resources for other Asian countries.
About the Organizations
The Centre for Asian Philanthropy and Society (CAPS) is an independent research and advisory entity focused on enhancing philanthropy throughout Asia. Established in 2013, its mission is to improve both the quality and quantity of philanthropic efforts in the region.
The Japan NPO Center, designated as an infrastructure organization, was founded in 1996 to strengthen the social foundations of the non-profit sector and establish new partnerships between these organizations and enterprises or government.
For Further Inquiries
For more information regarding this release, please contact:
- - CAPS: Sonalie Figueiras, [email protected], +852 3611 0250
- - Japan NPO Center: 土屋, [email protected], 03 3510 0855

Topics People & Culture)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.