

Evaluating Residential Satisfaction: The 2024 Town Living Ranking Report by Daito Trust Construction
Overview of the 2024 Town Living Ranking Report
Daito Trust Construction, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, has published an extensive report on residential satisfaction titled "2024 Town Living Ranking Report." This survey, the most comprehensive of its kind, assesses living satisfaction across 1,890 municipalities in Japan, including responses from over 842,000 individuals aged 20 and above. It began publishing rankings in May 2024, focusing initially on the Greater Tokyo area, followed by insights from various regions over the year.
In this report, the impact of overtourism on residential satisfaction has been analyzed, revealing that the number of tourists does not significantly influence living conditions. The detailed results of this analysis are crucial for understanding how local environments coexist with tourism.
Key Points of the 2024 Report
1. Influence of Overtourism on Living Conditions
By 2025, Japan expects about 3.5 million foreign visitors, marking a peak and drawing media attention towards overtourism considered as "tourism pollution." Despite this, the correlation between tourist numbers and residential satisfaction is not straightforward. This report utilizes data from the Japan Tourism Promotion Association, combining visitor statistics for 2024 and living satisfaction metrics to assess this relationship.
2. Factors Affecting Living Conditions
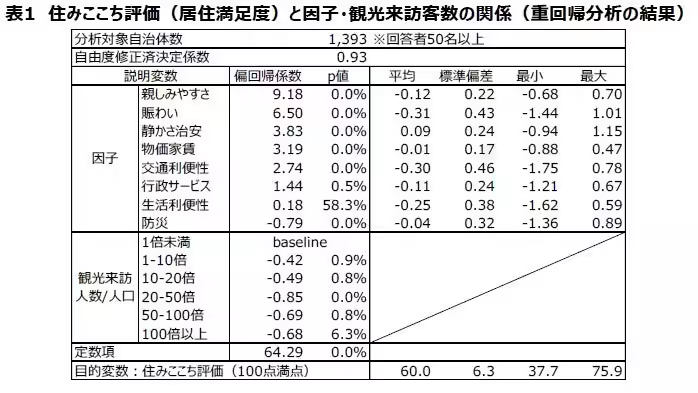
The analysis employed factor analysis on 47 questions from the living satisfaction survey, extracting eight factors that affect residents' experiences. Findings indicate that factors such as "friendliness" and "vibrancy" weighed heavily in influencing satisfaction, while the impact of "administrative services" was minimal. Each factor's significance was quantified against a scale of 100.
3. Limited Impact of Tourist Numbers on Residential Satisfaction
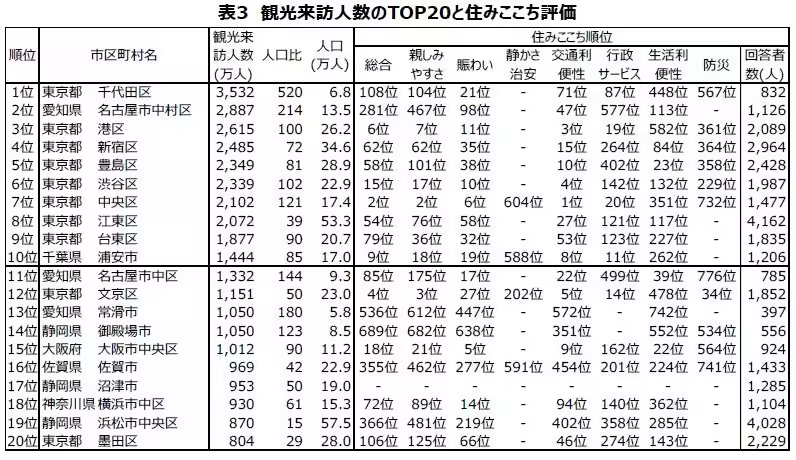
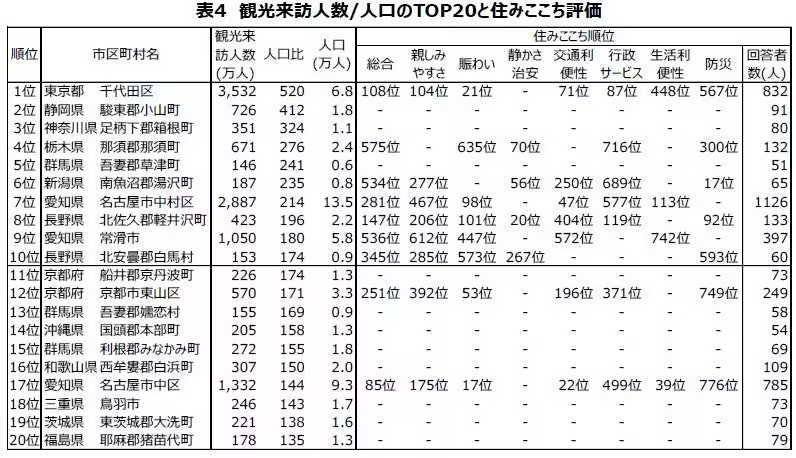
Calculating the ratio of tourist numbers to the local population revealed that areas with more tourists did not correlate positively with higher living satisfaction scores. Most municipalities saw a score below one, indicating virtually no effect on satisfaction ratings, which averaged around 60 out of 100 with a standard deviation of 6.3. Even in popular tourist areas, high tourist volumes did not correspond with higher satisfaction levels.
Regression Analysis of Influencing Factors
- - Friendliness and vibrancy hold significant weight: A fluctuation in the friendless score by one unit results in an approximately 9 point change in satisfaction ratings.
- - Administrative services have a negligible impact: Any slight change in this area only shifts the overall satisfaction rating by about 1.44 points.
- - Convenience of living showed no significant correlation, with a p-value demonstrating lack of statistical significance.
Observations from the Data
The statistics reveal interesting patterns: urban destinations noted for large tourist volumes also generally rate higher in living satisfaction. However, municipalities renowned as tourist hotspots with a larger visitor-to-resident ratio often present lower satisfaction scores, suggesting other factors substantially influence residents' experiences.
Survey Methodology
Conducted by MacroMill, this survey collected data through online questionnaires distributed to registered monitors, spanning 47 prefectures and involving a total of 842,238 respondents between 20 and older, from 2019 to 2024.
The results from these analyses provide critical insights for municipalities to manage tourism growth while enhancing residential satisfaction. With more data available upon request for specific areas, Daito Trust Construction continues to support community development aligned with resident needs.
For further details, visit Daito Trust Construction’s Survey and their press release page here.


Topics People & Culture)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.