

The Alarming Rate of School Absence Among Children with Developmental Differences
The Alarming Rate of School Absence Among Children with Developmental Differences
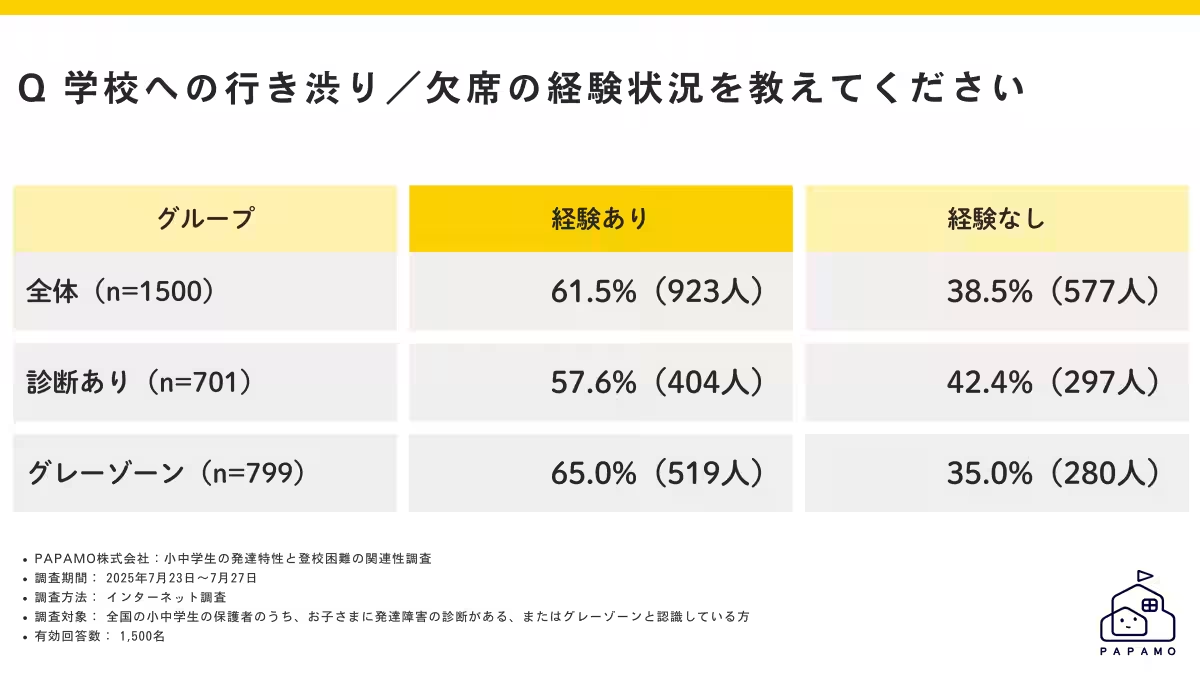
Recent data highlights a concerning trend regarding school attendance among children with developmental differences. A survey conducted by PAPAMO, a Tokyo-based company providing online developmental support services, has revealed that the absenteeism rate for elementary and middle school students with developmental traits is a staggering 35.5%. This statistic demonstrates that children exhibiting these developmental characteristics are nearly 9.5 times more likely to experience difficulty attending school than their peers.
The survey, which gathered responses from 1,500 parents of children diagnosed with or suspected of having developmental disabilities, also uncovered that 61.5% of these children have experienced reluctance or absence from school, indicating a significant issue that requires immediate attention.
Key Findings from the Survey
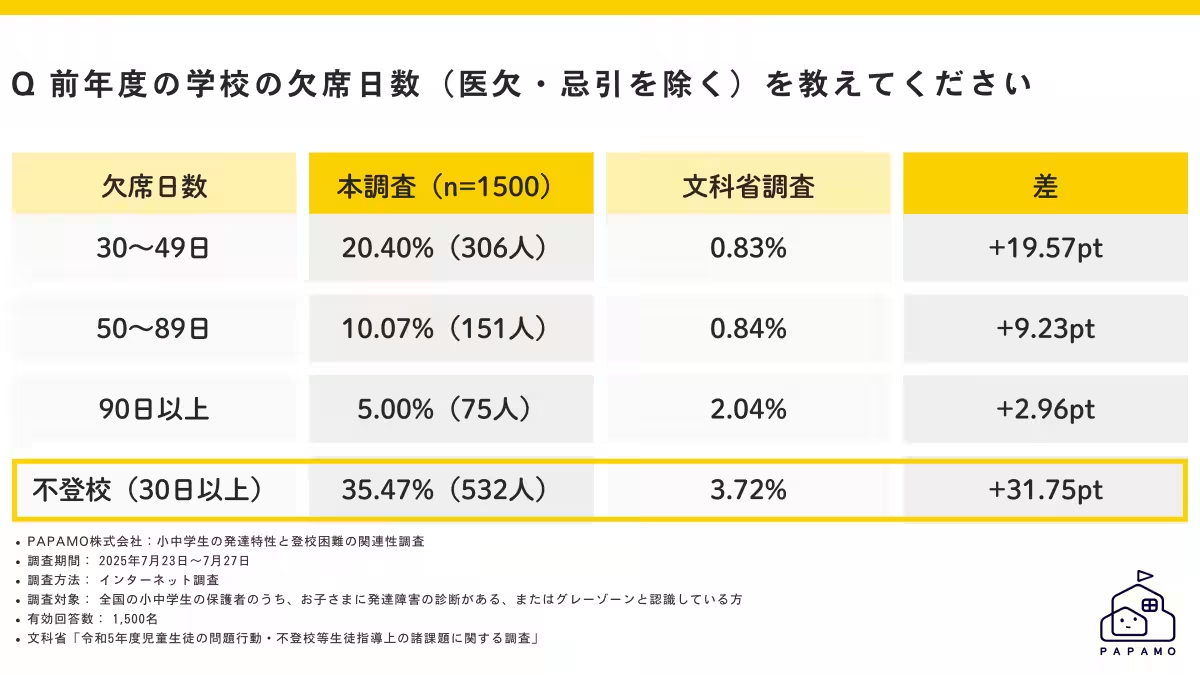
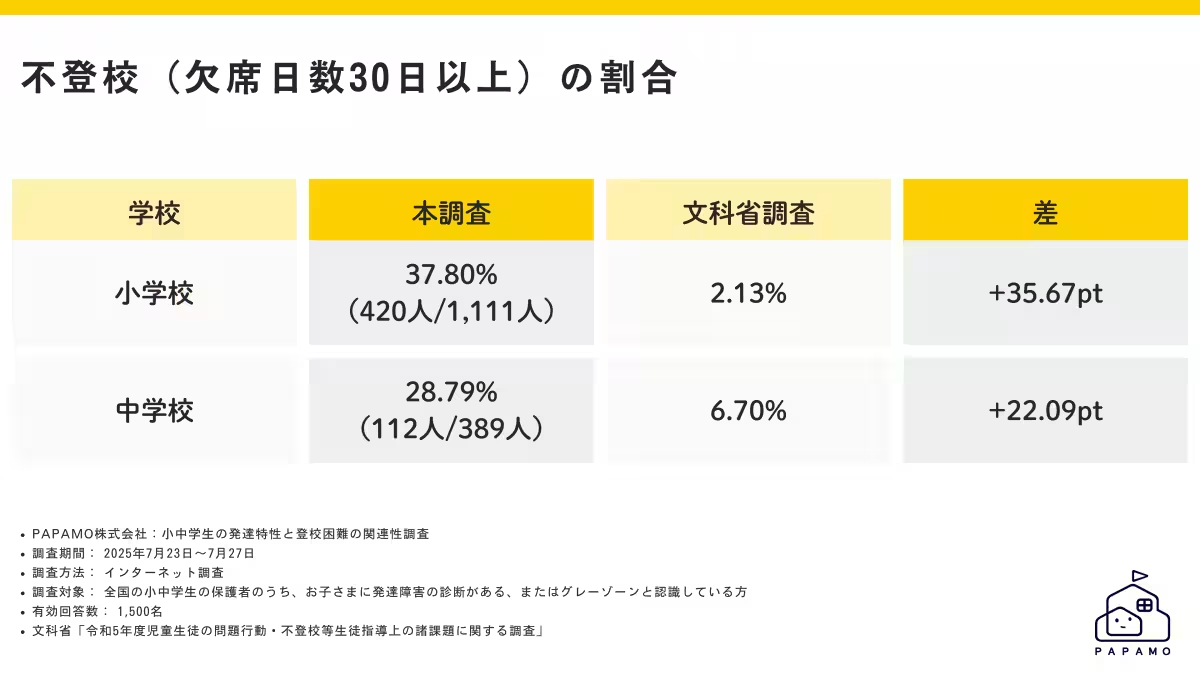
- - High Absenteeism Rates: The survey revealed that 35.5% of children with developmental traits missed 30 or more school days last year, excluding medically exempt absences. This figure starkly contrasts with the national absenteeism rate of just 3.72% for elementary and middle school students.
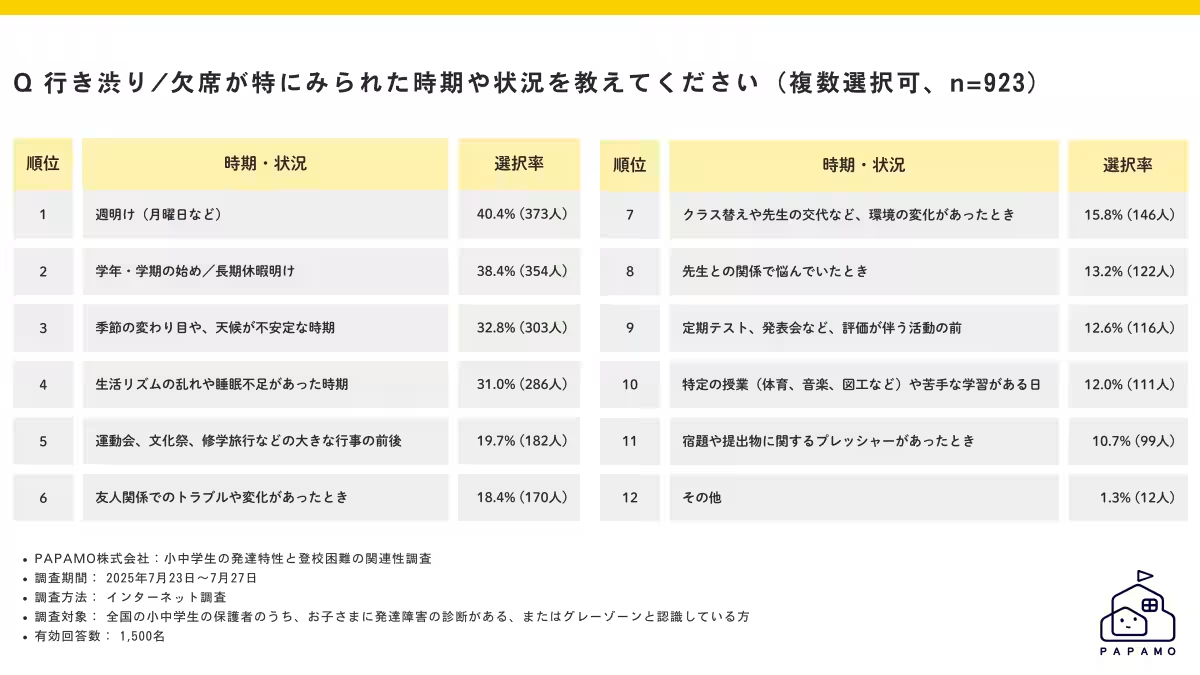
- - Anxiety Around School Attendance: Many children display difficulty in returning to school after vacations or weekends. The study revealed that a notable 40.4% of respondents cited difficulties returning to school on Mondays, with 38.4% reporting that these difficulties were particularly acute after long breaks, such as summer vacations, and during seasonal transitions.
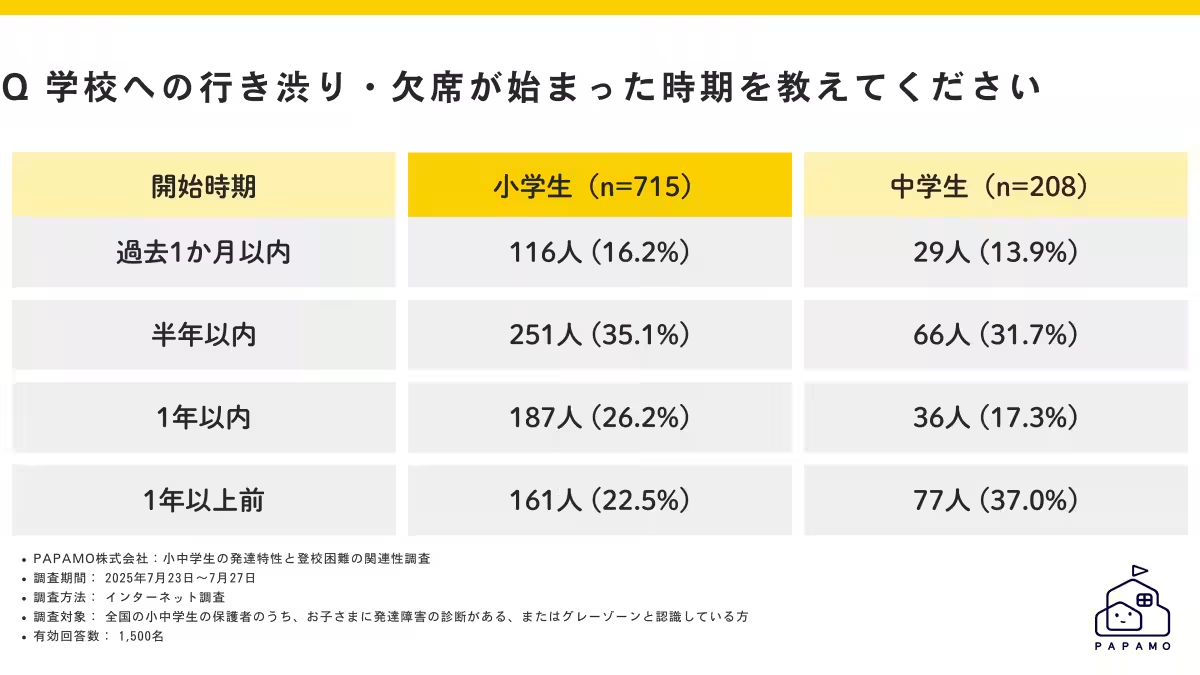
- - Long-Term Absenteeism: The results also indicated that 22.5% of elementary students and 37.0% of middle school students have been reluctant to attend school for over a year, suggesting that these issues have persisted over time and could benefit from early intervention strategies.
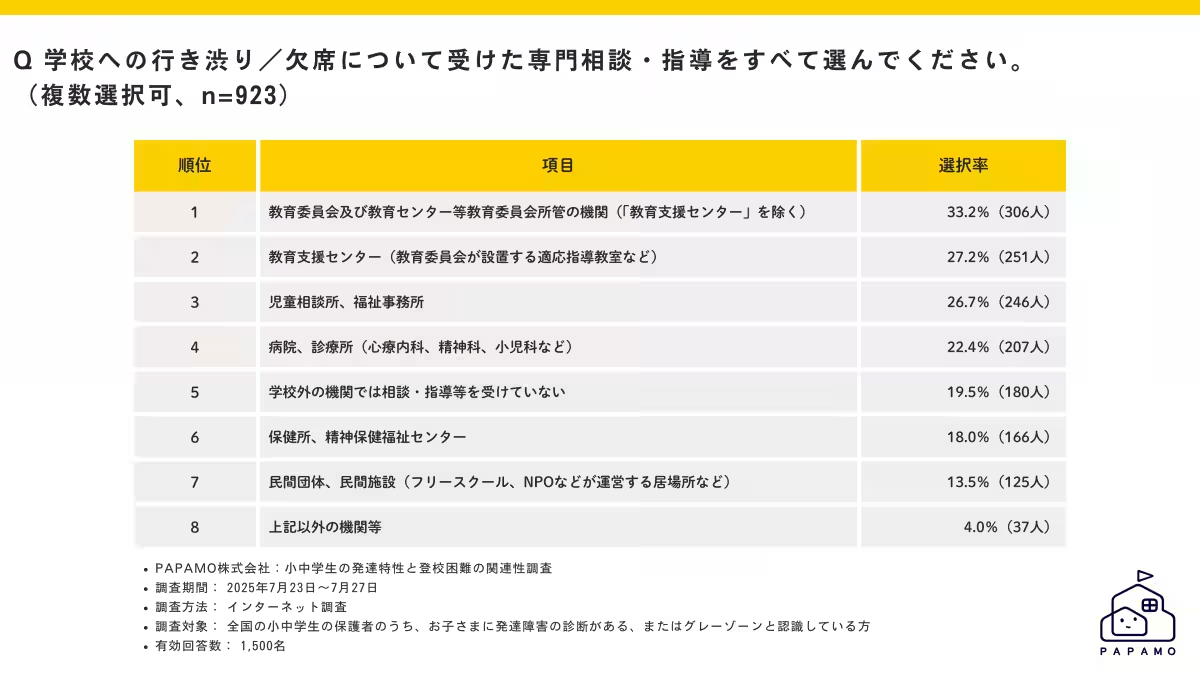
- - Access to Support Services: Alarmingly, 19.5% of respondents reported that their children were not receiving any external support that could assist with school attendance issues. This shows a significant gap in access to necessary resources that could help these children.
The Need for Inclusive Support
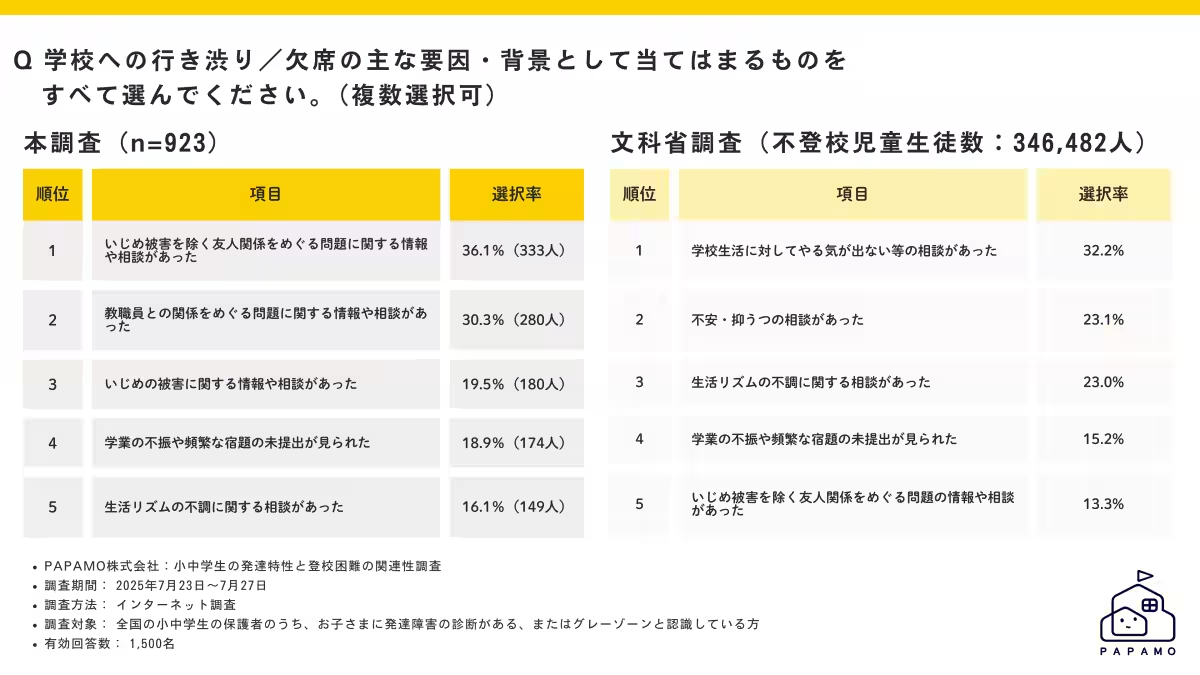
The findings suggest that many children with developmental traits encounter difficulties in interpersonal relationships, which may contribute to school avoidance. Parental responses indicated that the top reasons for reluctance to attend school were rooted in social challenges rather than a lack of motivation towards school activities.
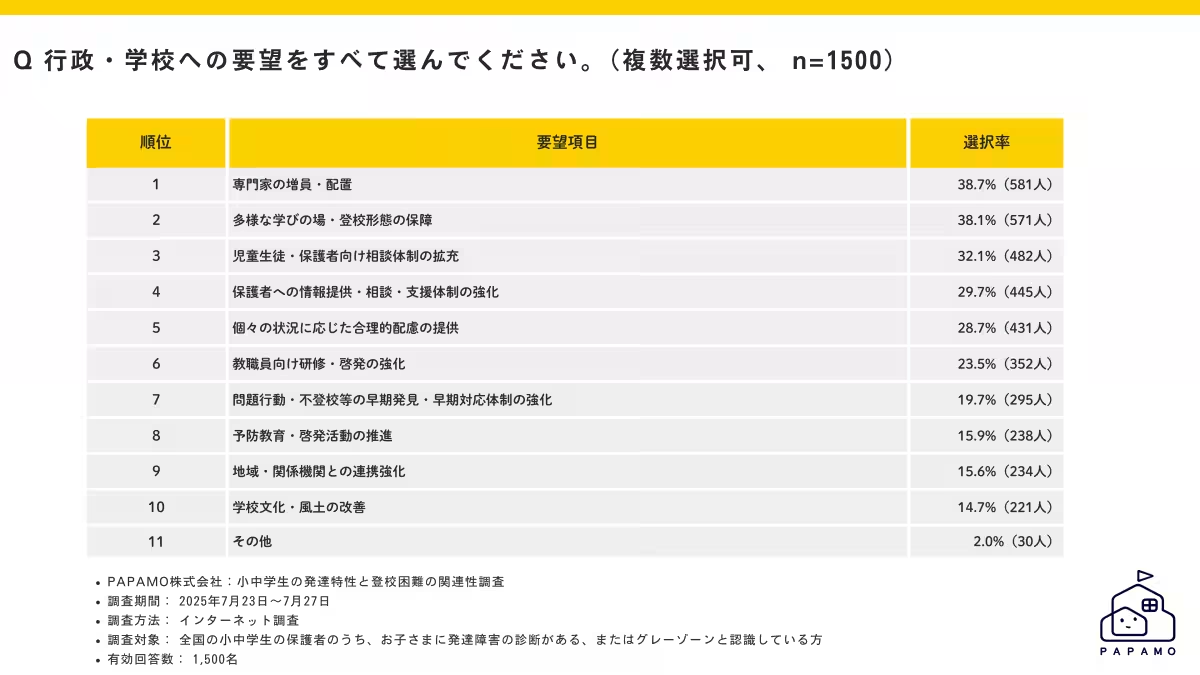
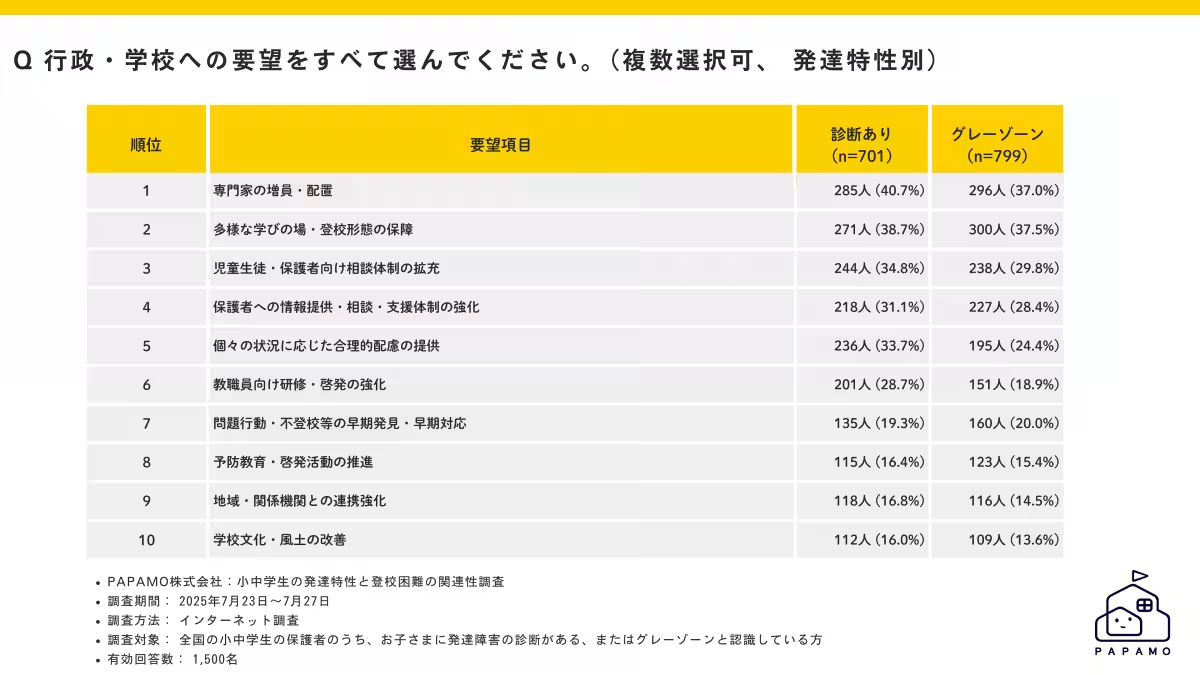
The data also pointed to the necessity for tailored support measures from both educational institutions and the government. The most requested adjustments from parents included an increase in the availability of professionals trained to assist children with developmental differences, as well as more diverse educational environments to cater to individual needs.
Expert Opinions
Tomoko Shirai, an influential figure in children's policy, expressed appreciation for the visibility provided by the data. She emphasized the importance of viewing these statistics as a societal responsibility—encouraging awareness that these challenges are not isolated to the children themselves but are indicative of a systemic need for better support frameworks.
Additionally, Sakiko Hashimoto, the CEO of PAPAMO, highlighted the urgent need for specialized interventions to ensure that no child is left behind due to a lack of appropriate resources. PAPAMO's initiative,






Topics People & Culture)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.