

Smartphone Addiction: A Deep Dive into the Impact on Youth in Japan
The Rise of Smartphone Addiction in Japan
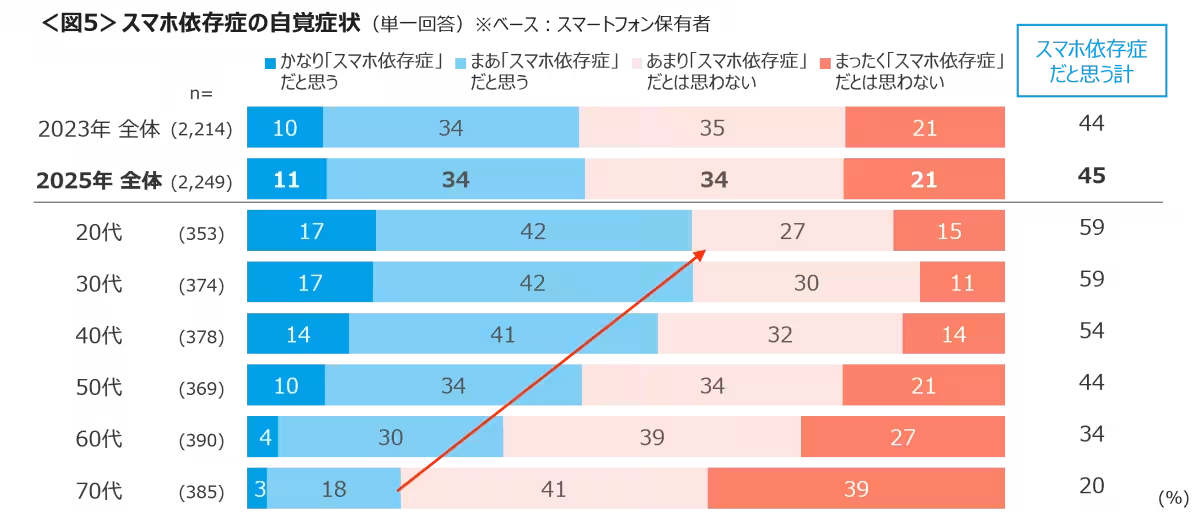
Smartphone usage has become deeply integrated into daily life, particularly among the younger generations. A recent survey conducted by Cross Marketing, a research firm based in Tokyo, shed light on the growing concern of smartphone addiction, highlighting that as of November 2025, an alarming 45% of participants consider themselves to be smartphone addicts. Among those aged 20 to 30, that number spikes to an overwhelming 59%. This dependency stems from various factors, including prolonged usage, unconscious interactions, and anxiety when away from their devices.
The Study: A Closer Look
This investigation surveyed 2,400 individuals aged 20 to 79 across Japan. It explored eye strain due to screen time, the age at which participants began corrective vision measures, smartphone usage habits, and self-awareness of their addiction.
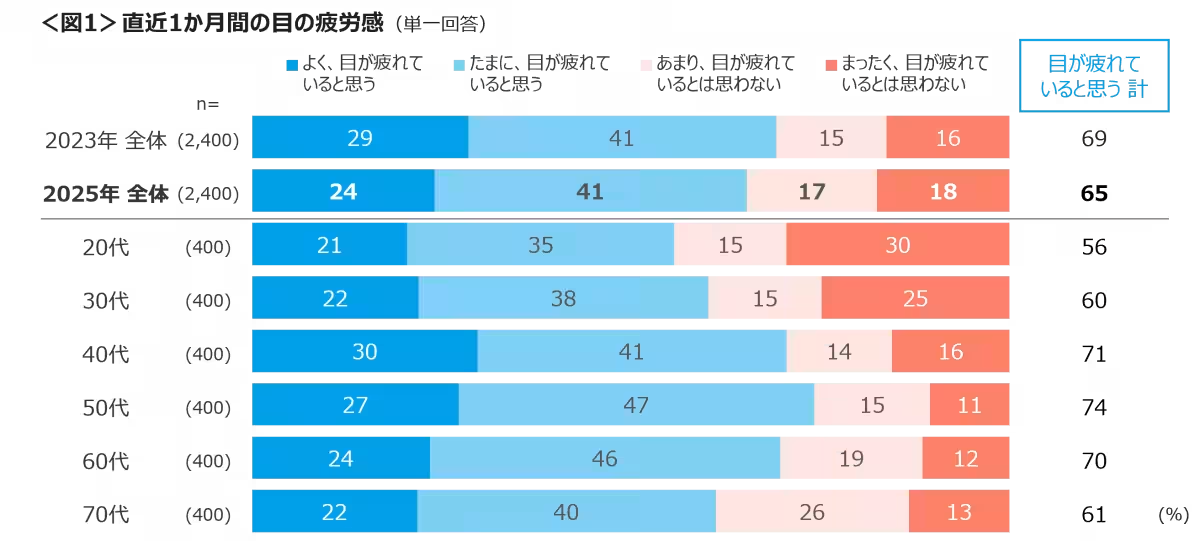
The findings indicate that 65% of respondents experience eye fatigue, with 24% reporting frequent strain. These figures are markedly high among individuals aged 40 to 60, where more than 70% reported experiencing eye fatigue regularly.
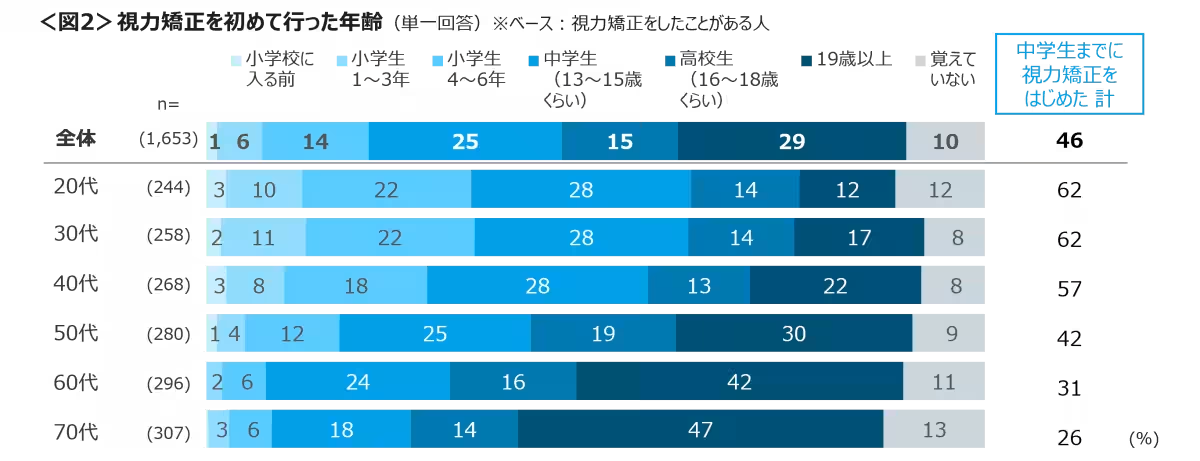
Regarding corrective measures, the study found that many begin wearing glasses or contacts in their teenage years, particularly those in their 20s and 30s, with over 60% having sought vision correction by middle school. Such findings reflect an alarming trend of deteriorating eye health among youth due in part to excessive screen time.
Smartphone Usage Patterns
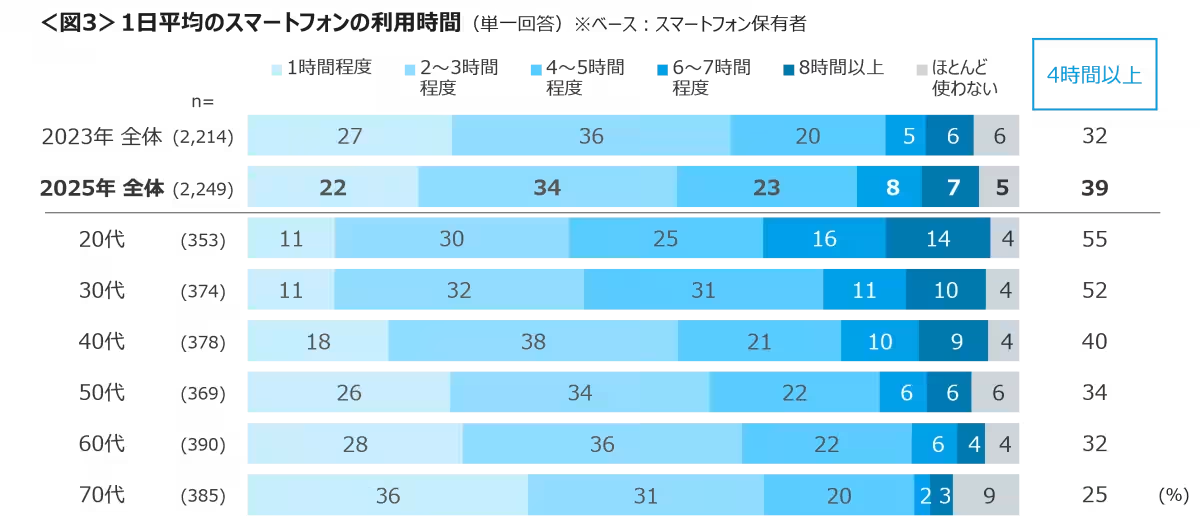
Surveying smartphone users, the average daily usage revealed some alarming trends. Individuals in their 20s to 60s typically spend 2-3 hours per day on their devices, while those over 70 average around 1 hour. However, over half the respondents in their 20s and 30s reported usage extending beyond four hours daily.
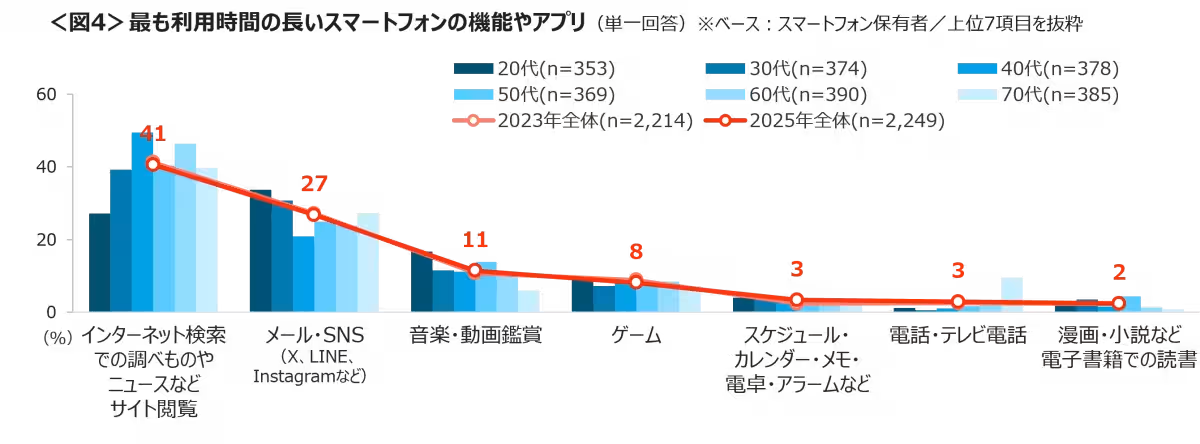
The study also differentiated reporting on the functions most commonly used: 41% engage in web searches or news browsing, 27% utilize email or social media, while only 11% spend time on music or video streaming. Interestingly, even among youth, social media engagement led web search usage, indicating shifting preferences in platform interaction.
Acknowledgment of Smartphone Addiction
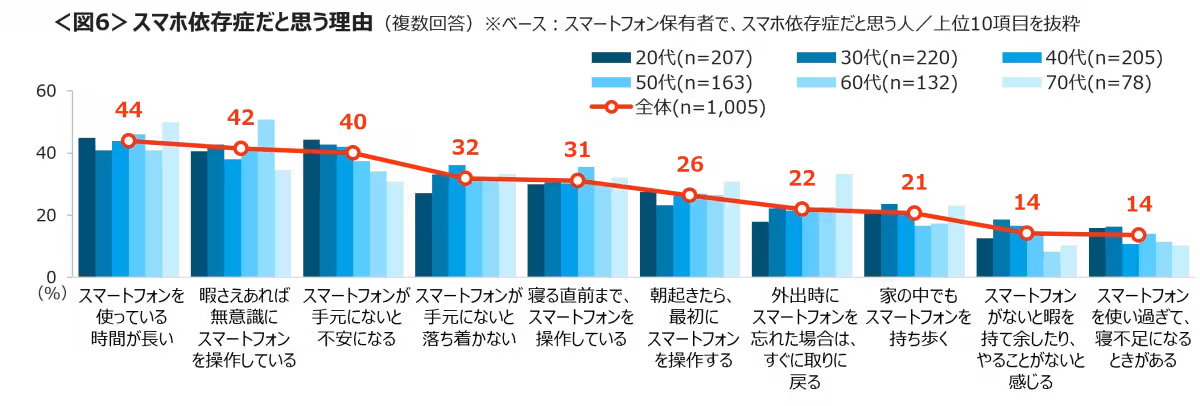
When questioned about their experiences with smartphone dependency, 45% acknowledged potential addiction, with a stark majority of 59% from the younger demographic voicing concerns about their habits. Those who self-identified as smartphone addicts attributed their feelings to spending too much time on their devices and a compulsive need to check their phones, particularly in idle moments. Over 30% confessed to feeling anxious without their devices, reflecting a growing societal issue among younger generations.
Survey respondents noted that the rising trend is not merely a personal concern but a societal one that calls for awareness about balancing device usage with real-world interactions, as those between 20 to 30 years old exhibited particularly strong feelings of anxiety about smartphone absence.
Conclusion
The implications of this research call for urgent discussions about technology’s role in our lives, especially regarding youth welfare. As smartphone use continues to rise, both societal and individual efforts must focus on addressing overreliance on technology to support healthier lifestyle choices.
For more detailed insights and data from this study, visit the Cross Marketing report on eye health.

Topics People & Culture)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.