
The Shift Towards Retiring at Home: Remote Work Preferences Post-Retirement
Remote Work and Post-Retirement Preferences
In a compelling survey conducted by LASSIC, a Tokyo-based company promoting flexible working arrangements, a significant trend has emerged concerning post-retirement work preferences. The study, named "Telework and Post-Retirement Work Preference Study," involved 1,004 working individuals aged between 20 and 65 who have experience with remote or telework. The findings illustrate a growing inclination towards maintaining a remote work lifestyle even after reaching retirement age.
Key Findings
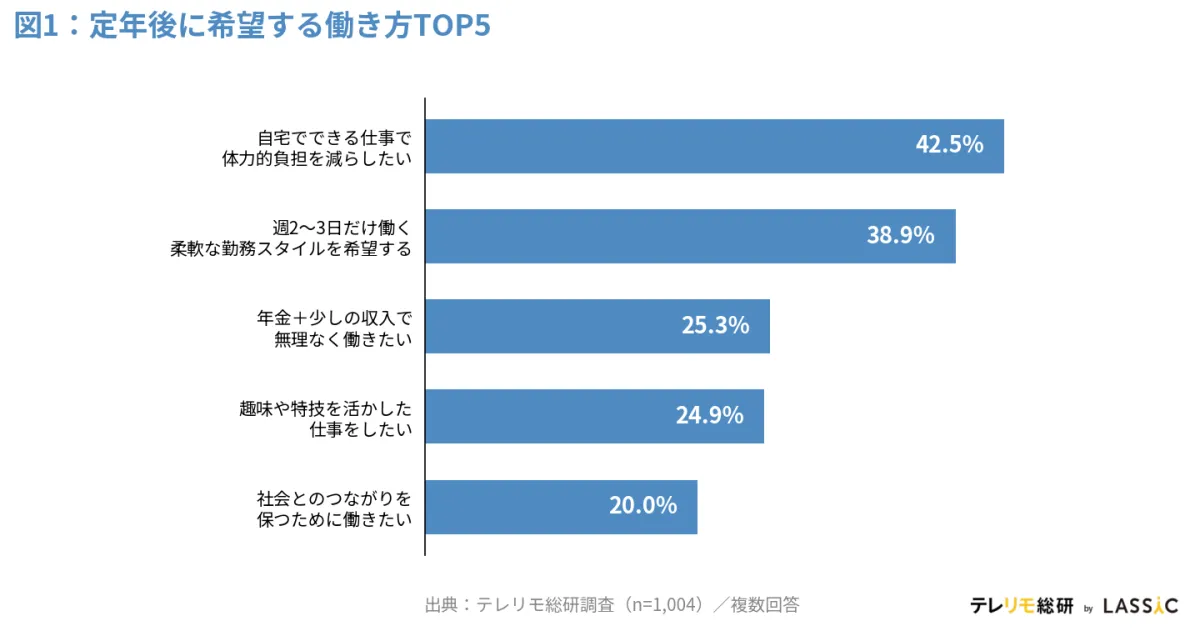
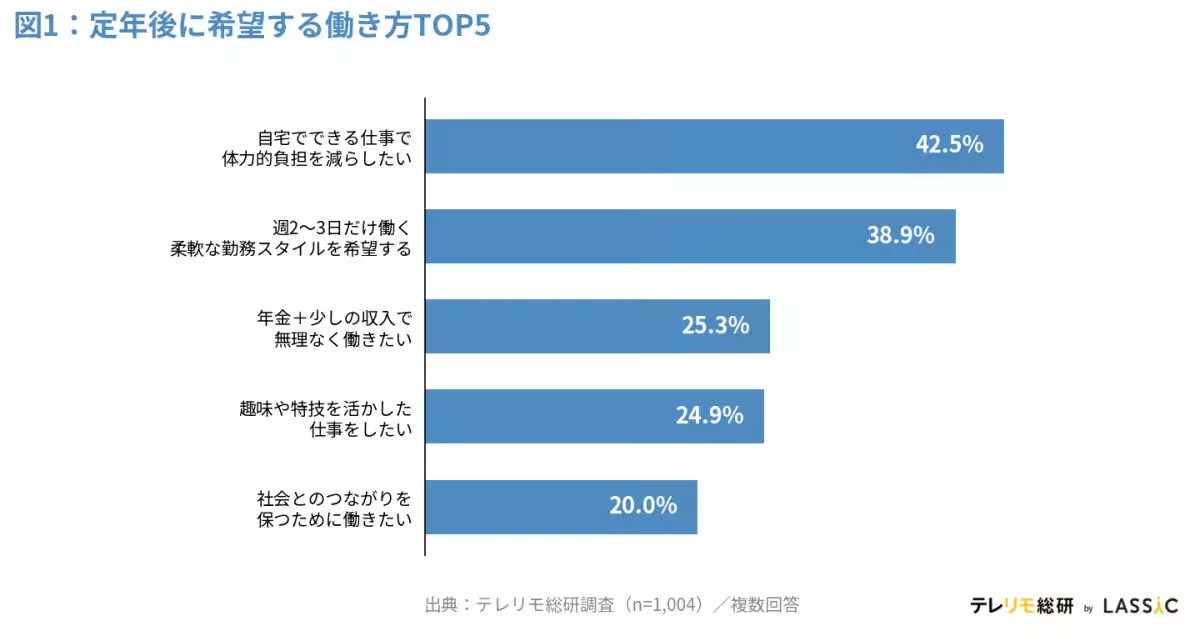
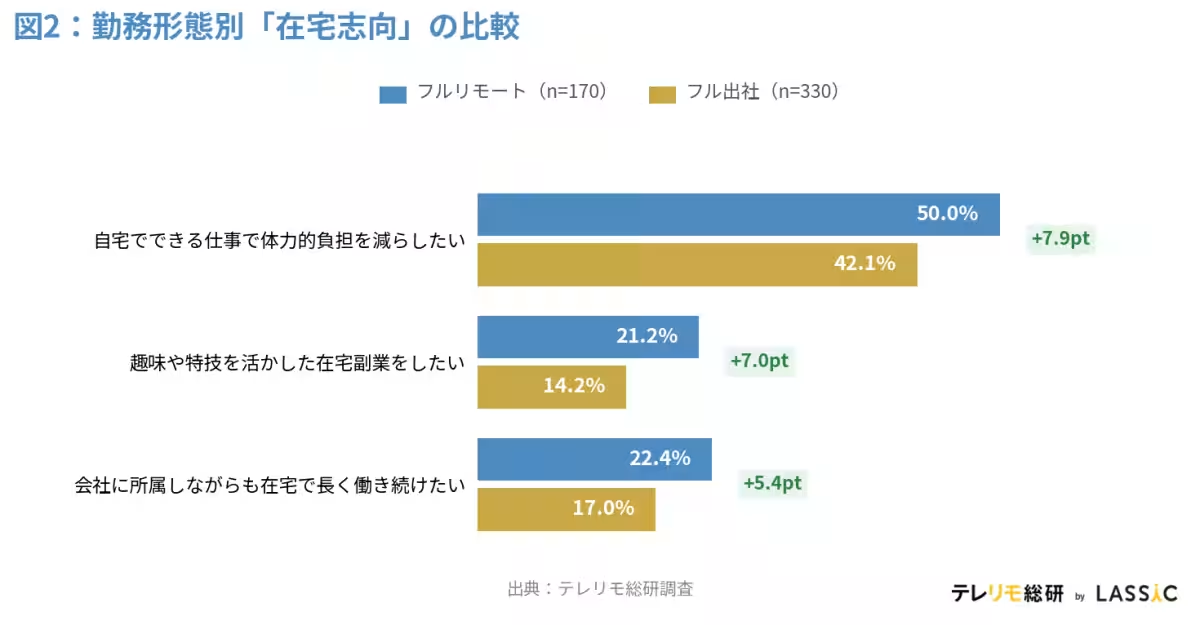
The survey revealed that a remarkable 42.5% of participants expressed a desire to "reduce physical burdens by working from home" after reaching the age of 65. This option emerged as the most popular choice among respondents. Further, when dissecting the data by current work arrangement, it was found that 50.0% of full-time remote workers preferred this option compared to 42.1% of those working full time in-office, marking a 7.9-point difference. Particularly noteworthy are the responses from workers in their 60s, where a striking 70.0% of full remote workers wish to continue working from home, significantly surpassing the 33.8% observed among full in-office workers, creating a substantial 36.2-point gap.
Interest in Alternative Work Styles
The survey also inquired about various modalities of work participants desire post-retirement. Following the preference for home-based jobs, 38.9% of respondents indicated a wish for a "flexible work style of working just 2 to 3 days a week" and 24.1% expressed interest in "working with a mix of pension and some income without strain."
With reference to recent data from the Cabinet Office, Japan has seen a record high employment rate among individuals aged 65 and older, with a reported 914,000 workers making up 25.2% of that demographic as of 2024. The insights from this survey highlight that among the rising reality of longer life expectancy, the desire to remain productive post-retirement is becoming commonplace, forming new perspectives on desired work conditions.
Comparative Insights by Work Arrangement
Analyses further revealed the disparities in preferences based on current work arrangements. Comparing full remote workers to full in-office workers, a significant difference was noted in responses regarding preferring to work from home. Those fully remote were notably more inclined, with 50.0% wishing to reduce physical burdens, compared to 42.1% from those who commute to work. When exploring additional preferences such as pursuing home-based side jobs leveraging personal hobbies, 21.2% of remote workers favored this option, illustrating moderate interest as opposed to the 14.2% from in-office workers, marking a 7.0-point variance. Interestingly, the desire for a part-time flexible work schedule remained consistently balanced between the two groups, signaling a shared need across working styles for more adaptable employment formats.
Age-specific Trends
Breaking down the data further by age brought significant findings to light, especially regarding remote workers in their 60s. An impressive 70.0% of this group preferred to work from home, indicating a clear correlation between age and preference for a remote work style. For those in their 50s, 52.6% expressed similar sentiments, further indicating an upward trend towards valuing home-based work as one ages. As the age increased, the distinction between the preferences of remote and in-office workers became more pronounced, emphasizing a potential shift in workplace norms over time.
Additionally, among in-office workers, 12.1% reported feeling supported in their desire to work flexibly, suggesting that workplace environments' adaptability can play a crucial role in shaping employees' future career paths.
Implications of the Findings
These findings not only provide valuable insights for individuals contemplating their post-retirement path but also pose significant considerations for employers. By reevaluating their approach to working arrangements and developing remote work policies, companies stand to tap into a wealth of experience from senior talent, particularly if fresh avenues to engage with this demographic are provided. The potential challenges posed by commuting burdens for older workers illustrate that enabling remote work could serve as a means to accommodate these needs, while enhancing the operational efficiency of organizations leveraging this talent.
For individuals, the importance of current work styles on future career trajectories becomes evident. Engaging in remote work now could facilitate laying the groundwork for a fulfilling and adaptable career after reaching retirement age.
Source and Further Information
For a more comprehensive review of this survey, including detailed analysis and further findings, please visit LASSIC's Official Website.
Additionally, LASSIC offers free access to survey data for media companies wishing to explore telework and remote work issues further. Interested parties can contact LASSIC directly for more information.



Topics People & Culture)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.