
Exploring Employee Reskilling and Learning Behaviors in Large Corporations
Introduction
In recent years, the concepts of "reskilling" and "upskilling" have gained traction within corporations, largely driven by the rapid advancement of technology and significant shifts in labor market structures. This evolving landscape necessitates the dynamism in skill rebuilding. During the period of 2022 to 2023, the Corporate Vitality Research Institute conducted an in-depth survey focused on employee reskilling practices among large corporations, particularly those with over 300 employees. This article highlights the findings of that survey and delineates the behaviors and motivations behind employee learning.
Key Findings from Initial Survey
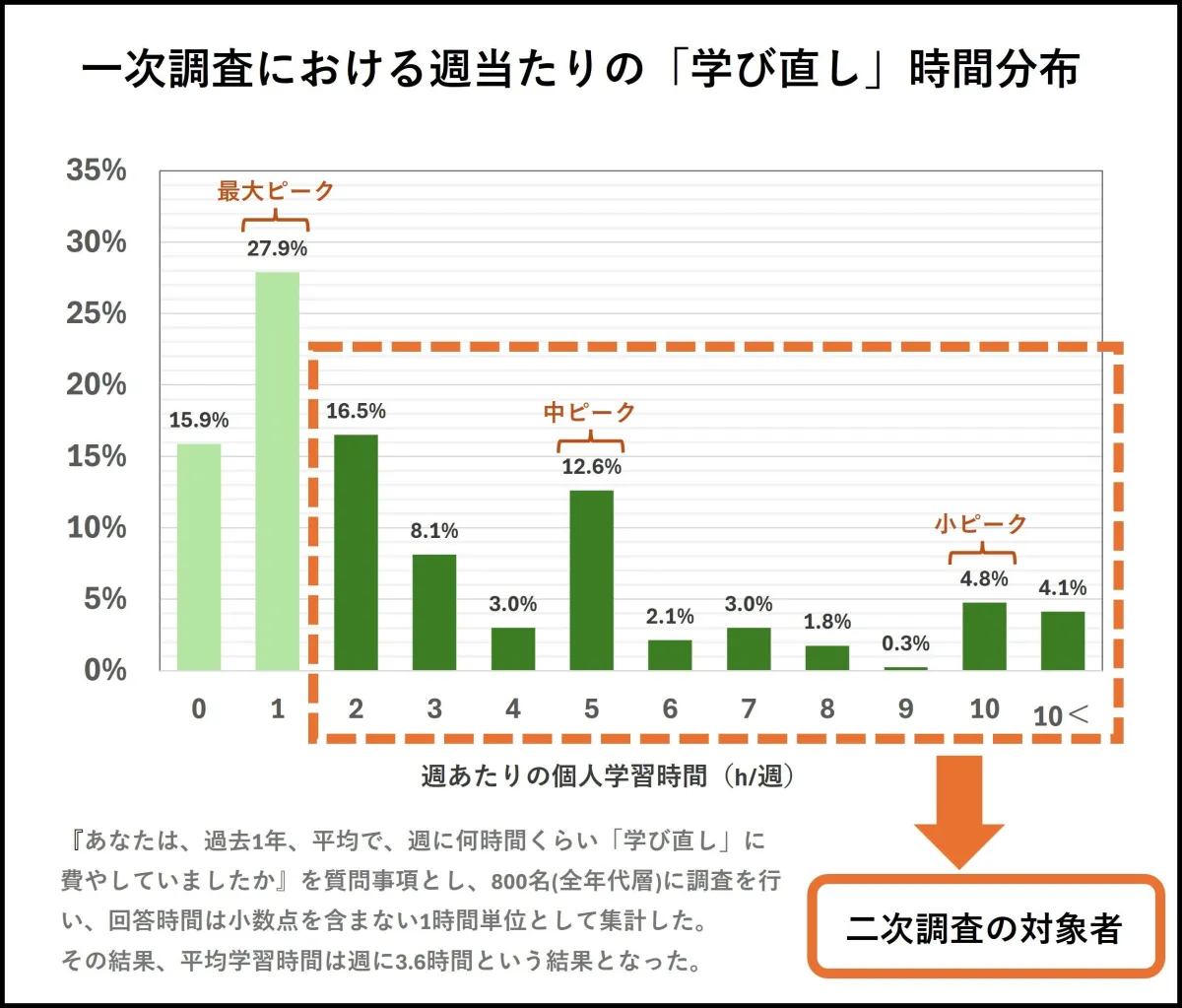
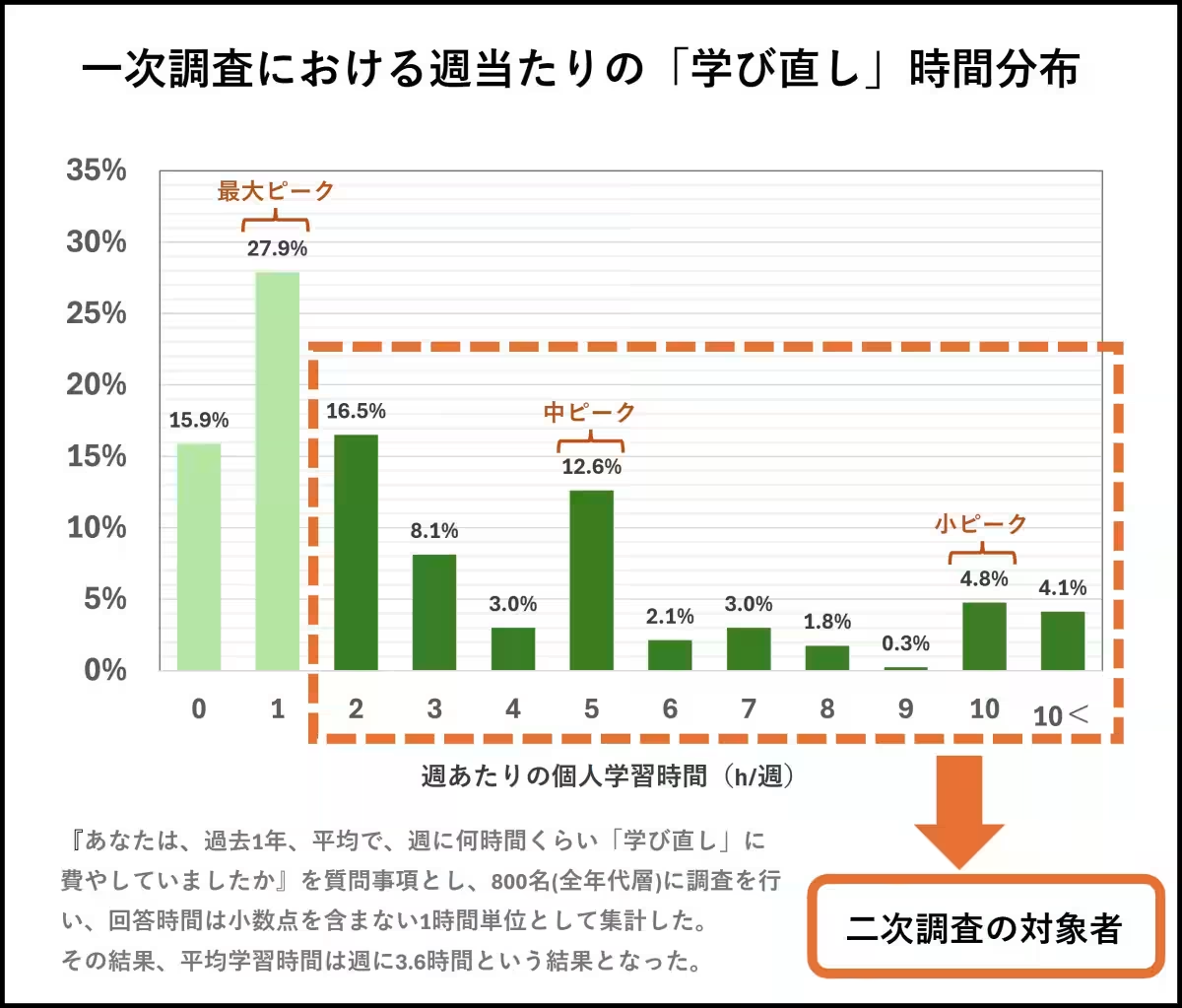
The initial investigation revealed several noteworthy points regarding the hours dedicated to reskilling. Employees in companies that actively promote reskilling reported an average weekly learning time of 3.6 hours. This duration represents a heightened figure primarily due to the contributions of those engaging in longer hours of study. Notably, the study pinpointed a distinct peak in learning hours, particularly among a subset of employees who invest significantly more time into their personal and professional growth.
Secondary Survey Insights
Building on the initial findings, a secondary survey conducted in early 2025 redefined the profile of a "learner" as employees who dedicate more than 6 hours monthly to learning. The secondary survey aimed to delve deeper into the circumstances and environments that promote effective learning. What emerged was an intriguing perspective on employee learning habits, with the results indicating that a considerable portion of employees engaged in limited learning, with 40% of responders averaging less than 1 hour of learning per week.
Evaluating Learning Time and Its Drivers
1. Learning Time Overview
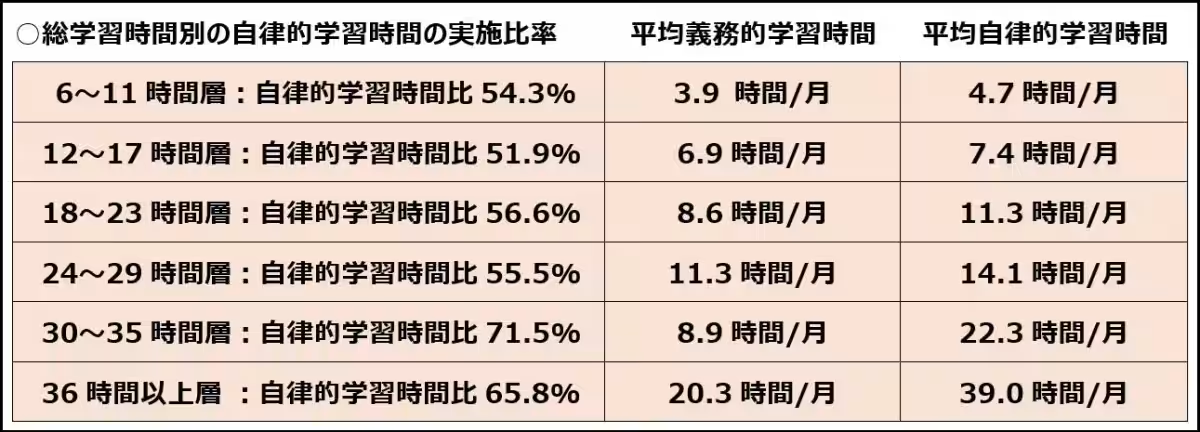
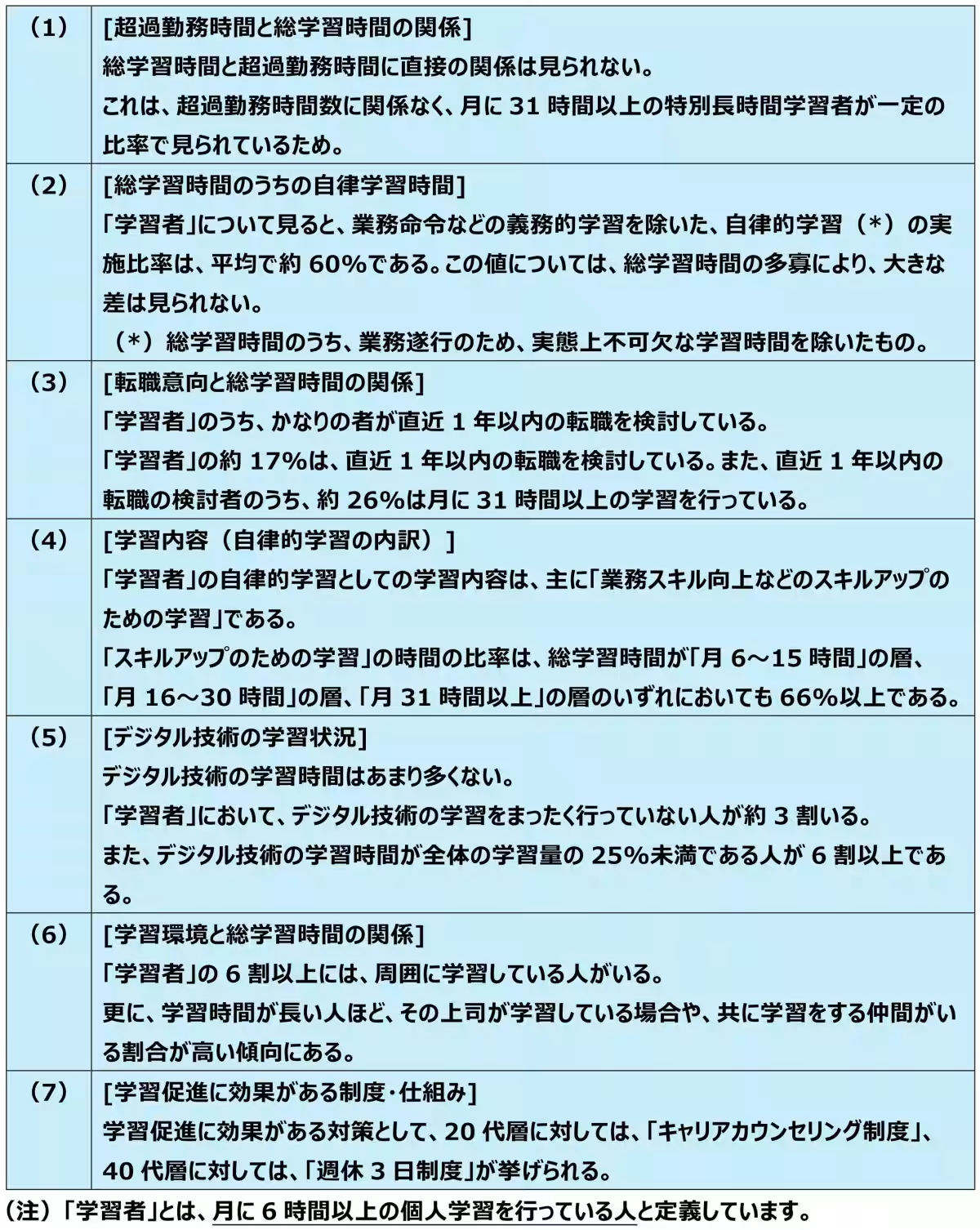
- A majority of employees were seen allocating insufficient time to skill enhancement, with frequent reports of learning frequencies of under 1 hour per week. Yet, amidst this, groups of employees dedicating 5 to 10 hours weekly were notably present, indicating a dichotomy in engagement levels. Furthermore, those involved in overtime were still dedicating upwards of 31 hours a month to personal development, suggesting that traditional work hours may not correlate directly with the commitment to learning.
2. Learning Motives
- Investigation into the motivations behind learning disclosed that a significant percentage of learners—17%—were contemplating a job change within the last year. Within this group, approximately 26% reported committing over 31 hours to learning, thereby indicating that career advancement and market mobility serve as powerful motivators for education.
3. Content of Learning
- The study identified that most self-directed learning centers around improving work-related skills. This focus appears to correlate with employees' genuine interest in enhancing their job performance. Additionally, the presence of job change considerations among the learner group further emphasizes skill development targeted toward new employment opportunities.
4. Learning Environment
- The presence of peers engaging in learning was highlighted as enhancing personal learning times. Those who reported that their supervisors engaged in learning tended to log longer study sessions, suggesting the value of a learning-focused corporate culture. Effective institutional frameworks, particularly those benefiting younger and older employees, were found to facilitate this environment.
Effective Strategies for Learning Promotion
As the research revealed, certain institutional strategies notably enhance learning opportunities:
- - Career Counseling: Particularly effective among individuals in their 20s, this strategy garnered a favorable response, enhancing motivation and self-improvement prospects.
- - Work-Life Balance Initiatives: Programs such as a three-day workweek received endorsement from employees in their 40s, suggesting that flexible working arrangements may correlate with increased learning engagement.
These revelations underscore the critical necessity for organizations to adapt their frameworks accordingly, enabling effective learning environments and appropriate countermeasures tailored to the diverse needs of employees across various age groups.
Conclusion
The survey's findings suggest that while challenges remain—such as limited engagement in digital skills training—there exists a clear pathway for corporations to enhance the learning dynamics within their workforce. As the workplace evolves, such initiatives not only benefit the employees but also fortify the corporations facing the challenges of an ever-changing market. By fostering an educational culture, employers can gain a competitive advantage through a skilled, adaptable workforce equipped to meet future demands.

Topics People & Culture)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.