

2025 Office Worker Survey: Motivation and Values Across Generations
2025 Office Worker Survey: Diverse Motivations and Work Values Evolution
Ito-Ki Co., Ltd., led by CEO Koji Minato, recently conducted a comprehensive survey titled "2025 Office Worker Survey: Redefining Work Motivation and On-site Value in a Diversified Working Environment." This survey, which involved 5,296 office workers across Japan, focused on various aspects of work, including preferences for work arrangements, commuting attitudes, and essential factors influencing motivation and retention.
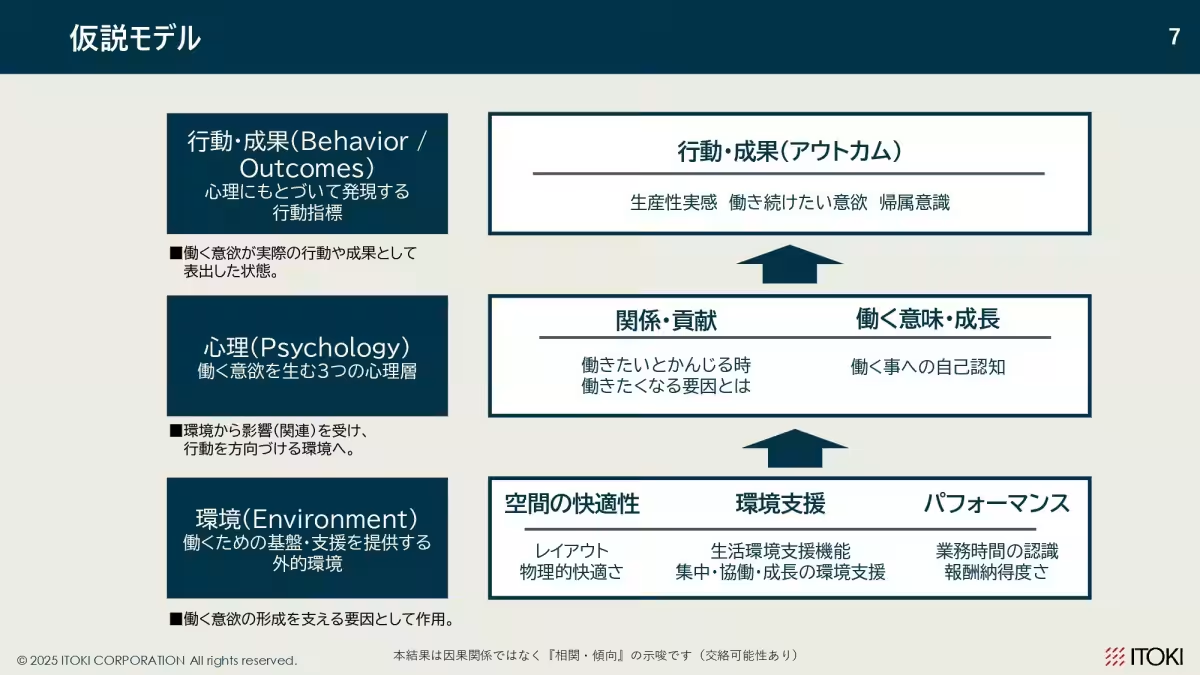
As the choices regarding work styles continue to expand, the survey aimed to understand the relationship between workplace environments and their effects on psychological well-being and productivity. It appears that distinct motivational structures vary by age group, suggesting a complex interplay between environment, psychology, and individual behavior within the workplace.
Key Highlights from the Survey
1. Desire for Traditional Office Return: While there is a general yearning for a return to traditional office settings, about 40% express reluctance to commute at times.
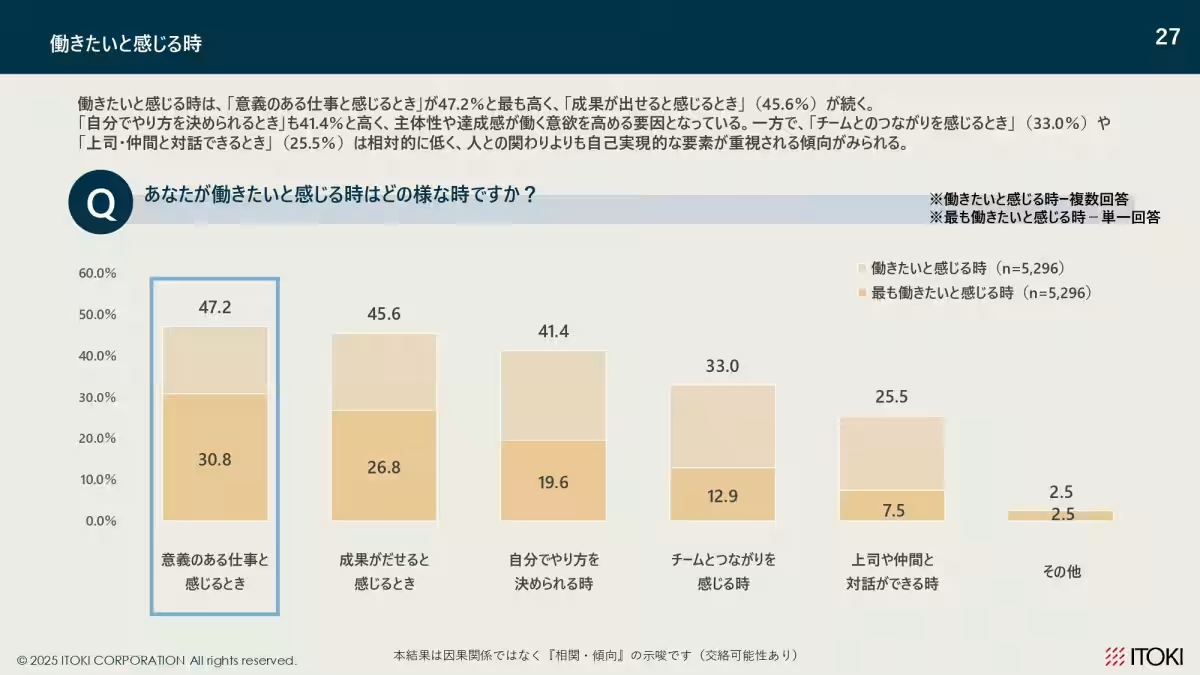
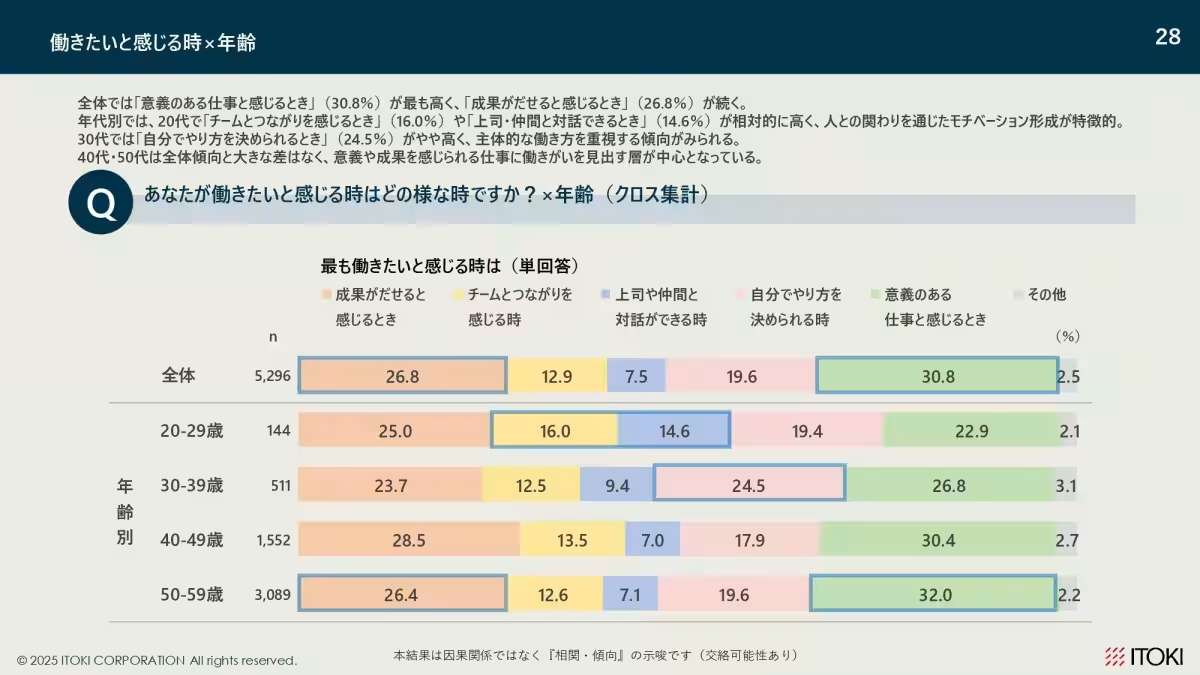
2. Motivation by Age: The impetus for wanting to work varies with age; relational factors dominate for those in their 20s, autonomy for those in their 30s, and achievement and purpose for individuals in their 50s.
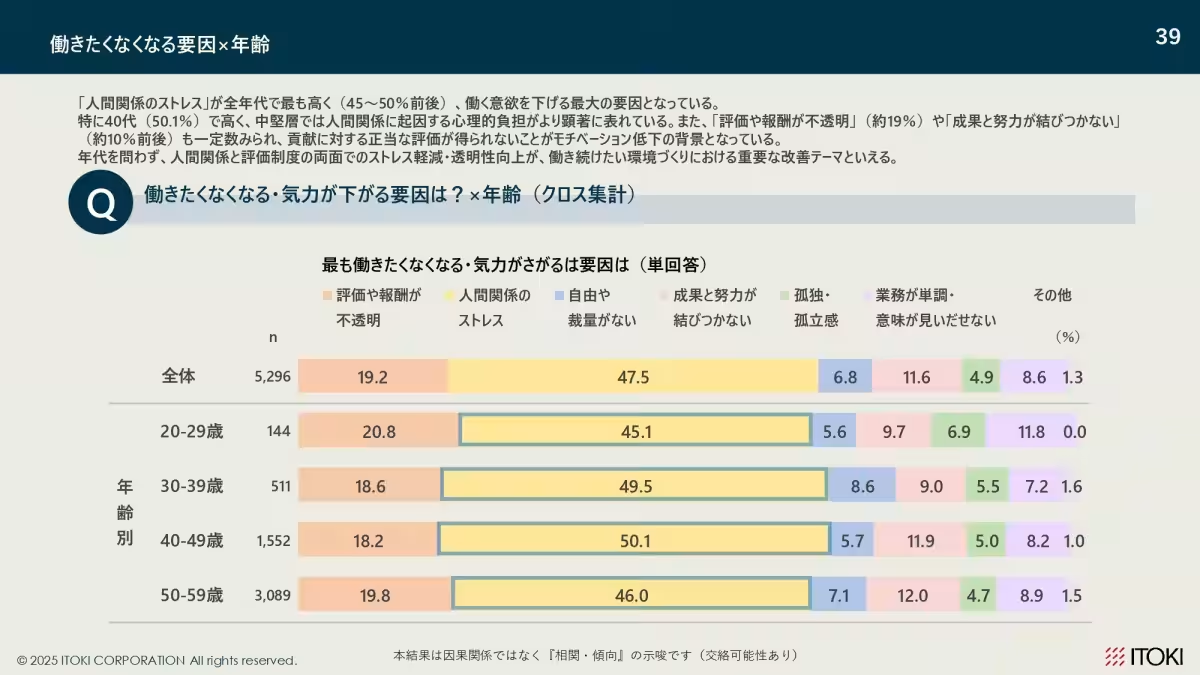
3. Stress from Relationships: Workplace stress primarily stems from interpersonal relationships. This impacts the overall willingness to engage in work activities.
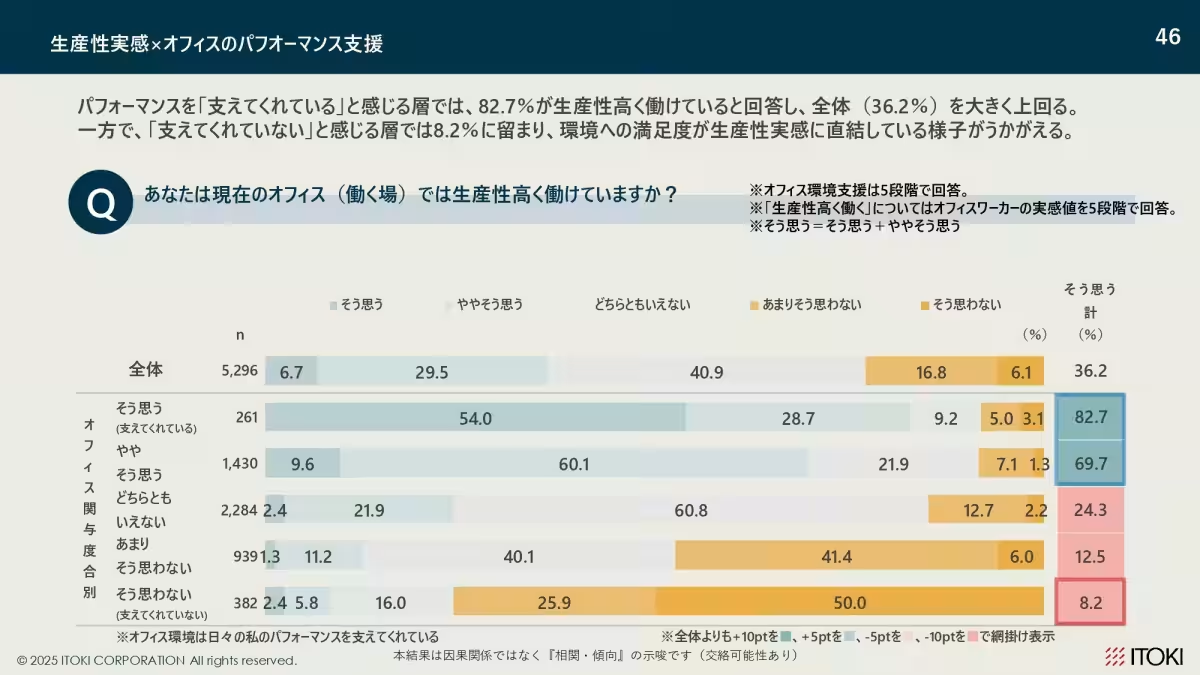
4. Self-perceived Productivity Gaps: The survey found a dramatic disparity in self-reported productivity, with those feeling supported by their environment rating their productivity significantly higher—almost tenfold, compared to those who did not feel that support.
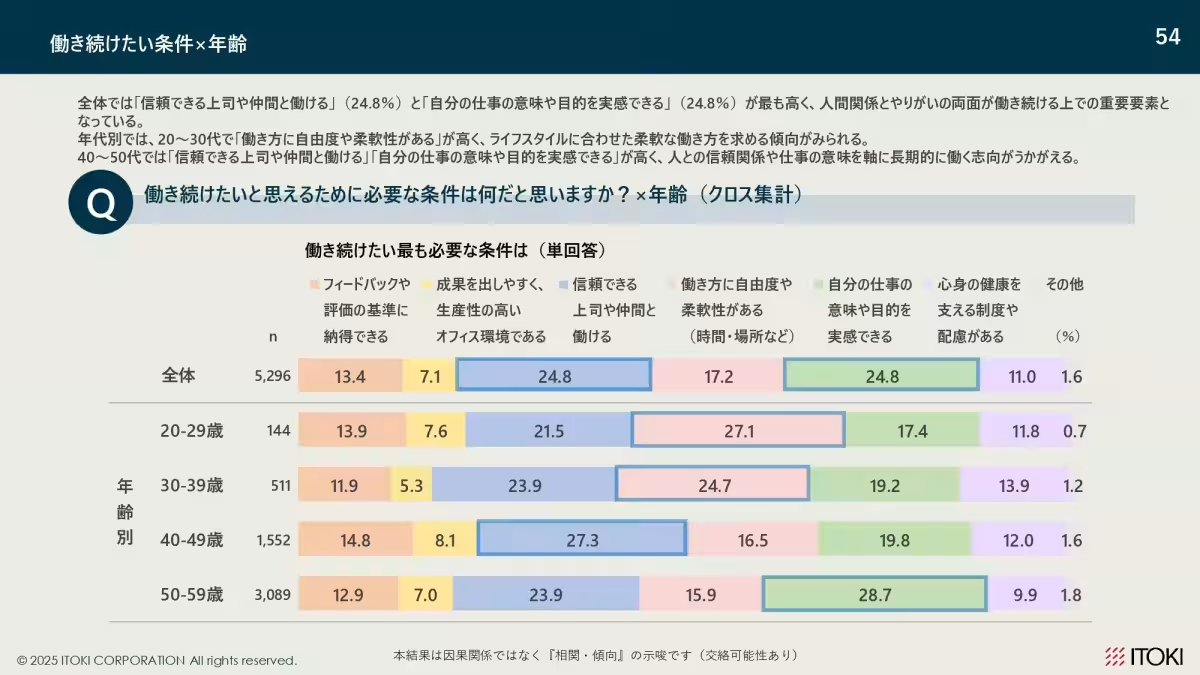
5. Trust and Meaning Over Time: Younger workers prioritize flexible work arrangements, while older workers place greater value on trust and meaningful work experiences.
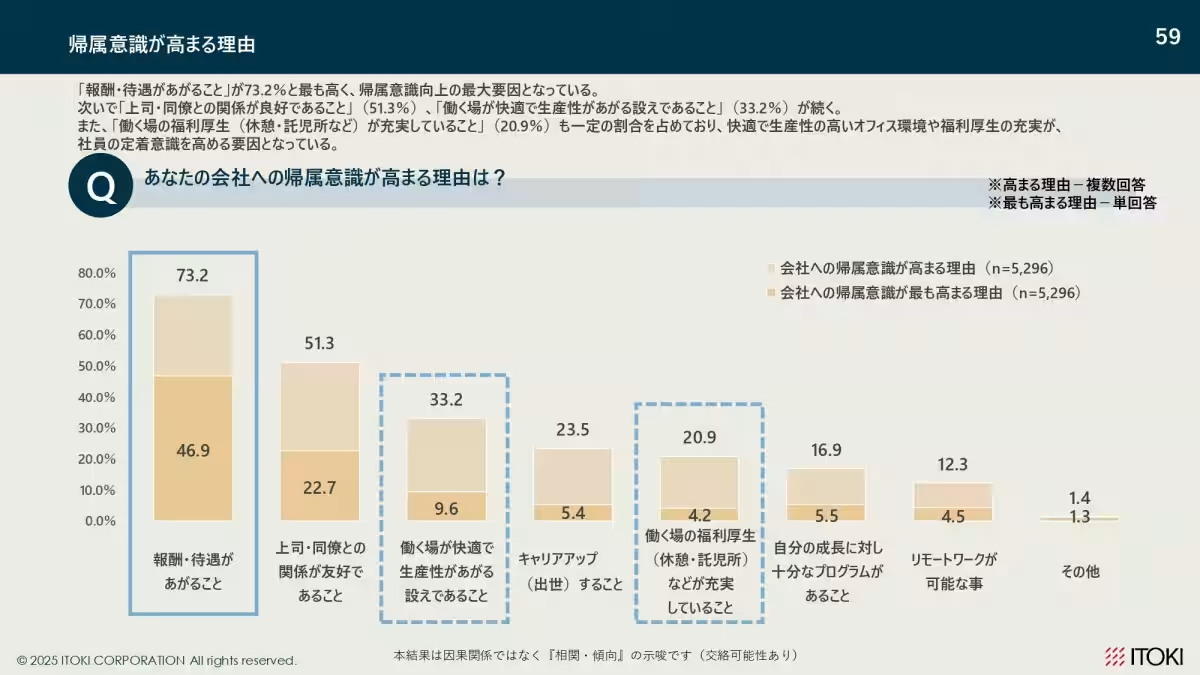
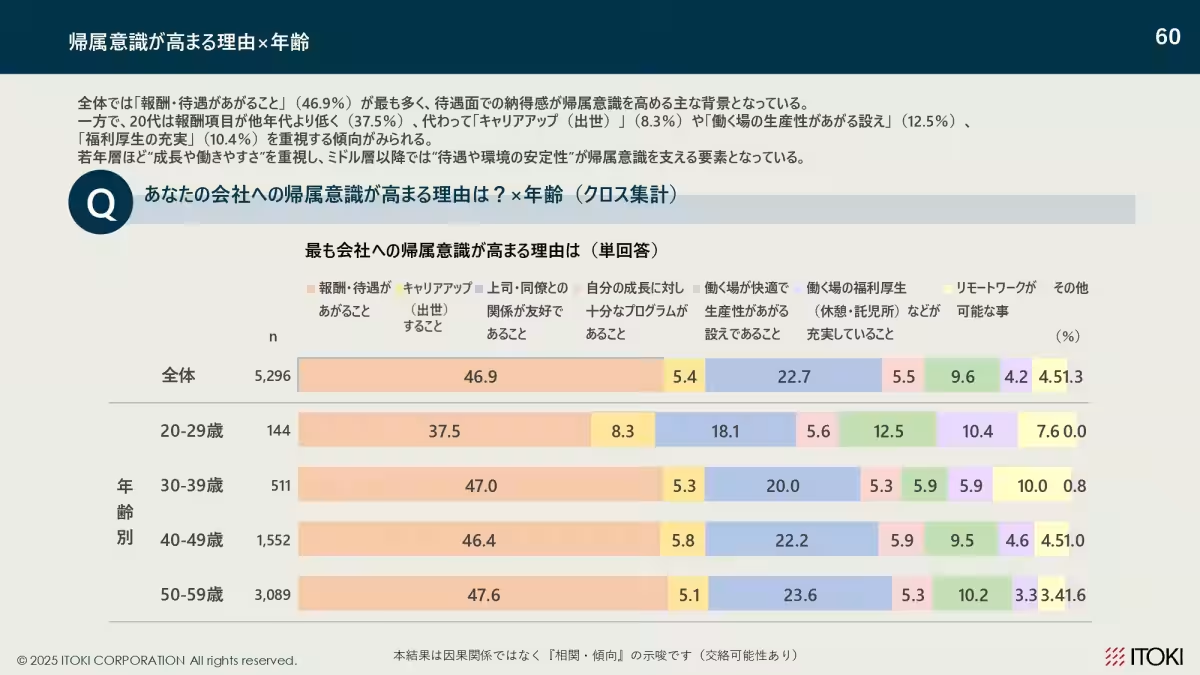
6. Belongingness Factors: To enhance workplace belongingness, salary, interpersonal relationships, and overall work environment are crucial, with younger employees emphasizing growth and ease of work experiences strongly.
Analysis of Work Preferences
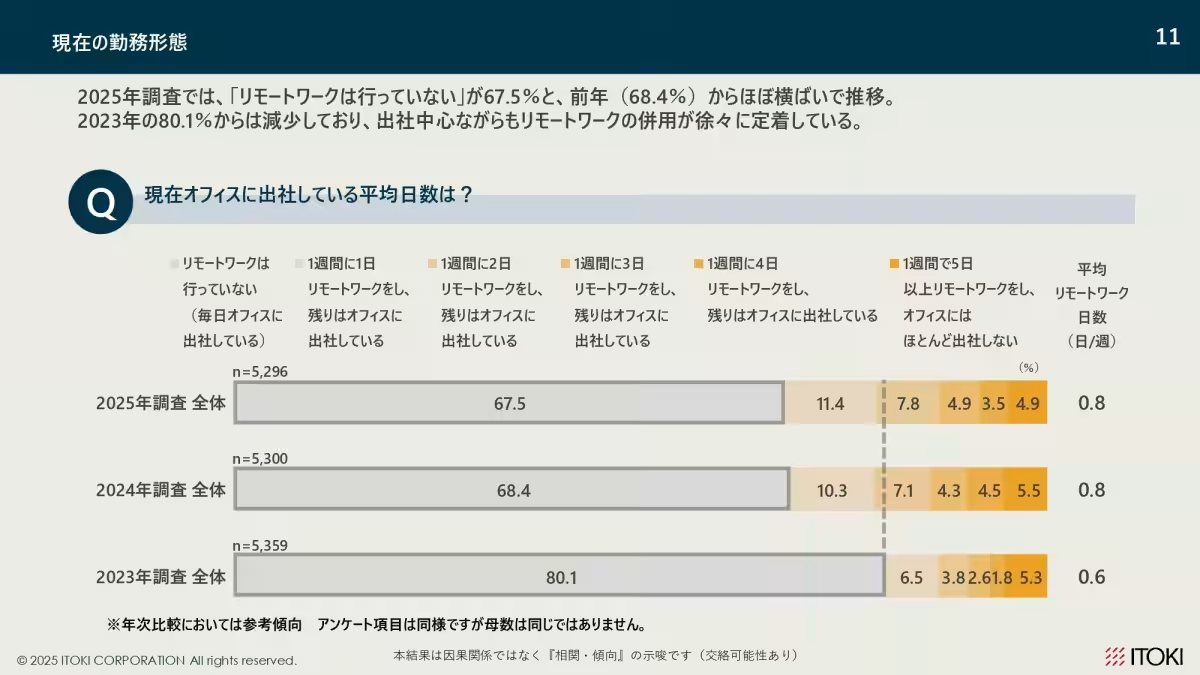
The survey revealed that 67.5% of respondents currently do not engage in remote work, a noticeable decrease from 80.1% in 2023, indicating a shift toward more hybrid work models. Despite more individuals favoring full-time office attendance (up to 61.1% from 48.4% last year), it is clear that a hybrid work approach is gaining traction, as seen in the declining preference for mixed remote and in-office arrangements.
Motivational Insights Across Generations
When asked about when they feel most motivated to work, respondents noted several key factors:
- - 20s: Connection with team members and human relationships were identified as significant motivators.
- - 30s: The ability to act autonomously was highlighted as crucial.
- - 40s and 50s: Achievement and the sense of purpose were prioritized, notably indicating a shift in focus as workers progress in their careers.
These insights suggest that motivation is not static and is deeply influenced by age and career stages. Therefore, organizations are encouraged to tailor their motivational strategies to address these generational characteristics.
The Impact of Supportive Environments
Importantly, the survey underscored that exposure to supportive workplace environments fosters a higher sense of productivity. Approximately 82.7% of those who felt supported reported a high sense of productivity, contrasting starkly with just 8.2% of those who felt unsupported.
Retention Dynamics
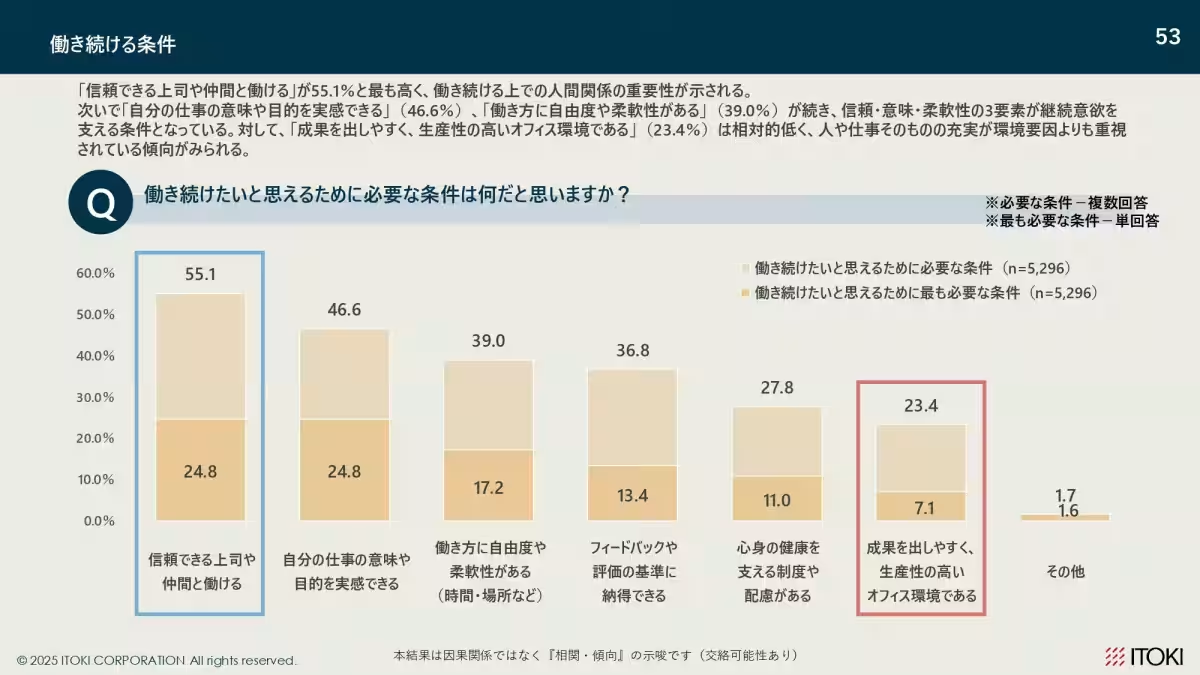
Responses regarding conditions for continuing employment showed that a trustworthy workplace environment (24.8%) and the meaningfulness of work (24.8%) were paramount. Notably, younger employees prioritized flexibility and autonomy in their work practices, while older employees leaned more towards trust between colleagues and recognizing the value of their work.
The findings suggest that while trust and purpose underlie employee retention across all age groups, younger workers increasingly demand flexibility, emphasizing a need for adaptive workplace policies.
Conclusion
This survey sheds light on the evolving nature of workplace dynamics, reflecting nuances in motivation and employee needs across generations. The research suggests that improvements in workplace environments directly correlate with heightened productivity and engagement among workers. Organizations should consider these insights within their workforce management strategies, accommodating diverse requirements based on employee age groups and career stages, to foster a positive, effective, and productive workplace culture.
For more details and the full survey report, please visit the Ito-Ki website.




Topics People & Culture)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.