
Understanding the Current State of Dating Apps Among Single Women in Their 20s and 30s
Exploring Dating Apps: Insights from Young Working Women
In a world where digital connections flourish, dating apps have gained significant traction among the younger population, especially among single working women in their 20s and 30s. Bright Management, a company based in Shibuya, Tokyo, conducted a survey to shed light on the dating app usage patterns among these women, revealing both behaviors and preferences in the dating landscape.
The Rise of Dating Apps
Over the past few years, dating apps have transitioned from being a niche platform to a mainstream method for seeking romantic relationships and potential spouses. This shift has been especially apparent among young professionals who often struggle to find time for traditional dating opportunities due to their demanding work schedules. However, this convenience comes with its own set of challenges, often termed 'app fatigue,' where users feel drained by the process of meeting people online.
Survey Summary
In a recent study conducted from May 12 to May 15, 2025, with a representative sample of 1,336 unmarried female employees in their 20s and 30s, the findings showed:
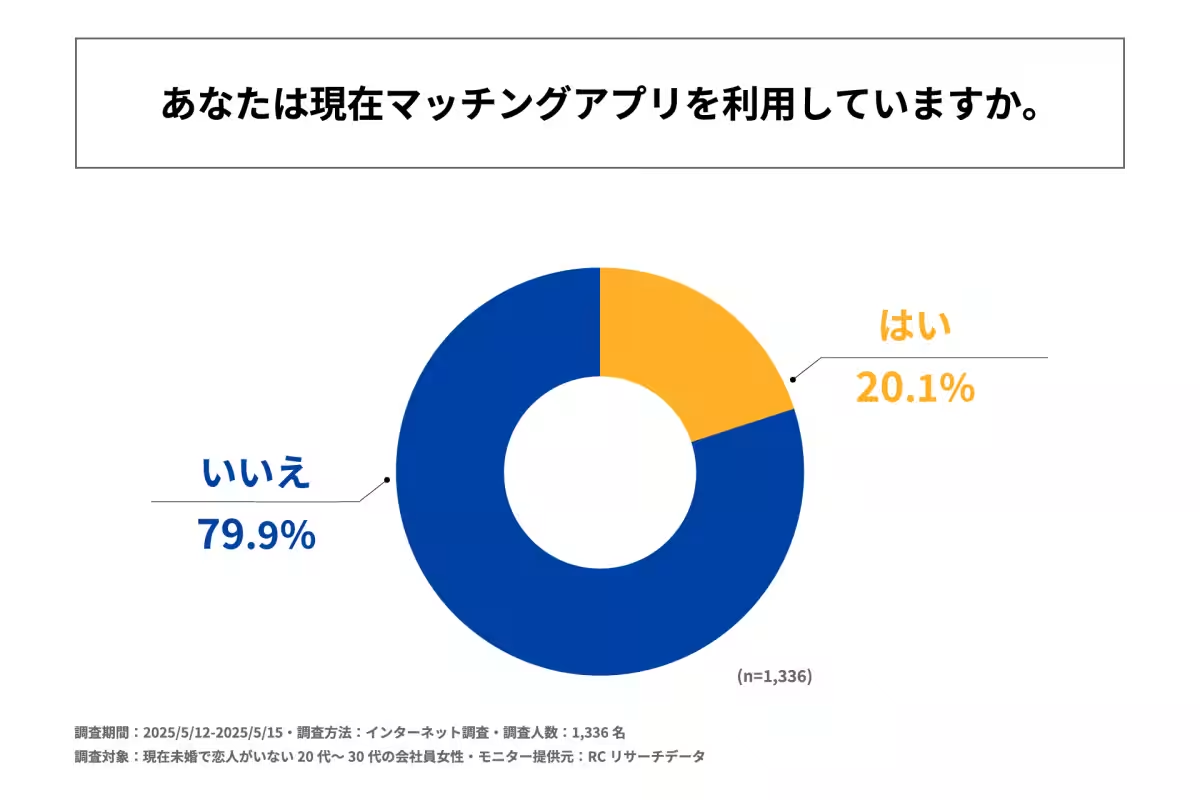
- - Approximately 20% of participants actively use dating apps.
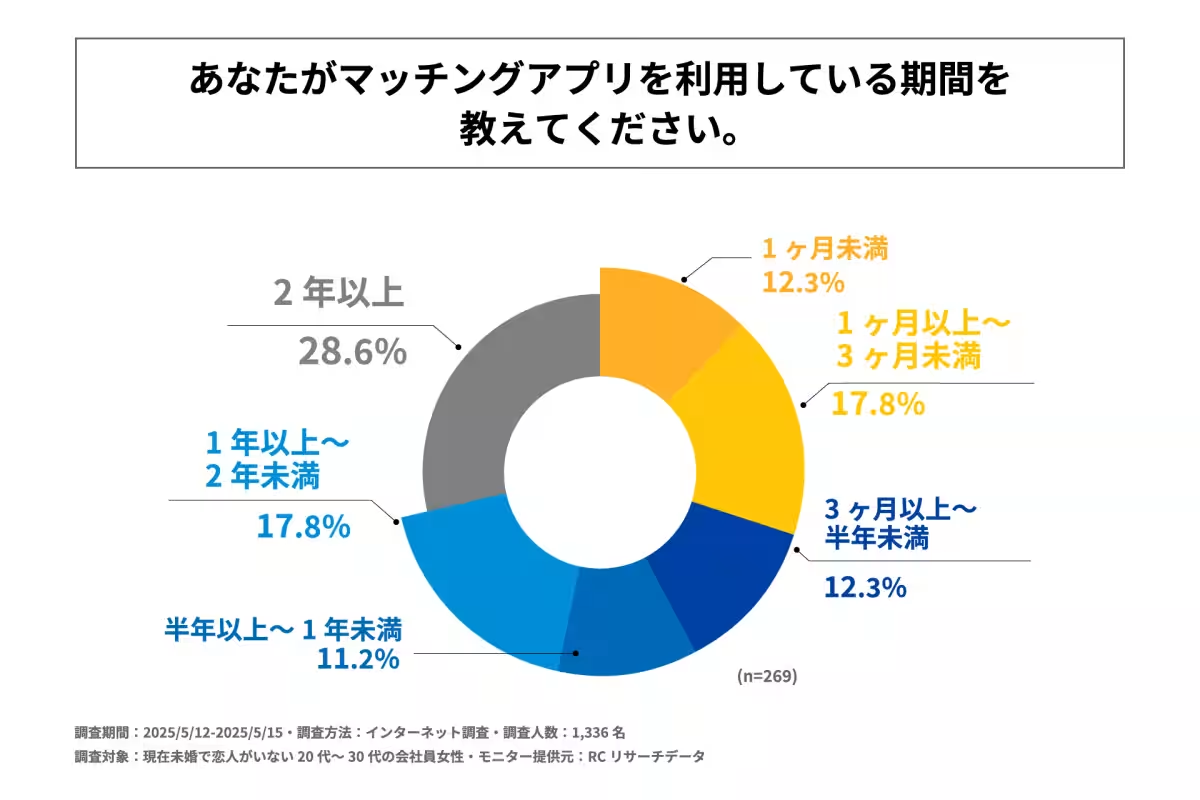
- - The majority of these users (28.6%) have been using dating apps for more than two years.
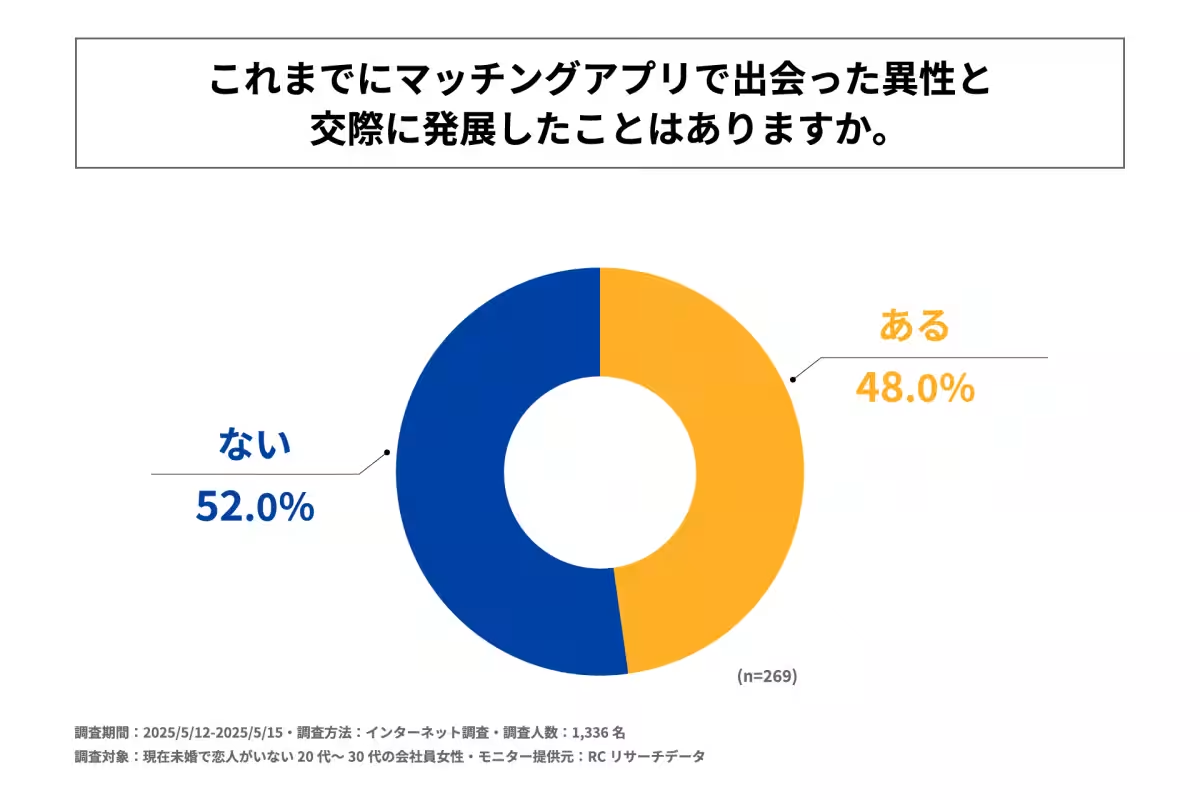
- - Nearly half (52.0%) reported never having progressed to a relationship through these apps.
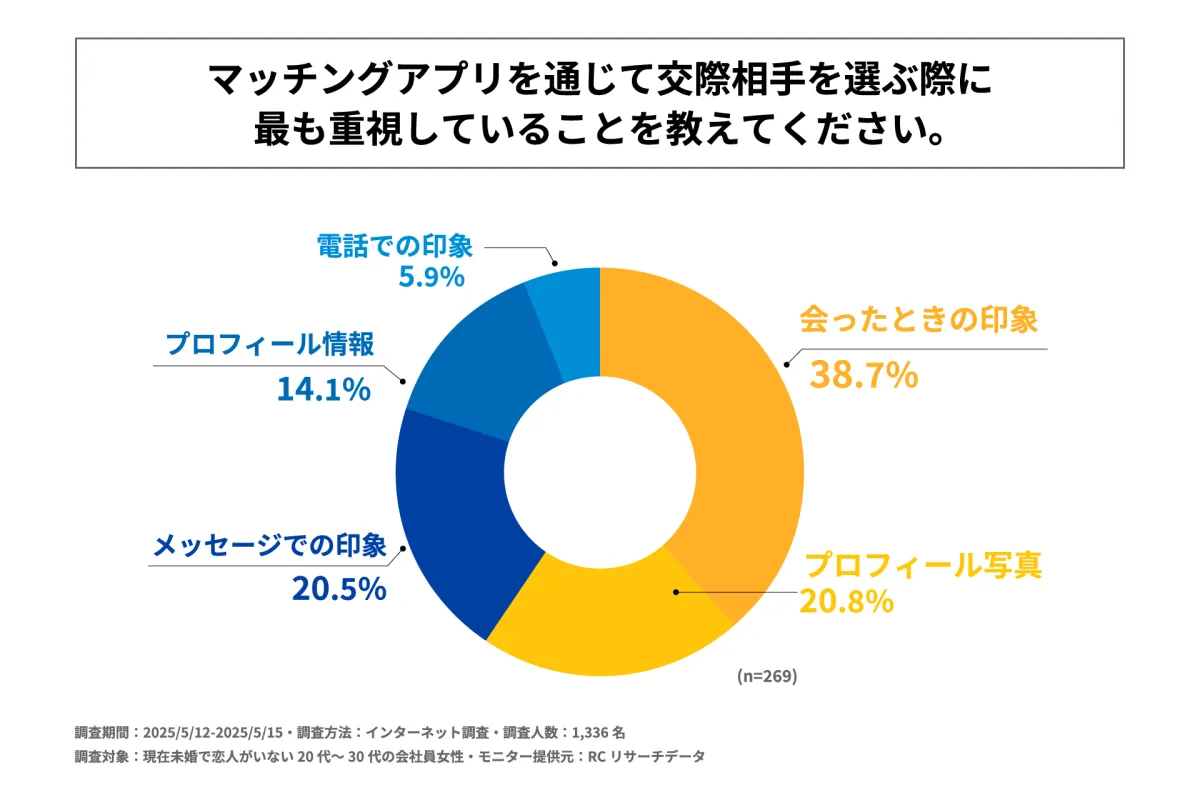
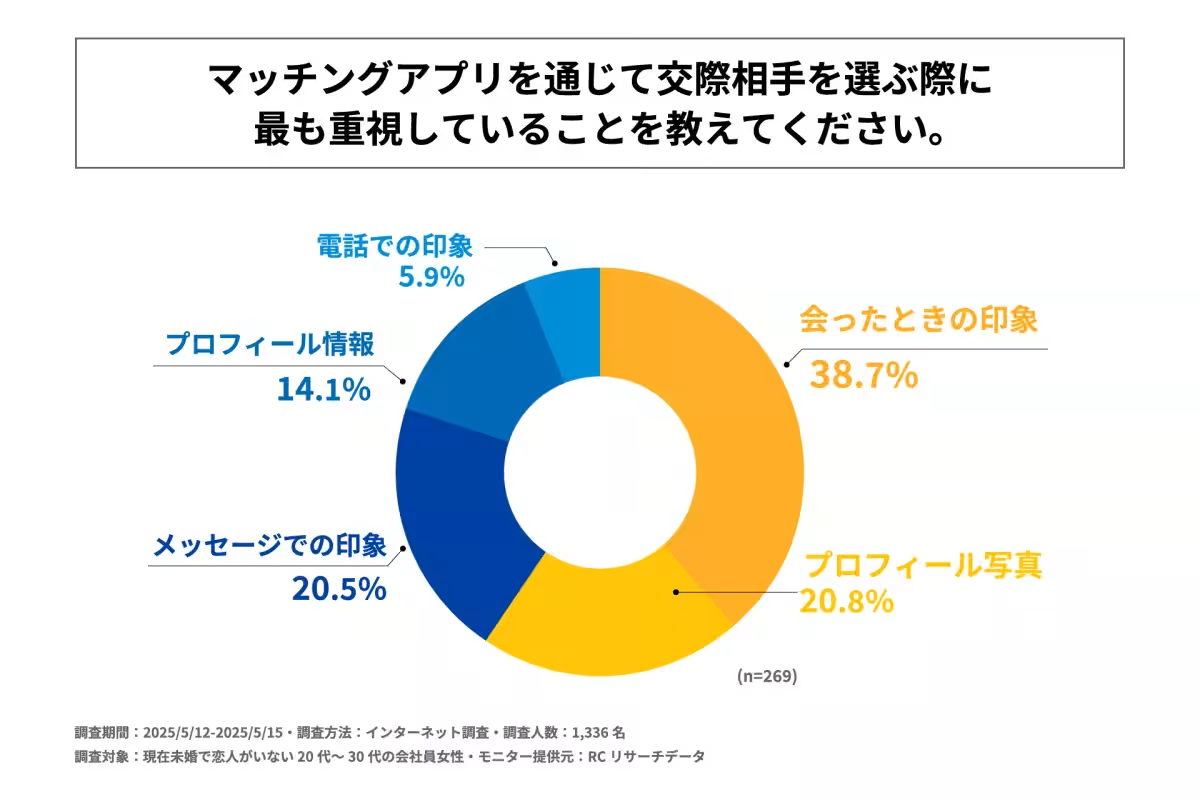
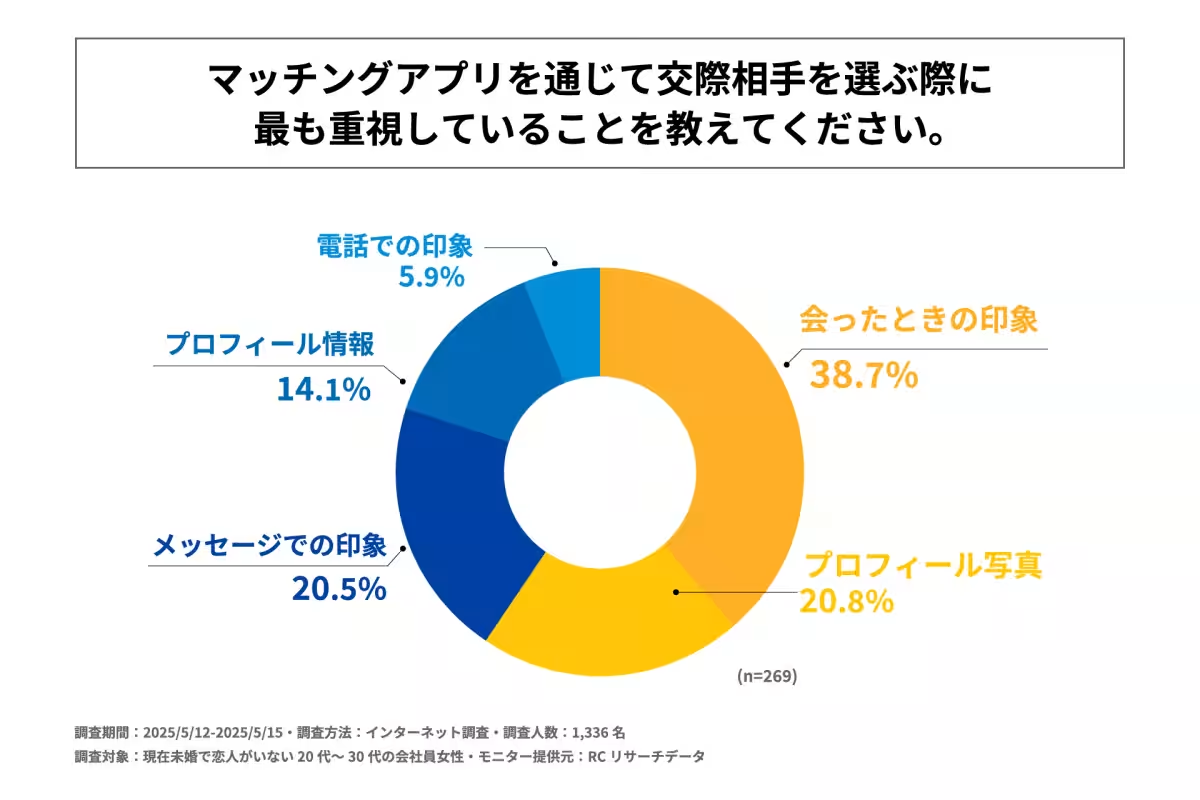
- - When selecting potential partners, the most crucial factor is the in-person impression made during meetings, valued by 38.7% of respondents.
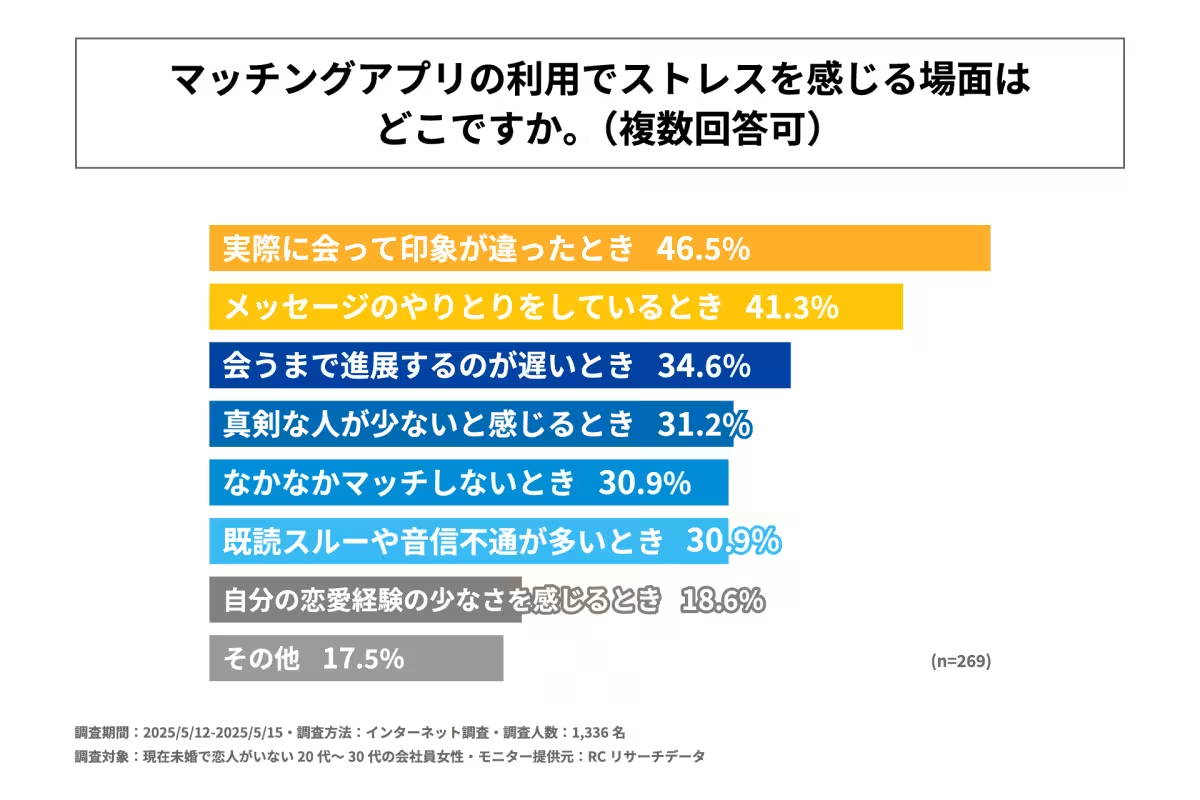
- - The top three stress-inducing situations in using dating apps include:
2. Stress while messaging (41.3%).
3. Slow progress towards meeting someone in person (34.6%).
Moreover, to mitigate 'dating app fatigue,' many women surveyed have adopted strategies such as communicating at their own pace to relieve stress associated with these platforms.
Trends in App Usage
The data indicated that a significant portion of the participants (79.9%) do not currently use dating apps, while 20.1% do. Among those using apps, two years of experience appears to be the most common duration. Interestingly, almost half of the respondents have not transitioned into romantic relationships through their experiences on these platforms. This statistic raises intriguing questions about the effectiveness of dating apps in fostering meaningful connections.
When selecting partners, the importance of in-person impressions stands out, reinforcing the idea that physical attraction and chemistry play critical roles in successful matches. Secondary considerations include profile photos and impressions formed through messaging, indicating a layered decision-making process.
Addressing Stressors in App Use
Many users expressed their frustrations, particularly around the stark contrast between expectations and reality during in-person meetings. These sentiments reflect a broader trend across many dating app users who often find the experience emotionally taxing. Messaging also appears to be a significant point of contention, leading many to advocate for a more streamlined process that alleviates unnecessary stress.
To combat these challenges, a notable 58.0% of participants emphasized the importance of maintaining a personalized pace in their interactions on the apps. This self-paced approach allows women to engage with the process more comfortably, reducing pressure and improving their overall experience.
Conclusion: Navigating the Digital Dating Landscape
The results from Bright Management's survey illuminate the complex landscape of dating apps for single women in their 20s and 30s. With around 20% actively using these platforms, many struggle with the transition from online interaction to real-life connections. This lack of successful conversions from encounters to relationships highlights the need for a reconsideration of how dating apps are structured and the experiences they offer.
Bright Management's



Topics People & Culture)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.