

Job Satisfaction Survey of Healthcare Practitioners Reveals Key Insights into Workplace Issues
Overview of the Job Satisfaction Survey
A recent survey conducted by SMS Co. examined the employment conditions of healthcare practitioners, including judo therapists and acupuncturists, across Japan. With a total of 2,742 respondents, this survey aimed to shed light on the working environment and job satisfaction in an industry where such data is scarce. The findings could contribute significantly to improving management practices in various healthcare settings.
Key Survey Findings
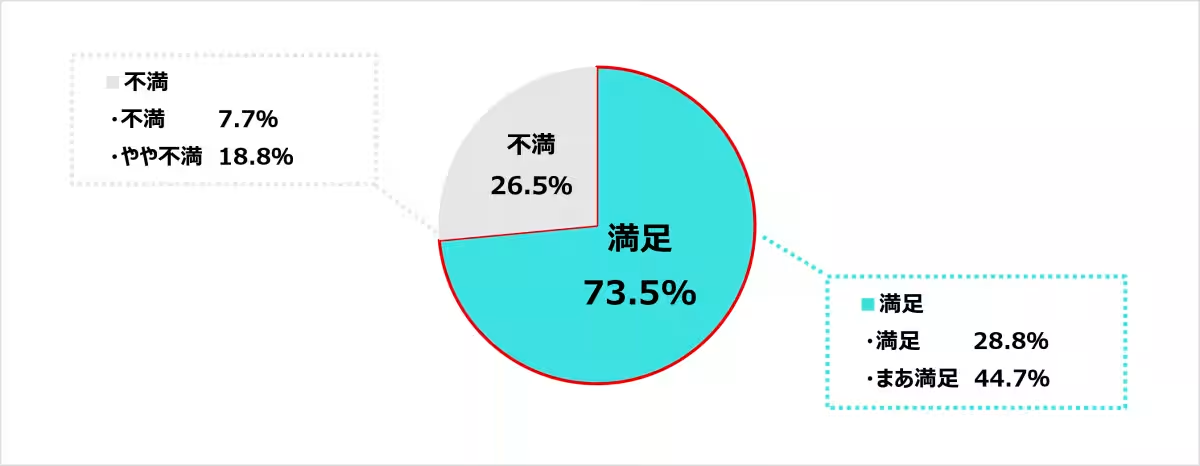
1. Overall Job Satisfaction: Approximately 73.5% of healthcare practitioners reported being satisfied with their current workplaces, which indicates a generally positive feeling towards their roles.
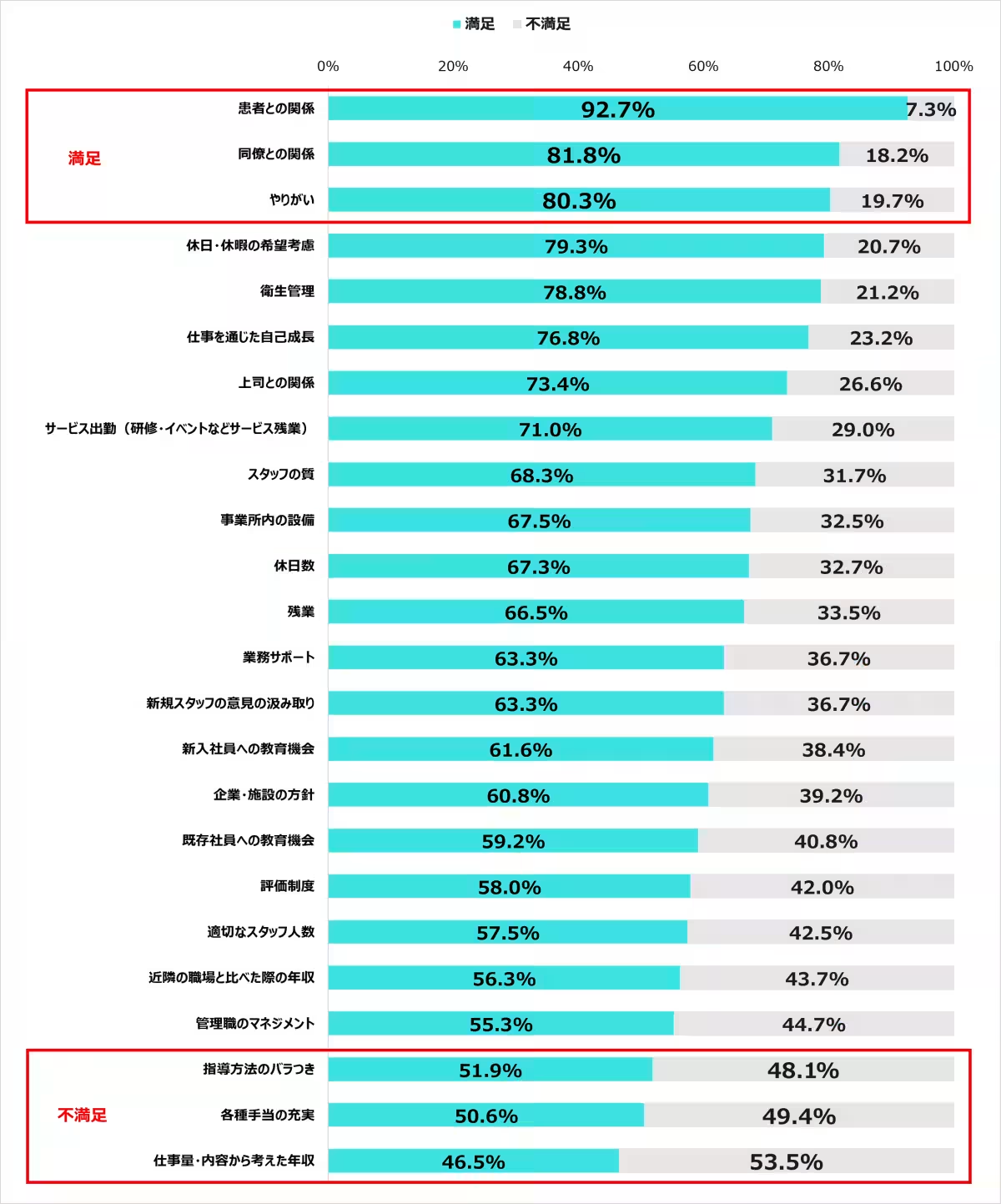
2. Reasons for Job Satisfaction: The most appreciated aspects of their work included relationships with patients (92.7%), colleagues (81.8%), and a sense of purpose (80.3%). These factors indicate that interpersonal relationships play a vital role in job satisfaction. However, dissatisfaction was notable regarding the balance of workload and income, with 53.5% expressing concern over their salaries in relation to their duties, highlighting a need for improvement.
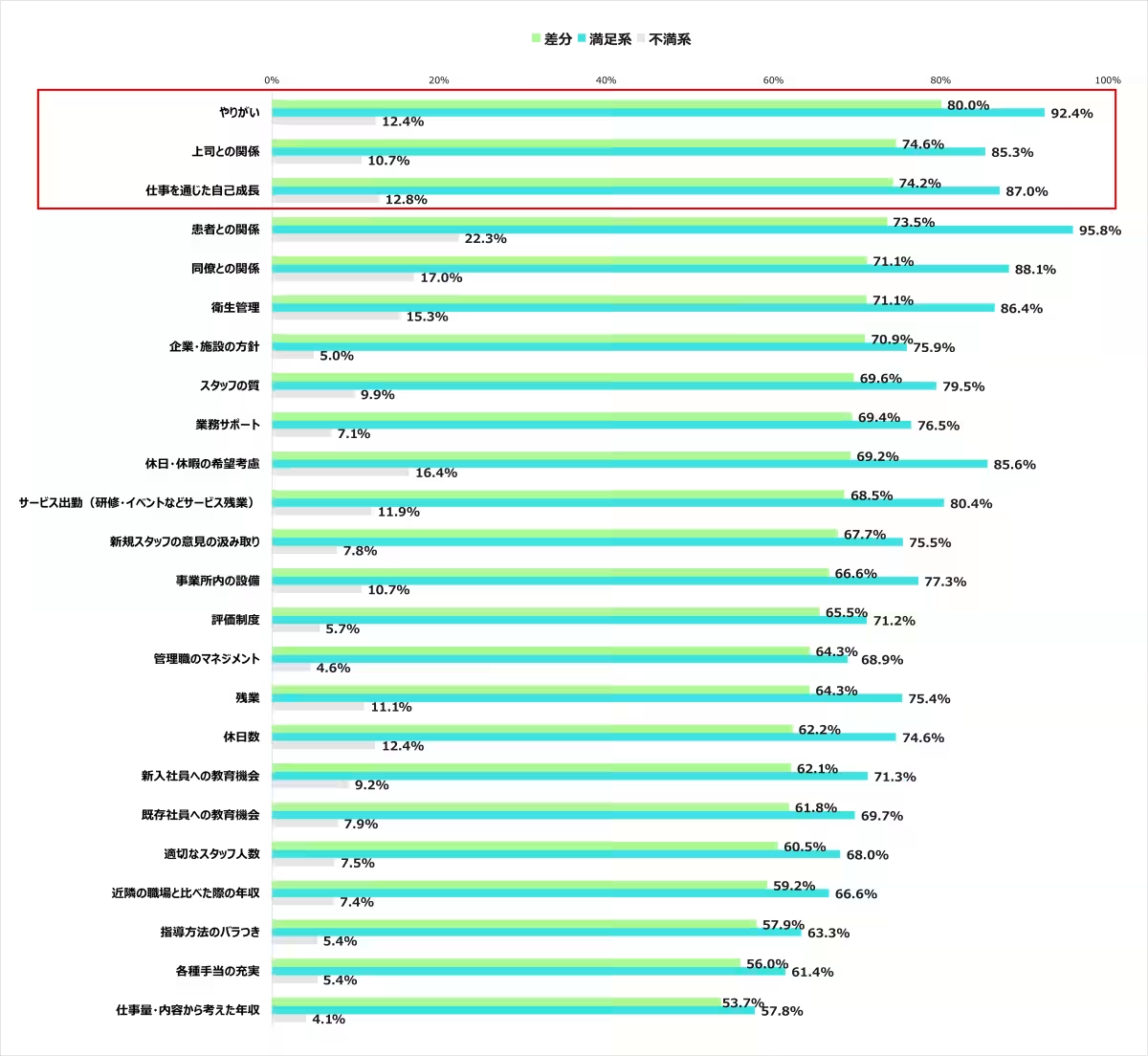
3. Differentiating Factors Between Satisfied and Dissatisfied Employees: The study revealed that elements contributing to satisfaction include a sense of purpose (80.0%), relationships with supervisors (74.6%), and opportunities for personal growth (74.2%). Meanwhile, practitioners expressing dissatisfaction pointed out issues such as inadequate income based on their workload and lack of support from management, suggesting these areas need to be addressed to improve retention.
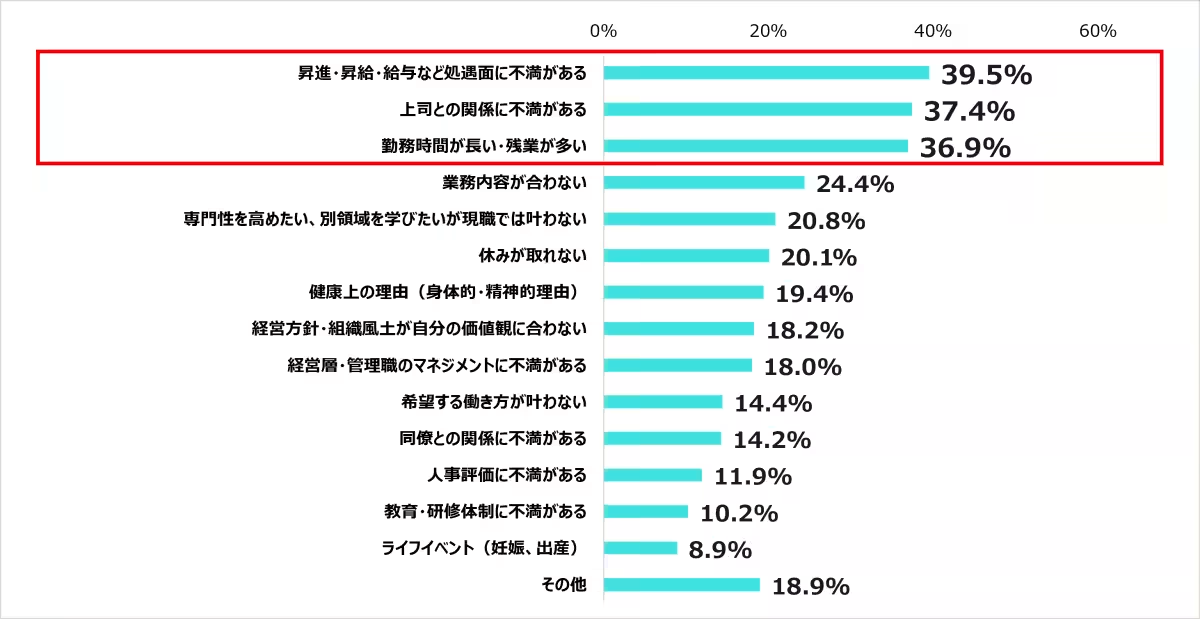
4. Reasons for Leaving Jobs: Among the common reasons for leaving, dissatisfaction with promotions and pay (39.5%) topped the list, followed closely by dissatisfaction with supervisory relationships (37.4%) and long working hours (36.9%). These insights indicate that addressing workplace grievances could enhance employee retention.
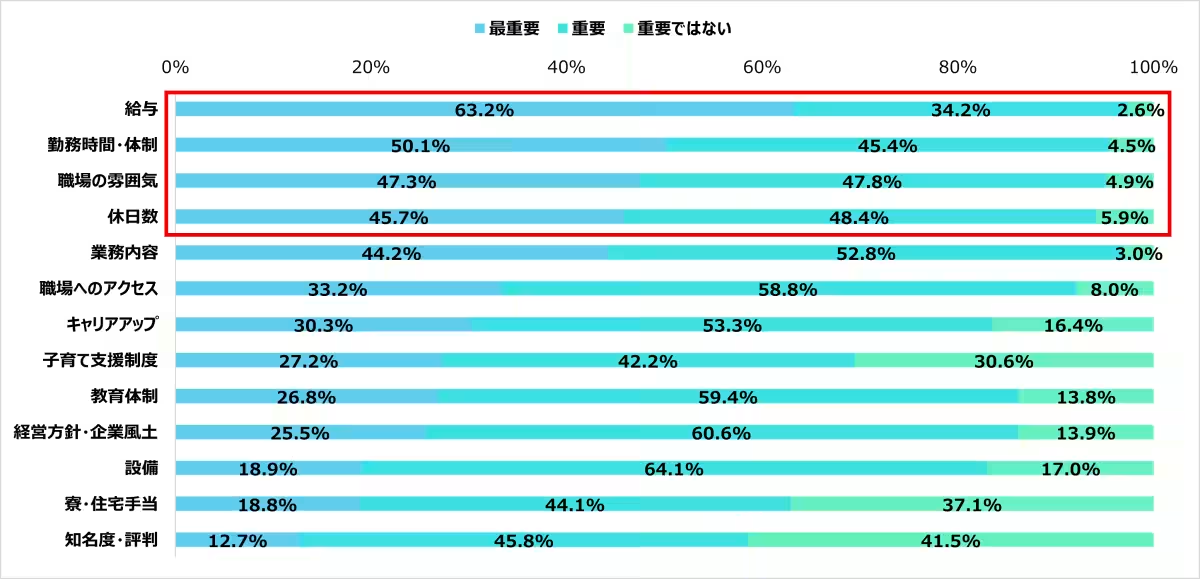
5. Priorities in Job Selection: When seeking new employment, practitioners rated salary (63.2%) as the most important consideration, followed by work hours and environment (50.1%) as well as workplace atmosphere (47.3%). Clearly, compensation remains a significant driving factor for job searches in this field.
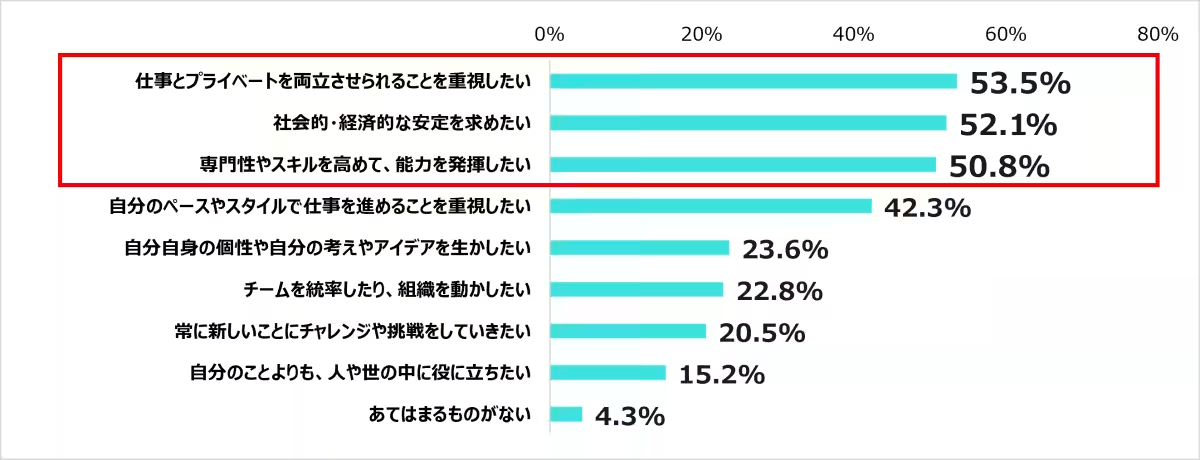
6. Work-Life Balance: The survey demonstrated that healthcare practitioners prioritize a balance between work and personal life, with 53.5% indicating that work-life balance is crucial during their job searches, aligning with economic stability and opportunities to enhance their skills.
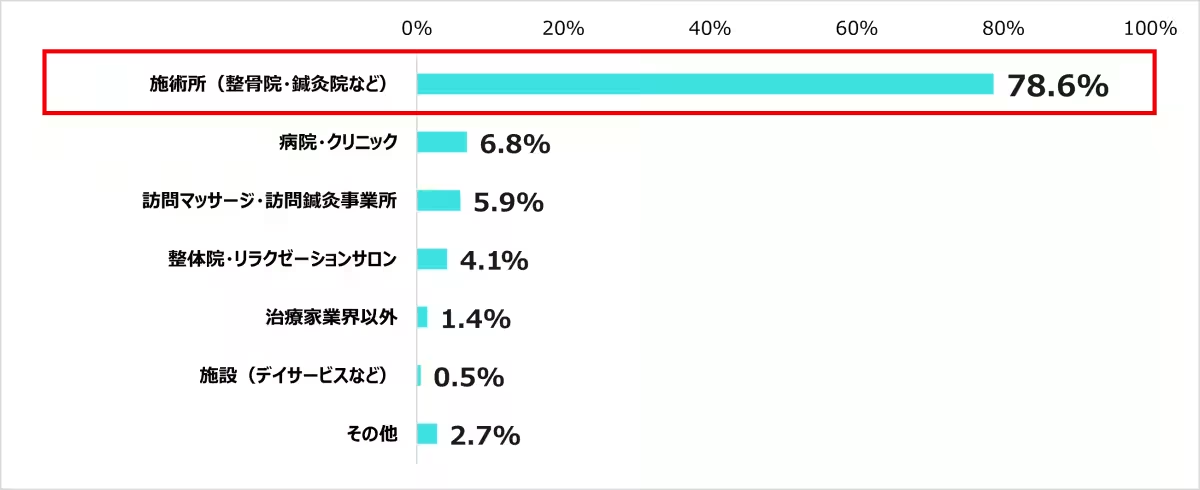
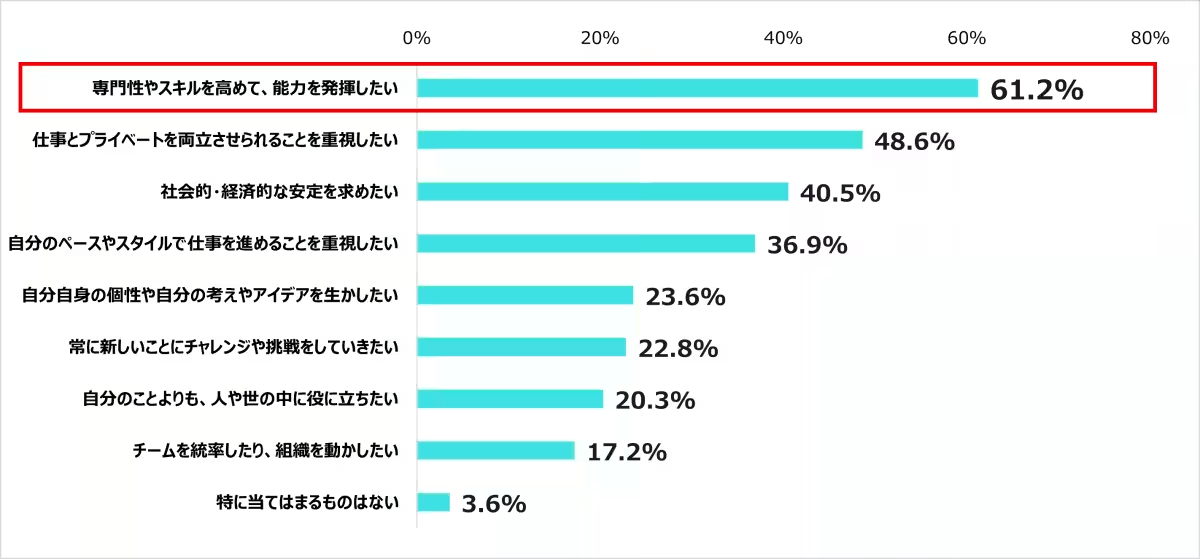
7. Trends Among Students: Of the students aiming to enter the healthcare field, a significant 78.6% preferred working in treatment facilities. When evaluating future employment, students prioritized skill development (61.2%), emphasizing a shift in focus from job relationships to personal growth between their educational and professional lives.
8. Diverging Values Post-Employment: Notably, there was a discrepancy between the values students held while job hunting compared to those who are already employed, showcasing a potential shift in priorities once they enter the workforce.
Conclusion
The results from this comprehensive survey highlight both strengths and areas for improvement within the healthcare sector. Given the lack of data on employment conditions in this industry, the findings are poised to encourage enhancements in workplace policies and management strategies. The overarching trend suggests that while most healthcare workers maintain a positive outlook on their work environment, disparities in workload, compensation, and managerial communication must be prioritized to foster greater job satisfaction and employee retention.
Going forward, ongoing research into the employment landscape for healthcare practitioners is essential in tackling these challenges, ultimately leading to improved workplace conditions for those dedicated to healing and supporting the community.

Topics People & Culture)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.