

New Enzyme Discovery Offers Hope for Adrenoleukodystrophy Diagnosis and Treatment
New Insights into Adrenoleukodystrophy Diagnosis
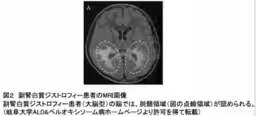
Adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD) is a rare genetic disorder that has been in the spotlight due to its portrayal in the film "Lorenzo's Oil." It is characterized by the accumulation of very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs) in the body, caused by a genetic dysfunction impacting specific transport proteins. This buildup leads to inflammation of the brain and progressive demyelination, severely affecting neurological functions and adrenal gland health.
Currently, the only known effective treatment for ALD is hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, which can only slow disease progression rather than restore lost brain function. Hence, timely diagnosis and early intervention are paramount. To facilitate this, newborn screening tests, which identify the presence of C26:0 lysophosphatidylcholine, are increasingly being implemented in countries such as the USA, Europe, and more recently, Japan. However, the mechanisms behind the elevation of this diagnostic marker in ALD patients have not been fully understood until now.
Major Breakthrough in Understanding C26:0 Production
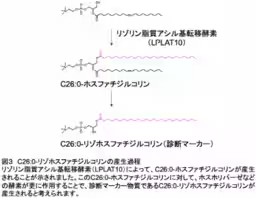
A research group from Teikyo University, led by Associate Professor Kotaro Hama, analyzed how C26:0 lysophosphatidylcholine, a key marker in diagnosing ALD, is synthesized in cells. They focused on a precursor molecule, C26:0 phosphatidylcholine, which is critical for producing the diagnostic marker. Through their research, they successfully identified an enzyme named LPLAT10, which plays a vital role in this production process.
By utilizing molecular dynamics simulations, the team unveiled the detailed workings of this enzyme at an atomic level, providing insights into how it interacts with its substrate. Understanding this mechanism not only aids in improving the accuracy of ALD diagnoses but also contributes to clarifying the disease's pathogenesis.
Significance of the Research Findings
The revelation of how C26:0 lysophosphatidylcholine is produced marks a significant step forward in comprehending the entire process of this important diagnostic marker's generation. This foundational knowledge could lead to the development of more precise diagnostic methods, allowing healthcare professionals to better predict disease progression. Moreover, understanding the relationship between C26:0 lysophosphatidylcholine levels and disease onset is expected to propel future research aimed at unveiling the underlying mechanisms that enable VLCFAs to instigate various symptoms and complications associated with ALD.
Broader Implications for Patient Care and Research
Currently, no comprehensive treatment exists for ALD, yet early detection through newborn screening could prevent severe neurological damage. Genetic testing related to fatty acid transport proteins highlights the complexities and ethical debates surrounding the diagnosis, as gene mutations do not always correlate with disease severity. As research continues into how VLCFAs contribute to ALD and their toxic effects, the role of the identified enzyme in disease pathology may open new pathways for therapeutic interventions.
Ongoing studies will explore whether therapeutic strategies can be developed to counteract the extremes of VLCFA accumulation or to enhance the efficiency of existing treatments. With the support of numerous research grants and initiatives, including those from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, the team anticipates that their findings will significantly influence future studies and improve the lives of those affected by this devastating condition.
Conclusion
The identification of the enzyme responsible for producing C26:0 lysophosphatidylcholine not only enhances our diagnostic capabilities for ALD but also lays the groundwork for a deeper understanding of the disease mechanisms. As subsequent research unfolds, there is hope that improved predictions regarding disease progression and potential therapeutic strategies will emerge, paving the way for better outcomes for ALD patients.
Relevant Dates and Acknowledgments
This research was published on December 30, 2025, in the Journal of Lipid Research. It was supported by several prestigious organizations, emphasizing its importance and potential impact on the future of ALD diagnosis and treatment.





Topics Health)









【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.