

Shifting Perspectives: Middle Career Employees' Attitude Toward Managerial Positions
Shifting Perspectives: Middle Career Employees' Attitude Toward Managerial Positions
In a recent survey conducted by ALL DIFFERENT, a company specializing in organizational development and talent cultivation, the perspectives of mid-career employees regarding managerial roles have come to light. The survey targeted 800 mid-career professionals who are not currently seeking managerial positions. The results suggest a growing reluctance among these employees to accept managerial roles and reveal significant trends in their career aspirations.
Understanding the Context
Advancement into management has traditionally been a pivotal point in a professional's career. However, recent observations indicate a declining interest in managerial roles among mid-career employees. Pressures associated with managerial responsibilities, coupled with a shift toward diverse career paths, have made employees less inclined to aim for conventional leadership positions. This trend suggests that businesses must adapt to the evolving preferences of their workforce, fostering a culture that values diverse career trajectories and individual aspirations.
Survey Highlights
1. Management Acceptance Rates
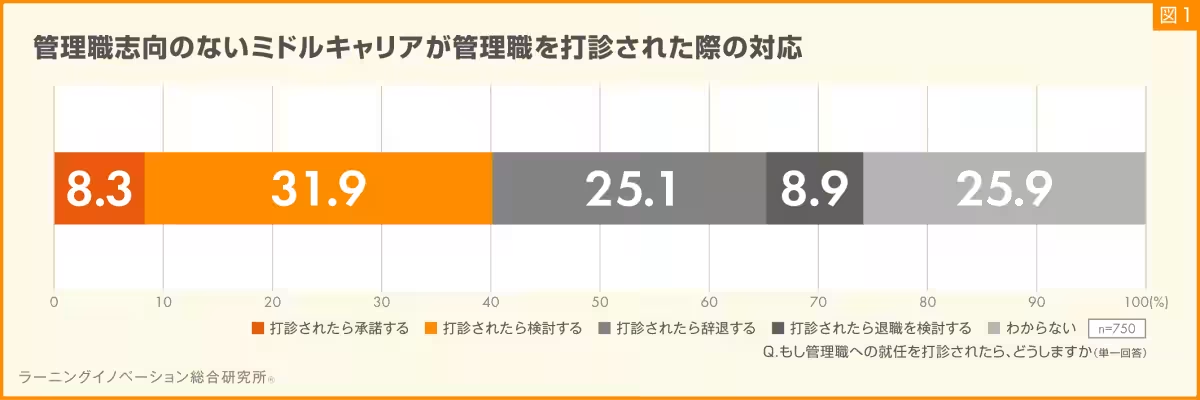
The survey results showed that only 8.3% of mid-career respondents who do not aspire to management roles would accept a managerial offer. Conversely, a considerable 25.1% indicated they would decline such an offer, while 31.9% were unsure, illustrating a hesitance in commitment to traditional career advancement. Notably, 8.9% of respondents stated they would consider leaving their positions if offered management roles.
2. Gender Disparities in Acceptance
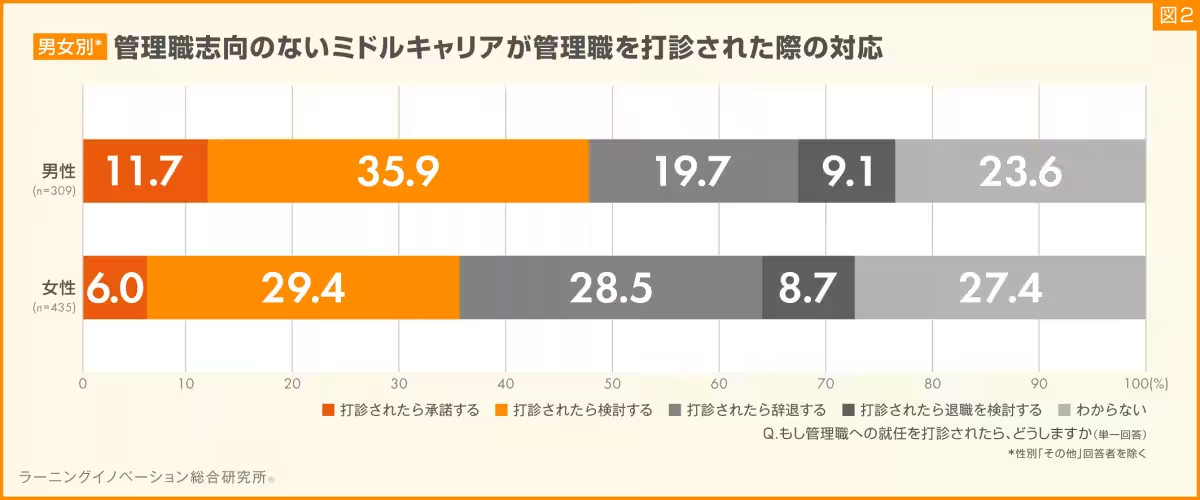
The survey also explored gender differences. Male respondents exhibited a higher tendency to be open to management roles than their female counterparts. While 35.9% of men expressed willingness to consider an offer, only 29.4% of women stated the same. Additionally, 11.7% of men indicated they would accept a managerial position, compared to just 6.0% of women, revealing a stark gender divide in attitudes toward management.
3. Specialist Roles and Acceptance Rates
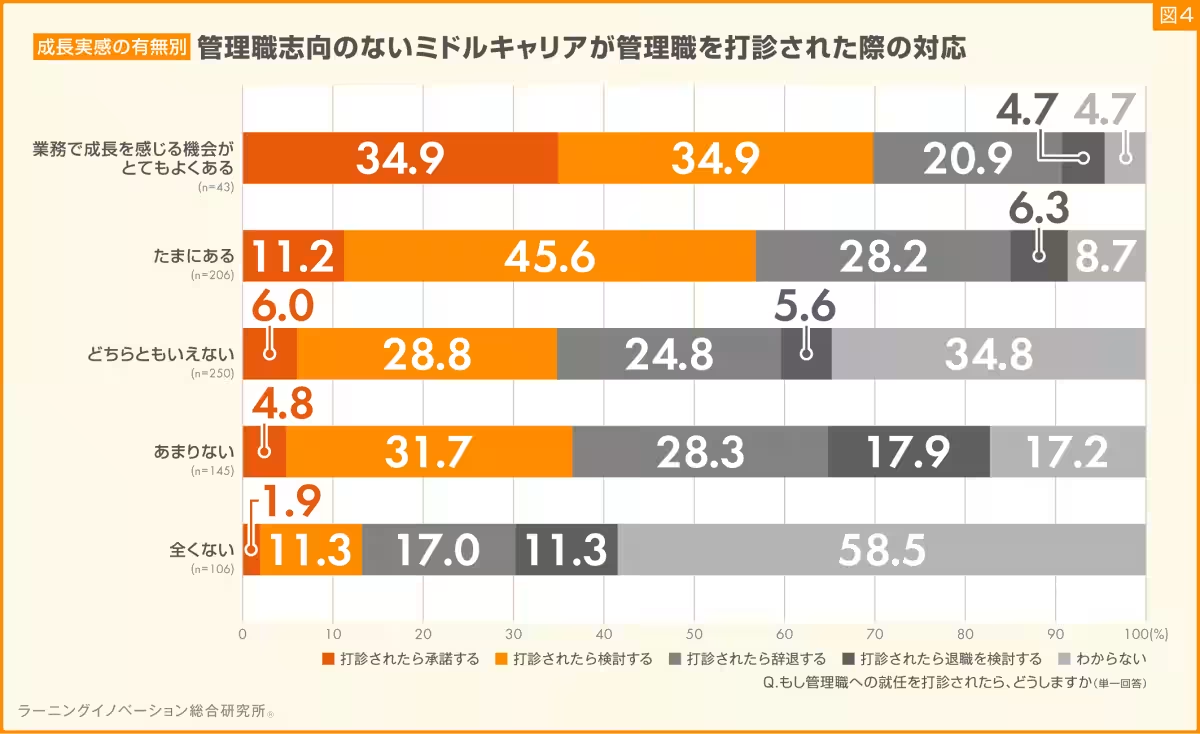
Among those who identified their career aspiration as specializing in their field, 22.4% reported that they would accept a managerial position. This is the highest acceptance rate observed when compared to other career orientations, highlighting that those with a specialized focus are more likely to embrace managerial roles, viewing them as an extension of their expertise rather than a departure from it.
4. Growth Opportunities Influence Acceptance
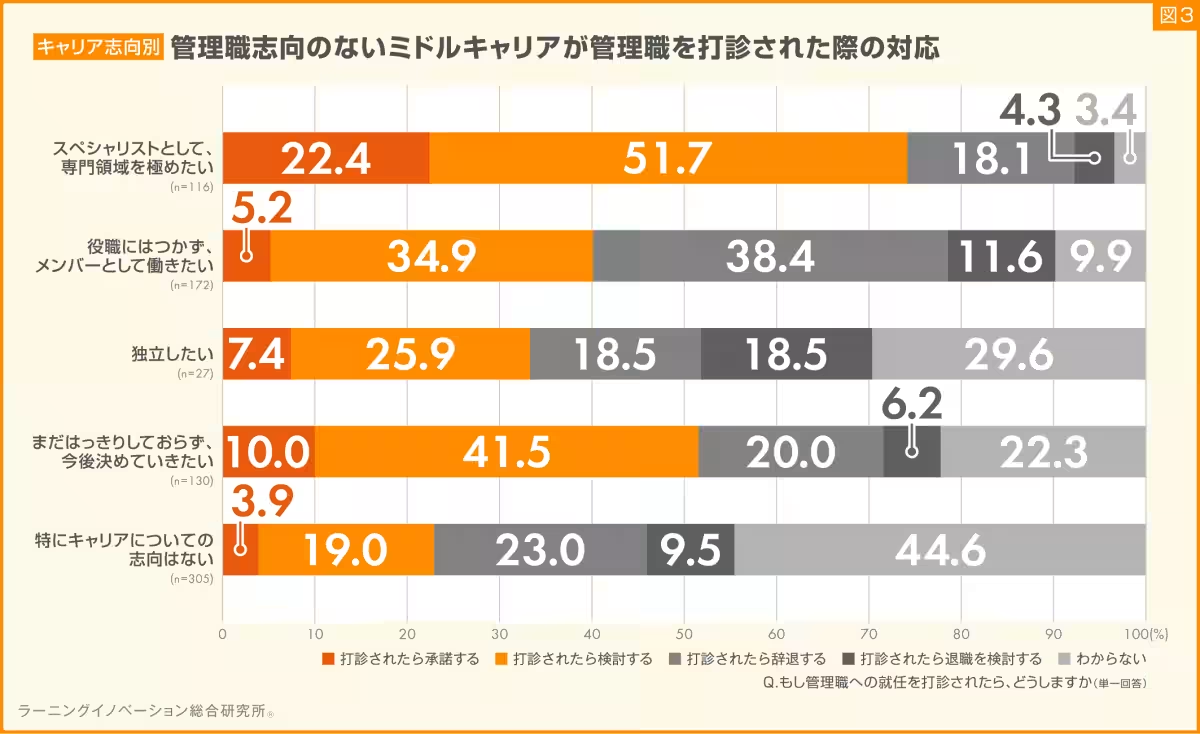
The relationship between feelings of professional growth and acceptance of management roles was also analyzed. Mid-career employees reporting regular opportunities for growth had a significantly higher acceptance rate of 34.9% when offered managerial positions, compared to a mere 1.9% acceptance rate among those who felt no growth possibilities were present.
5. Interdepartmental Opportunities Impact Attitudes
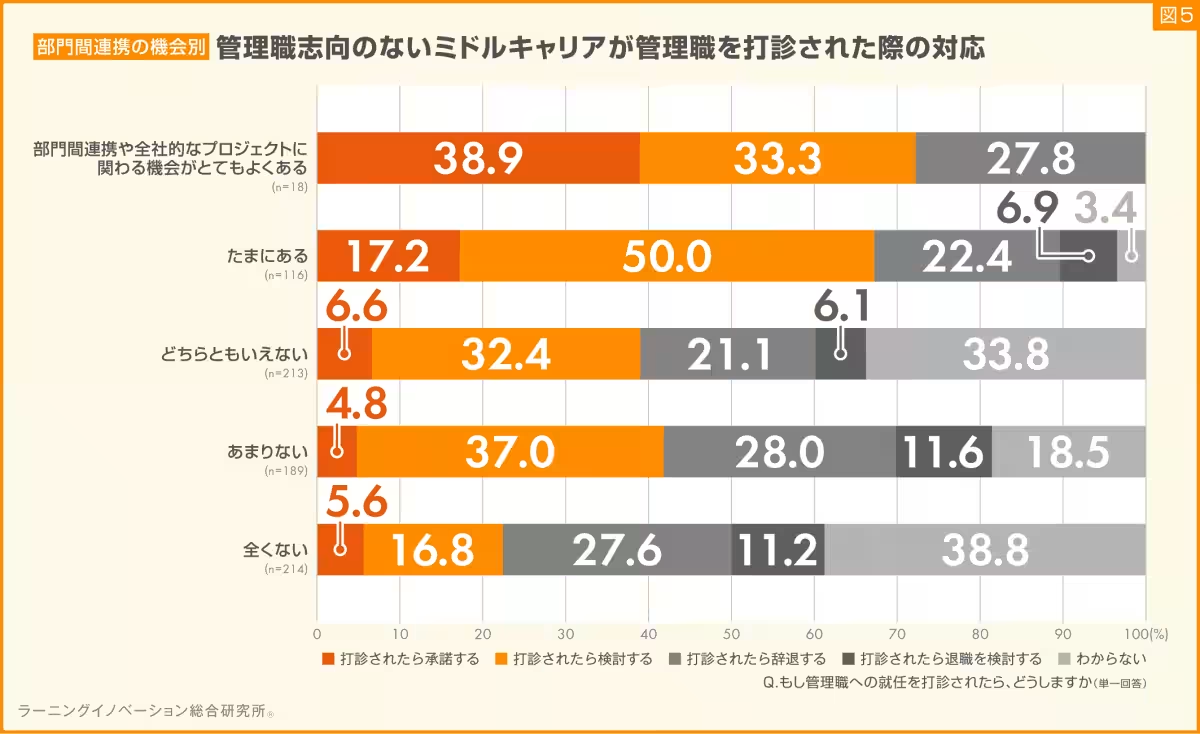
Similar results were noted concerning interdepartmental collaboration and involvement in company-wide projects. Those exposed to such experiences showed a more favorable response to management positions, with 38.9% willing to accept an offer when actively engaged in collaborative projects.
6. Perceptions of Promotion Practices
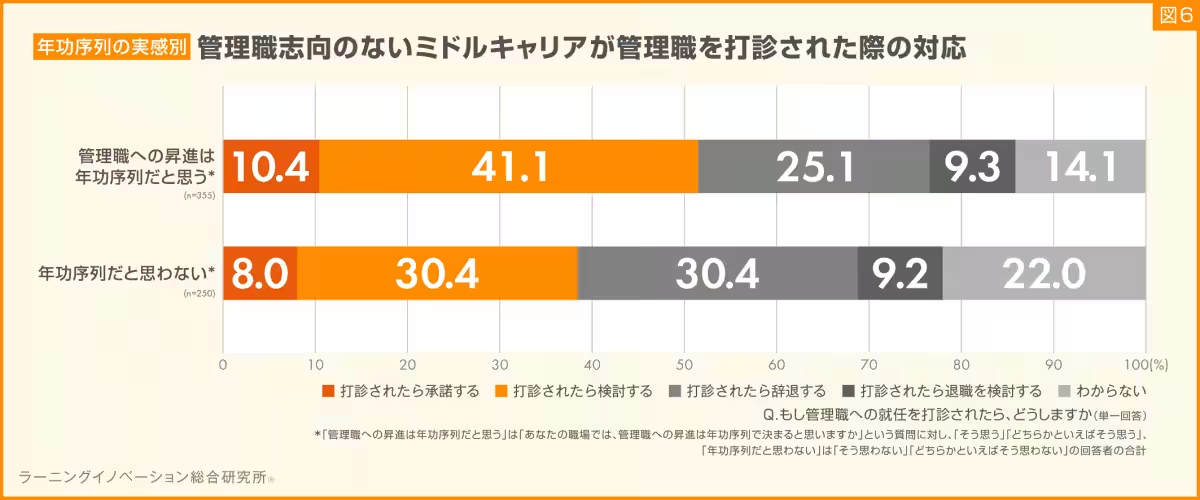
The survey also raised questions about the perceptions of promotion systems within organizations, specifically regarding age-based hierarchies. Employees who believed their workplace operated on seniority principles showed higher rates of acceptance and willingness to consider management roles compared to those who did not share this perception.
7. Role Awareness Matters
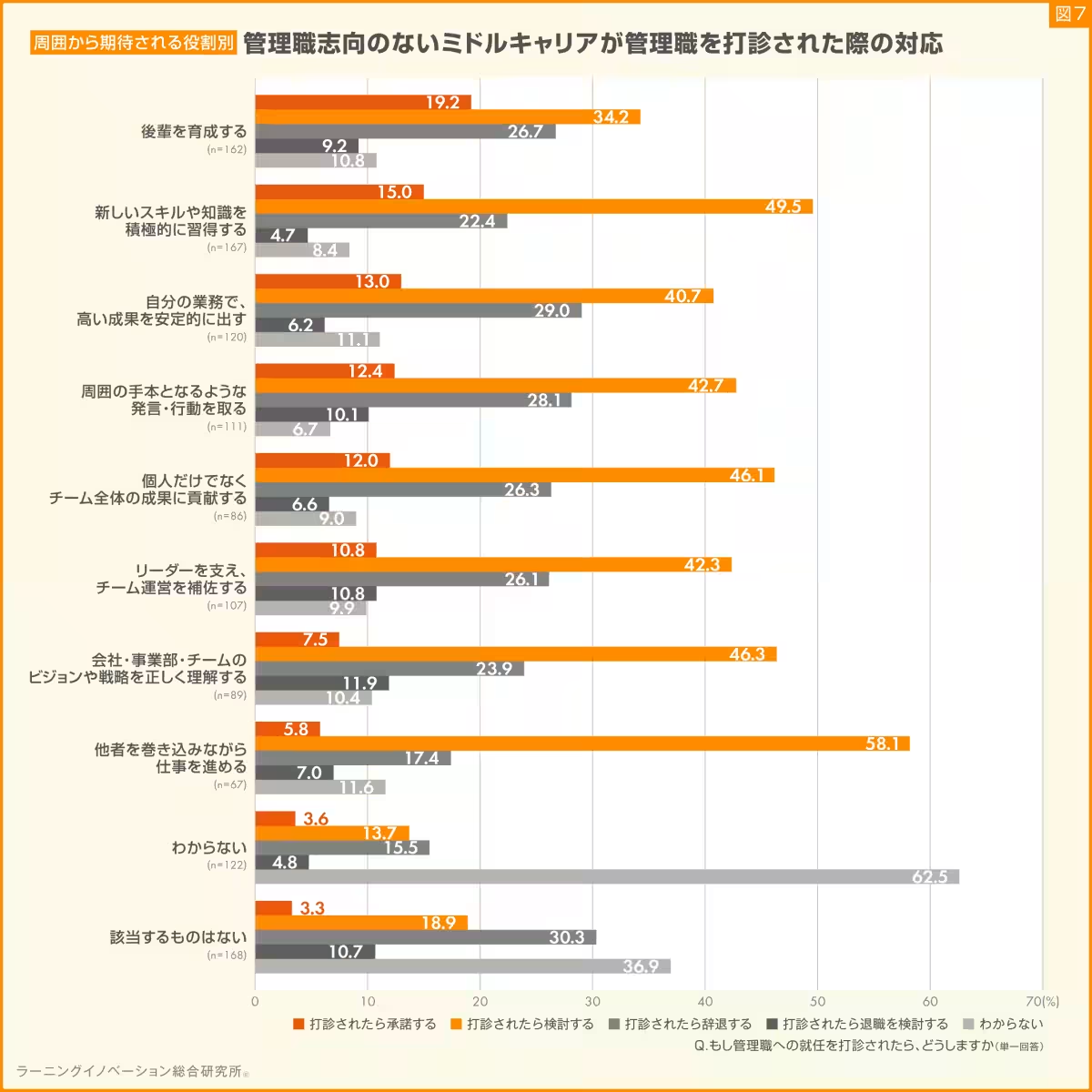
The final segment examined the relationship between employees' understanding of their roles and their responses to management offers. Those who perceived their role as guiding and developing others exhibited the highest acceptance rates compared to individuals unsure of their roles. This suggests that clarity around role expectations positively influences the willingness to consider leadership positions.
Conclusion
The survey reveals that even among mid-career employees who are not actively pursuing managerial roles, nearly 40% of them show a willingness to consider such offers. However, the willingness to accept is markedly low, with acceptance rates falling below 10%. Future strategies for organizations should center around enhancing clarity around roles, fostering professional growth, and recognizing individual aspirations to better inspire mid-career employees toward leadership roles.
Organizational Implications
Given the findings, it’s clear that organizations must adapt to the shifting mindset of their mid-career employees. Active measures to convey expectations regarding role fulfillment and opportunities for professional growth can cultivate a more engaged workforce. Implementing follower-type assessments can also help identify areas for development among employees, further supporting those who may be hesitant about management positions.
In summary, cultivating a workplace where mid-career employees feel growth and role clarity may enable organizations to bridge the gap in managerial aspirations and adapt to the evolving career interests of their workforce effectively.



Topics People & Culture)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.