

Harnessing AI for Efficient RNA Aptamer Drug Discovery with RaptScore Technology
Revolutionizing RNA Aptamer Drug Discovery with RaptScore
In a groundbreaking advancement in the field of drug discovery, researchers from Waseda University have unveiled a sophisticated technology named RaptScore. This AI-driven tool aims to streamline the evaluation of RNA aptamer binding activity, a crucial component in the development of next-generation therapeutics.
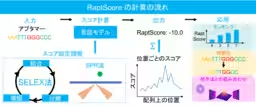
Typically, the process of identifying promising RNA aptamers involves exhaustive experimental trials, which are not only time-consuming but also resource-intensive. Aptamers, which are short RNA molecules capable of binding to target proteins, have gained immense attention for their potential as therapeutics and biosensors. The traditional method for aptamer selection is known as SELEX (Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment), which, despite its efficacy, poses challenges in evaluating new sequences not present in the experimental datasets.
One of the prominent hurdles in the SELEX process is that it heavily relies on prior experimental data, making it difficult to assess novel sequences or modify existing ones for optimal drug production without costly trials. With RaptScore, this limitation is now being addressed, leveraging a large language model (LLM) to provide accurate predictions of RNA aptamer binding activity.
Key Innovations of RaptScore
1. High Precision Outcomes: RaptScore offers robust predictions by comparing the scores derived from LLMs with experimental results from techniques such as Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR). The correlation between RaptScore values and empirical outcomes demonstrates its capacity to predict binding strength effectively, even with minimal experimental data.
2. Facilitating Shortening of Sequences: By utilizing RaptScore, researchers have successfully demonstrated that aptamer sequences can be shortened while maintaining or even improving their binding capabilities. This feature is critical in the manufacturing of RNA drugs, as shorter sequences typically lead to lower production costs and simplified quality management processes.
3. Integration with AI-generated Candidates: The synergy between RaptScore and a complementary AI tool, RaptGen, further enhances the research capabilities. This collaboration enables scientists to sift through AI-generated sequences and identify those most likely to yield strong experimental candidates, thus optimizing the drug discovery process.
Societal Impact and Future Prospects
The potential implications of RaptScore in the realm of RNA aptamer research are profound. As the global demand for cost-effective and rapidly developed treatments increases, RaptScore stands to not only accelerate the discovery of new therapeutics for diseases such as cancer and viral infections but also to make them more accessible and affordable.
Moreover, the advancement in AI technologies, such as RaptScore, signifies a transformative shift in biochemical research, promising to cut down both developmental timelines and costs. Researchers are optimistic that further integrating the structural information of RNA molecules will enhance the predictive capabilities of this tool, thereby significantly boosting its effectiveness.
Expert Commentary
As stated by Akira Kimura and Michiaki Hamada, the lead researchers behind this innovation, the goal of RaptScore is not to replace traditional methods but to augment the expertise of seasoned scientists in aptamer design. By incorporating AI and data analytics, researchers aim to enhance the efficiency and precision of creating therapeutics from RNA aptamers, maintaining a focus on practicality and delivery in drug development.
Conclusion
In summary, RaptScore represents a substantial leap forward in RNA aptamer drug discovery techniques. With its ability to harness AI for high-precision evaluations and its integration with existing research methodologies, it is poised to make a significant impact on how RNA-based therapeutics are developed in the future.
This research and its findings will be published in the prestigious journal Nucleic Acids Research on January 14, 2025, signifying its importance in the scientific community. The authors assert that further innovations and applications of RaptScore will continue to advance the field of drug discovery, transforming how new therapeutics are brought to market.

Topics Health)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.