

Collaborative Medical Care Essential for Schizophrenia Patients with Cancer in Japan
Enhancing Cancer Treatment for Patients with Schizophrenia in Japan
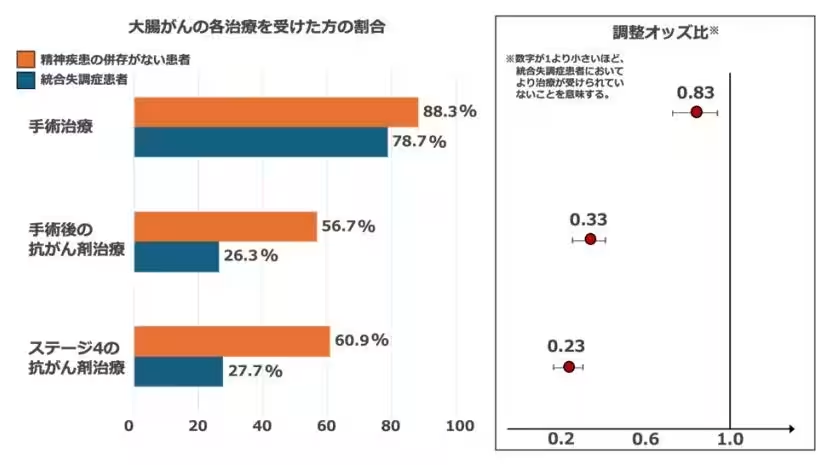
A significant new study conducted by Okayama University in collaboration with several leading medical institutions highlights alarming disparities in cancer treatment for individuals with schizophrenia. The research revealed that patients with schizophrenia are diagnosed with colorectal cancer at more advanced stages than those without such mental disorders. Consequently, they are less likely to receive standard surgical interventions and postoperative chemotherapy, critical components of effective cancer care.
Study Overview
This pivotal research, led by Dr. Masaki Fujiwara and Dr. Hiroshi Yamada from Okayama University’s Department of Psychiatry, along with researchers from the National Cancer Center of Japan, Tohoku University, and Shimane University, is groundbreaking in the context of Japanese healthcare. It asserts that schizophrenia patients are significantly underserved compared to their counterparts without mental health issues. Specifically, the adherence rate to recommended cancer treatments, including both surgical and drug therapies, is noticeably lower for schizophrenia patients.
The findings demonstrated that a substantial fraction of these patients only receive appropriate cancer treatment after experiencing a lengthy period of diagnosis delays. This situation can lead to worsened health outcomes and increased treatment burdens when cancer reaches more advanced stages, complicating the healthcare process.
Importance of Integrated Healthcare
The study emphasizes the necessity for an integrated healthcare framework that combines cancer treatment with mental health services. It is evident that healthcare professionals across multiple disciplines need to collaborate closely to ensure that patients with schizophrenia receive timely cancer screenings and subsequent treatment. The integration is crucial not only to recognize the early signs of cancer but also to provide holistic care that accommodates the complexities of patients dealing with mental health disorders.
Given that early detection greatly influences treatment efficacy and overall prognosis, the research urges healthcare providers to implement proactive measures promoting cancer screening among schizophrenia patients. Such initiatives would alleviate much of the burden posed by late-stage cancer diagnoses and subsequently improve survival rates and the quality of life for these individuals.
Dr. Fujiwara expressed pride in the research outcomes and acknowledged the challenges faced during the study, particularly amid the pandemic that restricted face-to-face meetings. He remarked, "We are thrilled to share our findings after five years of dedication to this research. The support we received from various stakeholders was instrumental in reaching this important milestone."
Global Context
The significance of this research extends beyond Japan, as very few studies globally have addressed cancer treatment disparities for individuals with psychiatric conditions. As such, this report marks a pioneering step in bridging the gap in healthcare services for these vulnerable populations. It underscores the urgent need for further investigations into how schizophrenia affects treatment accessibility and outcomes in countries worldwide.
Conclusion
Published on January 15, 2026, in the esteemed medical journal "Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica," this research not only underscores the critical need for multidisciplinary approaches in healthcare but also calls upon the medical community to innovate and improve cancer care frameworks for patients grappling with schizophrenia. Continuous efforts must be made to ensure equitable healthcare access, tailored support, and effective treatment pathways for all patients, regardless of their mental health status.







Topics Health)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.