
Impact of Consuming OLL1073R-1 and OLS3059 Fermented Yogurt on Oral Antimicrobial Substances
Effects of Fermented Yogurt on Oral Antimicrobial Substances
Introduction
Recent collaborative research between Meiji Co., Ltd. and Kanagawa Dental University has uncovered significant health benefits associated with the continuous consumption of yogurt fermented by two specific strains, Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus OLL1073R-1 and Streptococcus thermophilus OLS3059. The study, presented at the 68th Annual Meeting of the Japanese Society of Periodontology, focuses on the impact of this fermented yogurt on oral antimicrobial substances in elderly populations working in care facilities.
Research Overview
The primary objectives of this observational study were:
1. Assessing the levels of antimicrobial substances in saliva.
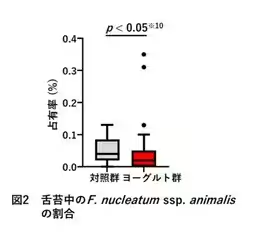
2. Evaluating the concentration of Fusobacterium nucleatum ssp. animalis in tongue biofilm, a pathogen linked to colorectal cancer.
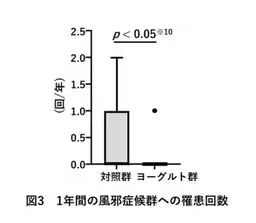
3. Determining the incidence of cold syndromes among participants over the past year.
Methodology
The study involved two groups of participants:
- - Yogurt Group: 40 individuals who consumed one 112g serving of yogurt containing the fermented strains daily for over a year.
- - Control Group: 13 individuals who did not consume this yogurt.
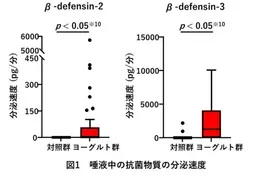
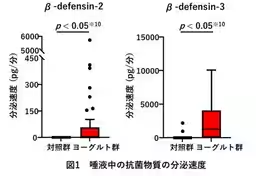
Saliva and tongue biofilm samples were collected for analysis of secretion rates of β-defensins (specifically, β-defensin-2 and β-defensin-3) and the bacterial composition of tongue biofilms. Participants also reported the frequency of cold syndromes experienced in the previous year. This data was subsequently analyzed using Bayesian network methods to understand causal relationships.
Findings
Increased Antimicrobial Activity
The research results showcased:
- - The yogurt group exhibited a significantly higher secretion rate of β-defensin-2 and β-defensin-3 compared to the control group. This increase in antimicrobial peptides indicates a stronger oral defense mechanism.
- - A notable decrease in the proportion of Fusobacterium nucleatum ssp. animalis in the tongue biofilm of the yogurt consumers was documented, highlighting an improvement in harmful bacterial profiles.
- - The yogurt group reported significantly fewer incidences of cold syndrome, indicating potential benefits in respiratory health through dietary intervention.
Causal Inferences
Utilizing the Bayesian network analysis, the study suggested that consistent consumption of yogurt fermented with OLL1073R-1 and OLS3059 positively contributed to:
- - Increased secretion rates of β-defensins in saliva.
- - Decreased incidence of cold syndromes, reaffirming the yogurt's role in respiratory health.
Conclusion
The research strongly indicates that consuming yogurt fermented with OLL1073R-1 and OLS3059 can enhance the levels of antimicrobial substances in the oral environment, potentially reducing the risk of respiratory infections and improving overall oral health. The findings suggest that these fermented yogurts may not only enhance oral health but could also play a crucial role in maintaining systemic health, especially in vulnerable populations such as the elderly.
Implications
Given that oral health significantly impacts overall health, these findings underscore the need for further research into the beneficial roles of probiotics in diet, particularly the strains assessed in this study. The evidence presented encourages exploring the potential of these fermented products as functional food options for improving immunity and health outcomes. Future studies should aim to delve deeper into the mechanisms behind these health benefits and further establish guidelines for incorporating such dietary interventions into everyday nutrition.
Topics Health)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.