

The Impact of May Syndrome: Insights from a Nationwide Survey on Stress Levels Across Generations and Professions
Understanding the May Syndrome: A Mental Health Concern
As the calendar turns to May, many feel the weight of new beginnings and the stress associated with them. This phenomenon, commonly referred to as 'May Syndrome,' often surfaces after the extended holiday breaks in April, leaving individuals feeling fatigued and mentally drained. To shed light on this issue, For-It Inc., known for its affiliate platform AFB, conducted a comprehensive survey targeting 500 men and women aged 20 to 69 across Japan. The findings underscore the significant impact of generational and occupational differences on the experience of May Syndrome.
The Backstory of May Syndrome
May Syndrome refers to the feelings of exhaustion and stress that many individuals experience as they transition back to work life following the Golden Week holidays in Japan. Initially, it was unclear just how prevalent these feelings were among the public. For-It’s survey aimed to illuminate the scope of this concern by asking respondents about their experiences. The survey, conducted via online methods on April 18, 2025, gathered data from individuals across the country.
Survey Results
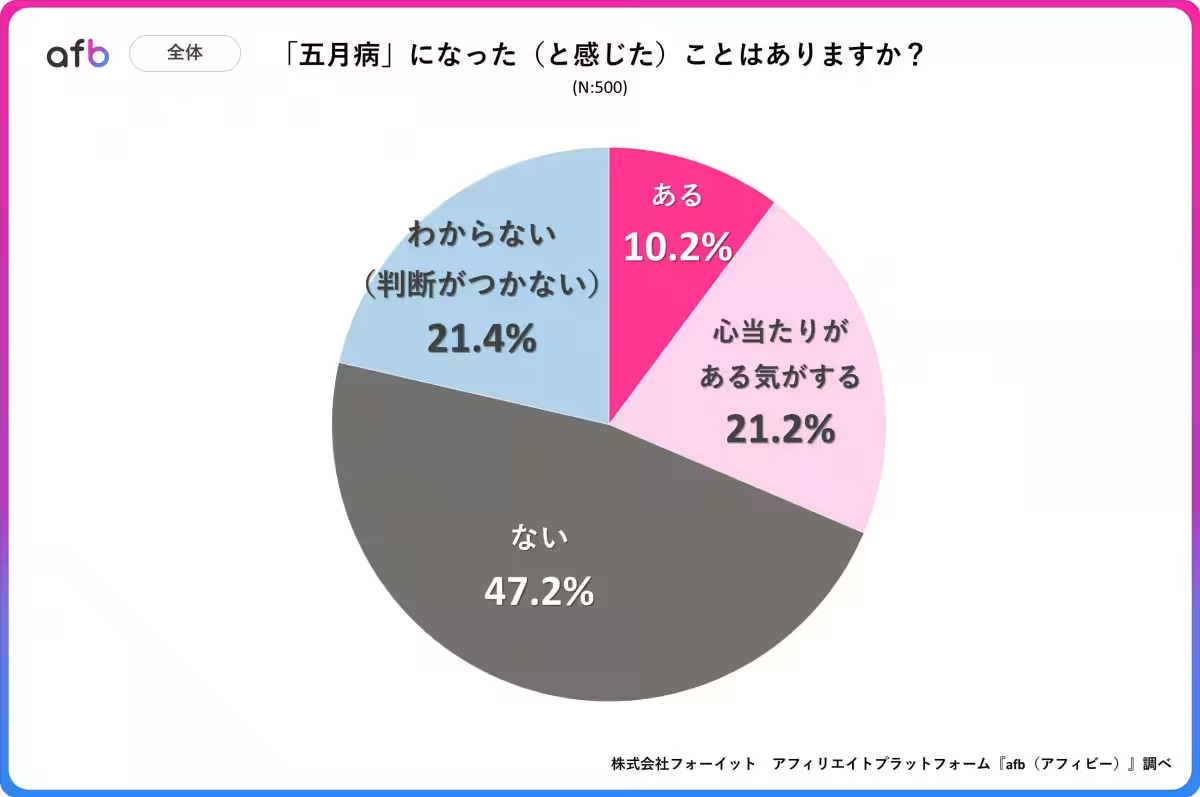
When asked if they had ever experienced May Syndrome, 10.2% of respondents answered affirmatively, while another 21.2% suspected they had felt its effects, bringing the total to over 30%. This indicates a substantial portion of the population grapples with the anxiety and strain associated with the transition back to working life after a break.
Generational Variations
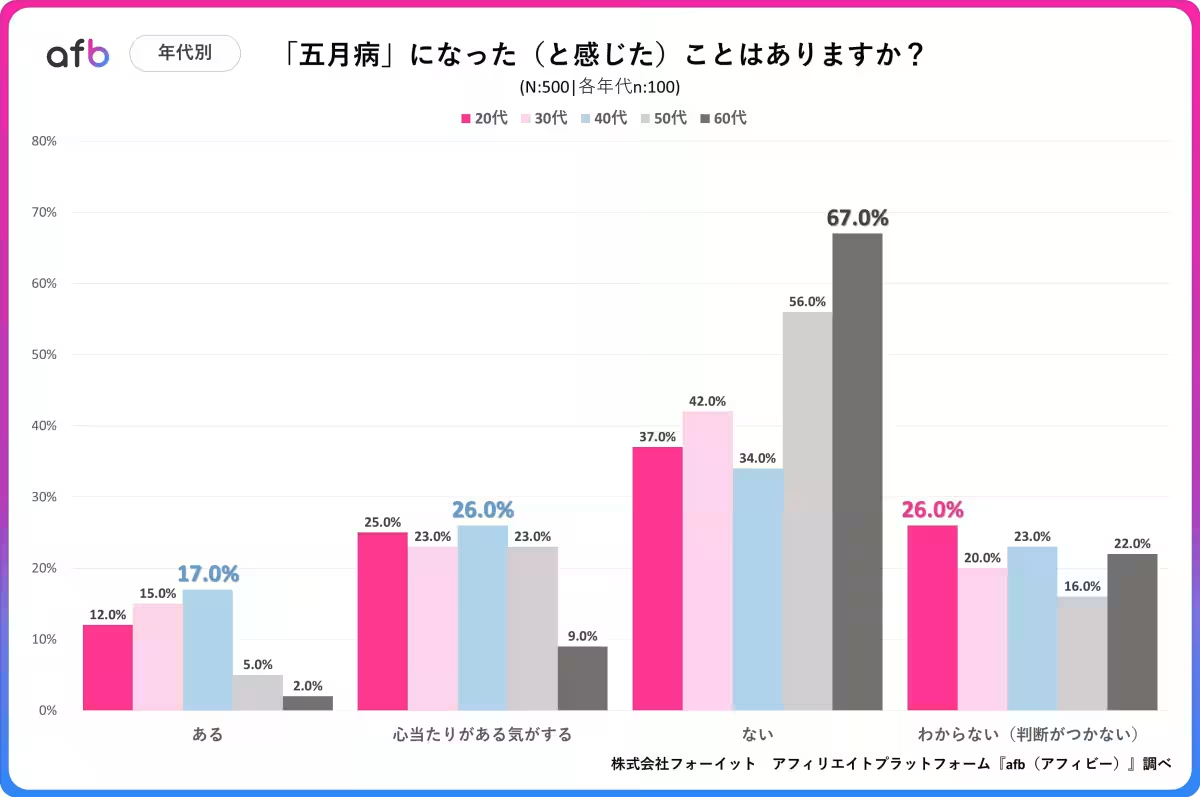
The survey results revealed stark contrasts between age groups. Among those in their 20s to 50s, approximately 30-40% acknowledged experiencing May Syndrome. In contrast, this was markedly lower for respondents in their 60s, with only 2.0% confirming they had experienced the syndrome and just 9.0% suspecting they had. This disparity suggests that younger individuals, often facing changes such as job transitions, promotions, or relocations, may confront higher levels of stress during this period than their older counterparts, who might have retired or settled into a more stable lifestyle.
Additionally, the influence of social media cannot be overlooked. As discussions surrounding May Syndrome proliferate online, younger individuals may be more prone to label their stress as May Syndrome because of increased social awareness.
Occupational Differences
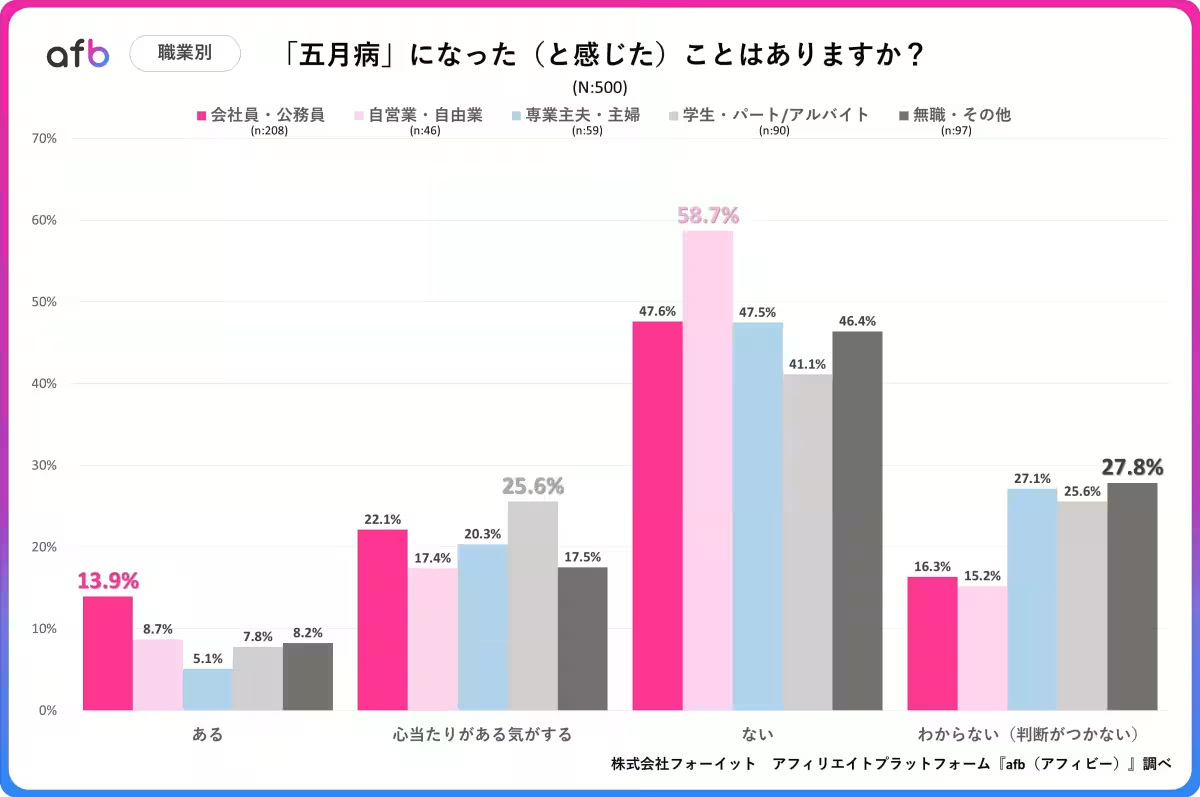
The survey further examined the occupational landscape, revealing a notable contrast in experiences of May Syndrome among different professions. Company employees and civil servants reported higher instances of feeling its effects, likely due to the pressures associated with switching between work and holiday modes. Conversely, freelancers and self-employed individuals reported a lesser impact, with 58.7% asserting they had not experienced May Syndrome. The autonomy of setting their own schedules may provide these individuals with a better work-life balance, reducing the stress associated with sudden transitions.
Addressing May Syndrome
It's particularly important for those embarking on new life chapters to be aware of the subtle accumulation of stress that may lead to May Syndrome. Suggestions for managing feelings of anxiety include regular breaks, physical activity, and mindset shifts to alleviate stress. It’s essential to prioritize mental well-being, particularly during these transitions.
About For-It Inc.
For-It operates the AFB affiliate marketing platform, boasting 12 consecutive years of high satisfaction ratings from partnered businesses. Their commitment to data-driven marketing and the promotion of transparency in online advertising has made them a leader in the field, serving over 1.15 million partners and aggregating an extensive media network.
For additional insights and statistics, visit AFB. Whether a new affiliate partner or an established client, For-It welcomes inquiries and engagement across its platforms.


Topics People & Culture)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.