

Analysis of COVID-19 Infection Rates and Healthcare System in Okayama Prefecture as of April 2025
Overview
As of April 27, 2025, Okayama University has compiled the latest data on COVID-19 infection rates and healthcare availability in Okayama Prefecture. This information, derived from the prefectural government’s data on reported cases and healthcare provisions, aims to keep residents informed about the current situation. Updates are anticipated weekly, adding valuable perspectives from local experts.
The pandemic has seen a levelling off, with the World Health Organization declaring the end of a global health emergency. As daily life gradually returns to normal, it’s crucial to remain vigilant and informed about COVID-19 cases and the healthcare system. This ongoing effort is designed to help everyone maintain appropriate prevention strategies in daily life.
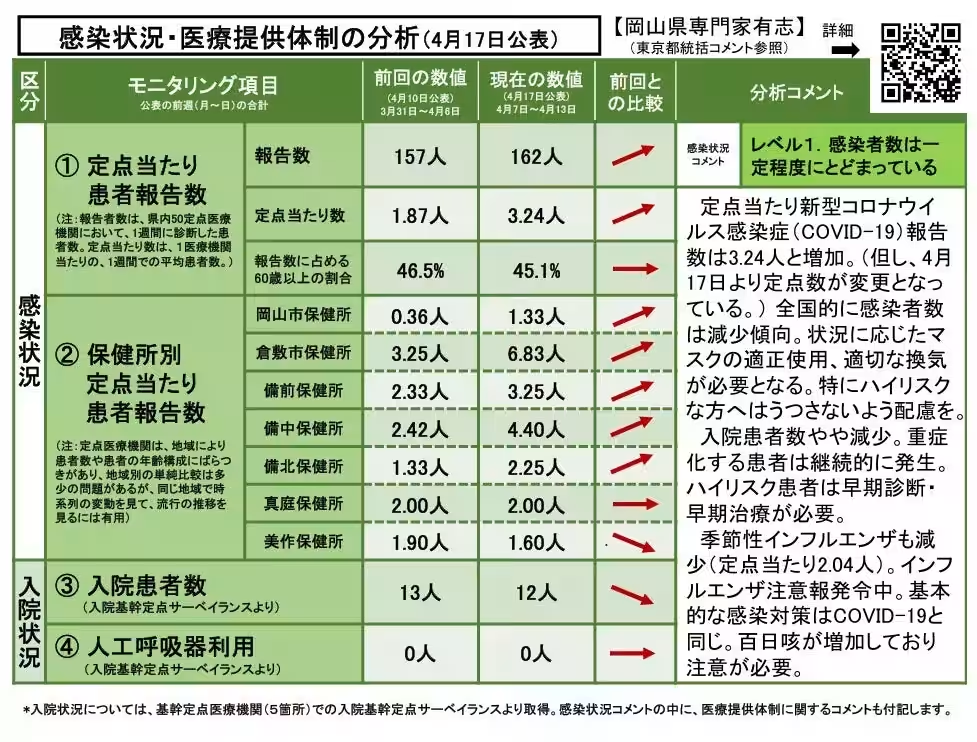
Infection Rates and Healthcare Analysis (As of April 17, 2025)
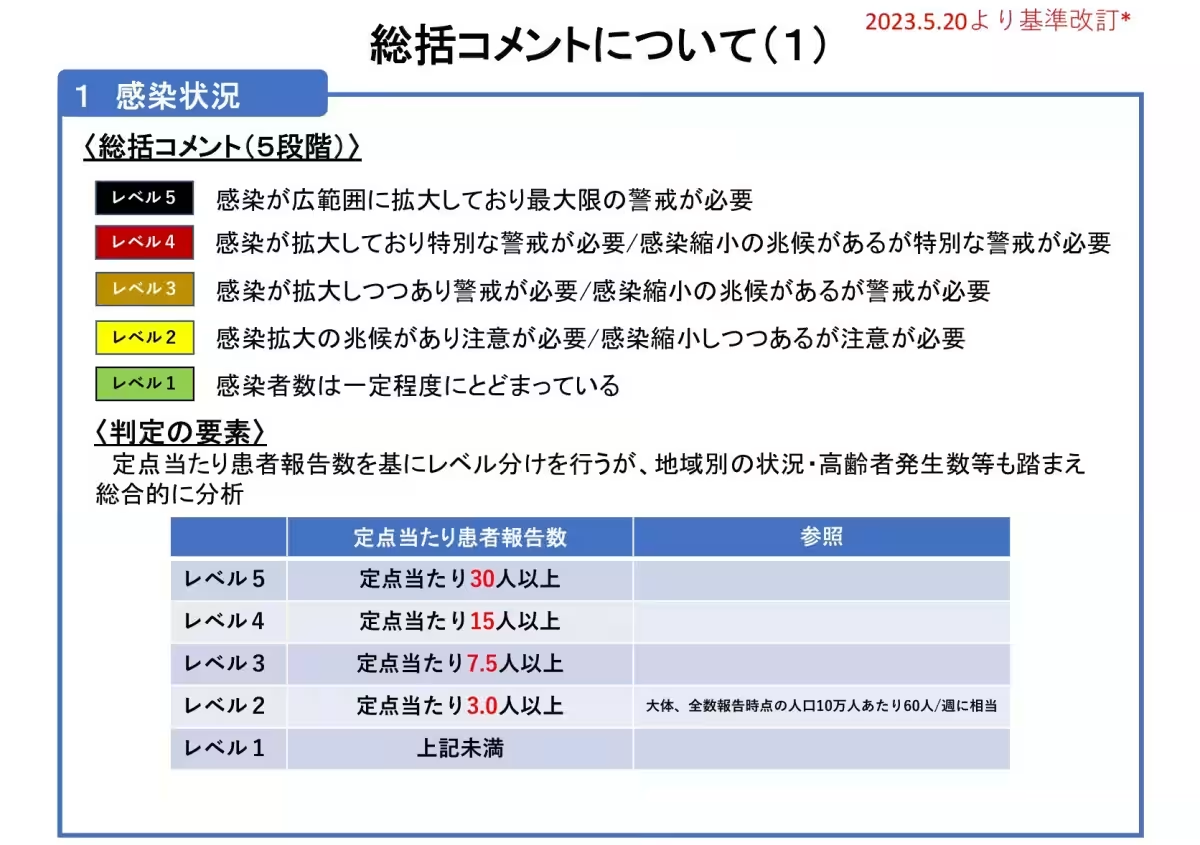
Current Assessment Level: Level 1
Currently, COVID-19 infection rates are stabilizing. As of April 17, there have been an average of 3.24 reported cases per monitoring point, indicating a slight uptick. However, it's important to note that adjustments were made to the number of monitoring points from this date. Overall, a nationwide trend shows a decrease in infection rates, making responsible mask use and adequate ventilation essential, particularly for high-risk individuals.
Here are key facts:
1. Hospitalization Rates: Currently on a decline although severe cases continue to emerge, emphasizing the ongoing need for early diagnosis and prompt treatment, especially among high-risk patients.
2. Seasonal Influenza: This also shows a decrease, currently at 2.04 cases per maintaining area, although a warning is in effect.
3. Whooping Cough: Notably, an increase in whooping cough cases has been recorded, warranting attention and precautions.
Community Contributions by Experts
Local experts contributing to this analysis include researchers and physicians from Okayama University and affiliated hospitals, aiming to disseminate practical information regarding the infections and healthcare response relevant to the community. These insights are a collaboration among experts in epidemiology and infectious diseases to ensure that the public has access to reliable data and guidance.
Future Directions and Ongoing Research
The continuous collection and analysis of COVID-19 related data will be integral for effectively managing this situation. Regular updates not only serve to inform but also assist in formulating public health strategies to tackle potential outbreaks. Residents are encouraged to remain proactive in observing suggested health guidelines to avoid resurgence and to support vulnerable populations.
Additional Resources
For ongoing updates, residents can refer to links provided by Okayama University and local health authorities, which outline vaccination strategies, preventive measures, and community health initiatives.
Furthermore, important collaborations with pharmaceutical and medical device companies to enhance healthcare provisions, research, and development are ongoing, thereby solidifying Okayama's commitment to effectively managing public health concerns.
Continued vigilance and community support will be critical as the landscape of COVID-19 evolves. Stay informed, adopt practices to protect yourself and others, and contribute to the overall health recovery efforts throughout Okayama Prefecture.
In conclusion, our understanding of COVID-19 and its impact on health systems continues to grow. With the cooperation of healthcare professionals, data analysis, and community involvement, we can navigate through these challenges effectively and ensure a brighter, healthier future for all.









Topics Health)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.