

Exploring the Costs and Motivations Behind Medical Weight Loss: Survey Insights
Exploring the Costs and Motivations Behind Medical Weight Loss
In a recent survey conducted by Grownavi, the landscape of medical weight loss procedures and their associated costs has been unveiled. The research encompassed a sample of 1,101 individuals who have undertaken dieting programs, highlighting key motivations, challenges, and experiences common among those embarking on weight loss journeys.
Key Findings from the Dieting Survey
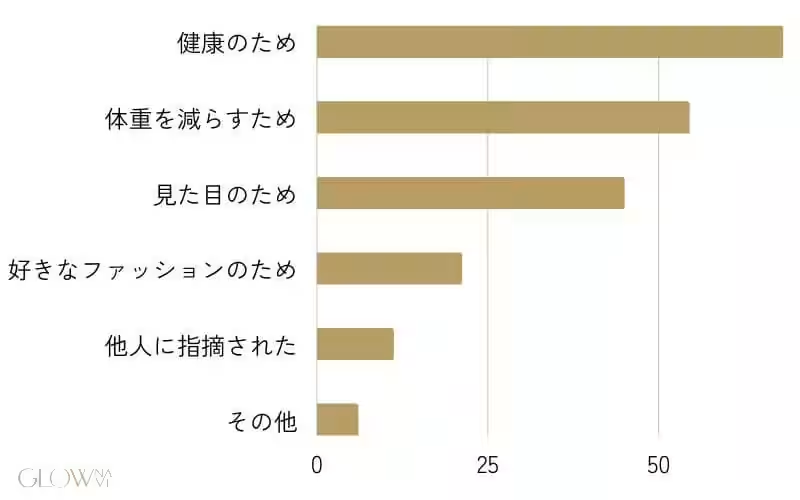
The most common motivation for initiating a weight loss journey was found to be health, with 68.2% of participants citing it as their primary reason. Following health, 54.5% aimed to reduce their weight, while 45.0% wanted to improve their appearance. Additional factors included fashion preferences and external influences from friends or family.
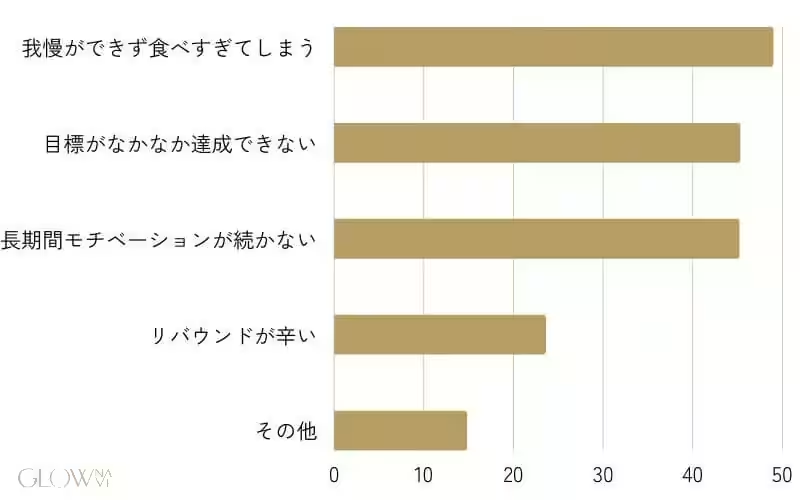
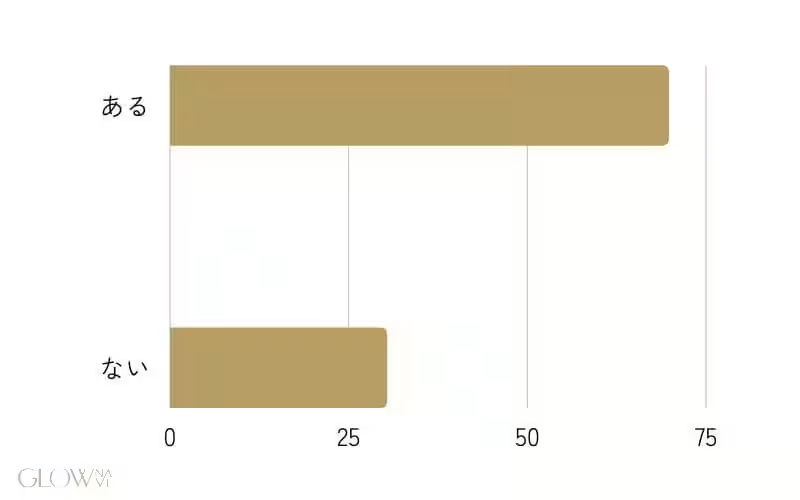
However, the journey to weight loss isn't without its hurdles. The survey indicated that 49.0% of respondents struggled with overeating and maintaining discipline during their dieting efforts. Furthermore, 69.7% admitted to experiencing weight regain, showcasing a common obstacle among dieters.
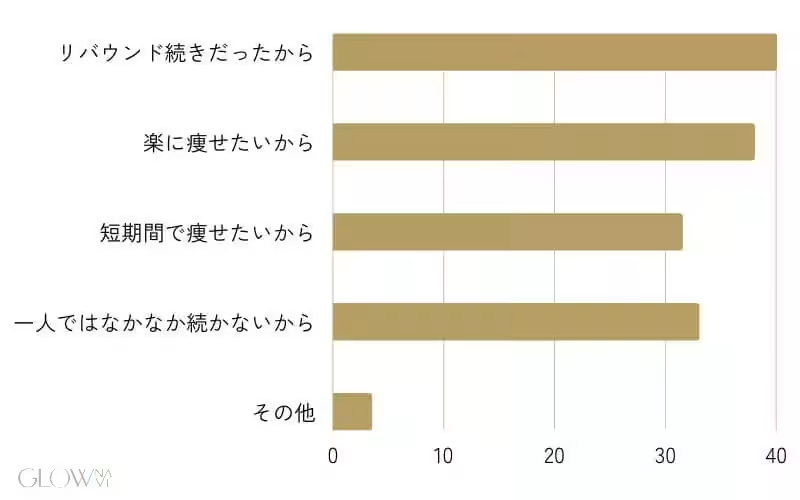
This cycle of trying to lose weight and then regaining it led many to consider medical weight loss options as a solution. Most notably, 40.0% of participants commenced medical weight loss procedures due to recurring rebound weight gain, while 38.0% sought an easier and more effective way to lose weight.
Insights from the Medical Weight Loss Survey
Focusing specifically on medical weight loss, a smaller cohort of 200 respondents shared their experiences. The survey participants disclosed their procedures and any financial concerns associated with their choices.
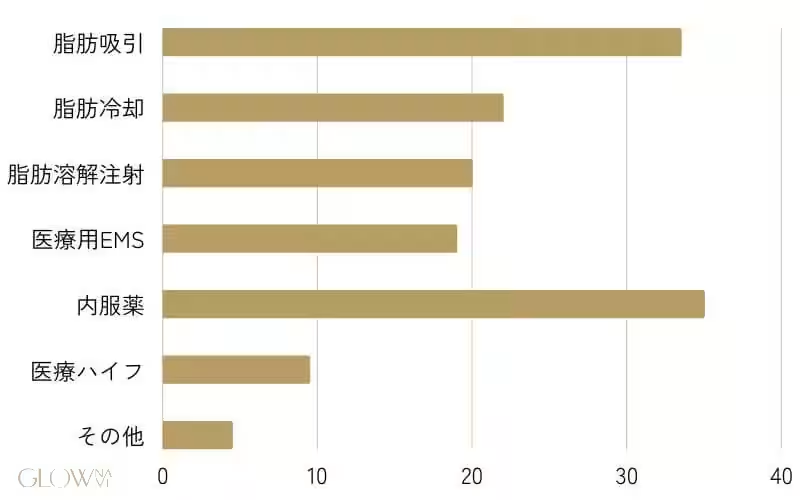
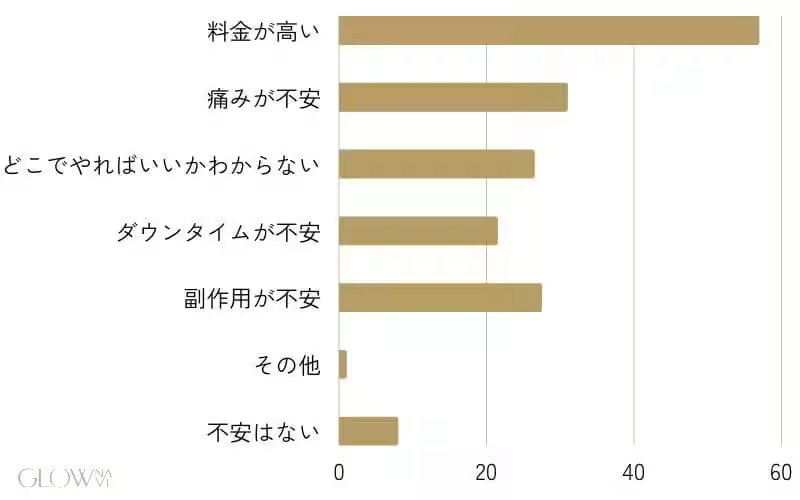
Procedures like liposuction and medication were common, with 33.5% opting for liposuction and 35.0% selecting medication to aid their weight loss journey. Notably, more than half (57.0%) indicated that high costs were a significant source of anxiety when considering these procedures. This apprehension reflects a broader concern regarding accessibility and affordability in medical weight loss options.
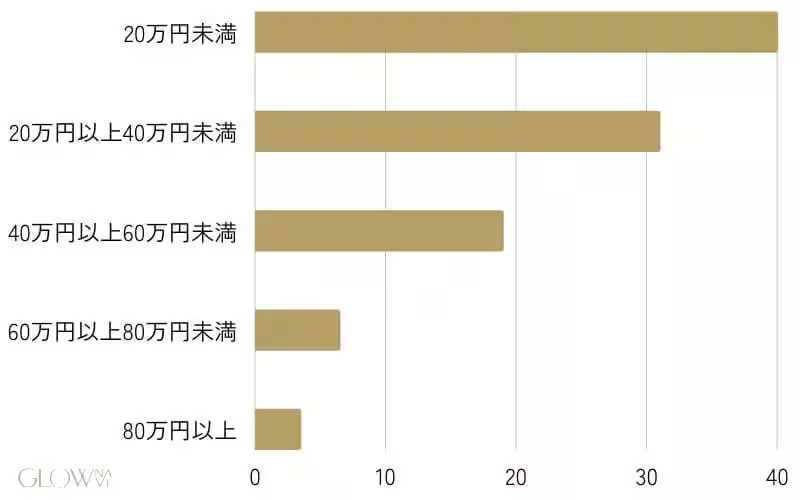
A substantial 40% reported that their total expenditure on medical weight loss was under ¥200,000, while 31% spent between ¥200,000 and ¥400,000. These results suggest a wide variance in personal budgets allocated for weight loss, indicating potential barriers for those with tighter financial constraints.
Conclusion
The insights from these surveys highlight significant trends and challenges within the realms of dieting and medical weight loss. The prevalence of rebound weight gain, financial concerns, and the quest for effective solutions paint a complex picture of the modern weight loss saga. As more individuals turn to medical interventions for assistance, understanding these motivations and experiences becomes essential in creating supportive structures and solutions tailored to their needs.
Organizations such as Grownavi play a pivotal role in providing transparent information, helping individuals navigate their options carefully and make informed choices regarding their weight loss journeys.
As we move forward, it’s crucial that the conversation surrounding medical weight loss evolves to emphasize not only the effectiveness of various procedures but also the importance of financial considerations, emotional factors, and support systems to sustain long-term results.
Topics Health)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.