
Research Shows Variations in Gum Bleeding Among Diabetics Related to Blood Indicators
Variations in Gum Bleeding Among Diabetics
Recent research by the Sunstar Group reveals significant differences in gum bleeding reactions based on the health status of individuals with Type 2 Diabetes. Although plaque control remains essential for preventing gum bleeding, the study indicates a concerning trend: those with higher HbA1c and hs-CRP levels exhibit increased gum bleeding rates, despite similar levels of plaque control as individuals with lower readings of these blood indicators.
The analysis, which reviewed the dental records of patients at the Sunstar Foundation affiliated Senri Dental Clinic, highlights the importance of tailored oral hygiene practices to mitigate these risks effectively. The findings are especially pertinent given the recent addition of the "High-risk Patient Addition" in the 2024 medical fee revision for periodontal disease management among diabetics.
Study Insights
The correlation between blood indicators and oral hygiene habits underscores the need for enhanced patient education and specific oral health guidance. The study also confirmed that frequency in oral hygiene practices such as inter-dental cleaning and mouth rinsing closely relates to effective plaque control.
As part of the ongoing research and to address these findings progressively, the Senri Dental Clinic has begun integrating blood indicator evaluations into the management plans for diabetic periodontal patients. This initiative aims to provide personalized guidance on plaque control, aligning treatment strategies with patients’ specific health profiles.
Research Context
The basis of this study stems from the established link between diabetes and periodontal disease. The Japanese Diabetes Society’s "Diabetes Care Guidelines 2024" recommends periodontal treatment among Type 2 diabetics as a means of improving blood sugar control.
Despite recognition of the correlation, previous research largely concentrated on initial treatment stages of periodontal disease, leaving a gap in understanding how to manage patients during the stable and maintenance phases effectively. The collaborative research led by the Sunstar Foundation therefore aimed to clarify the relationships between blood indicators and patients' oral health outcomes during their ongoing care.
Methodology
This observational study utilized existing data from patients visiting the Senri Dental Clinic between September 2021 and January 2024 for stable periodontal disease treatment or maintenance and who reported having Type 2 Diabetes. The analysis investigated various factors, including demographic variables (age, sex, BMI), blood indicators (HbA1c, hs-CRP), and oral health metrics (plaque amount, gum bleeding rates).
Key Findings
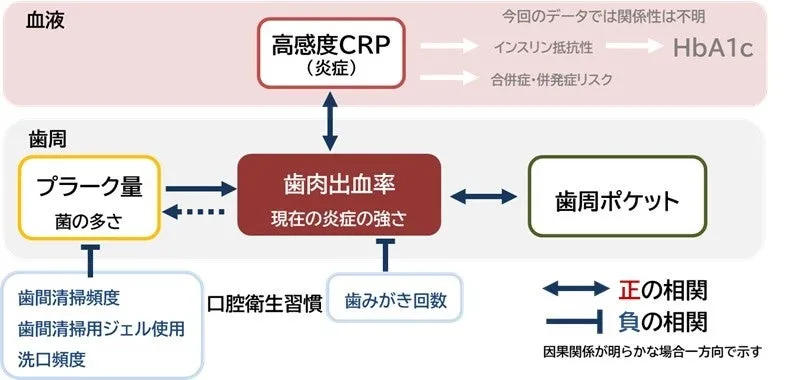
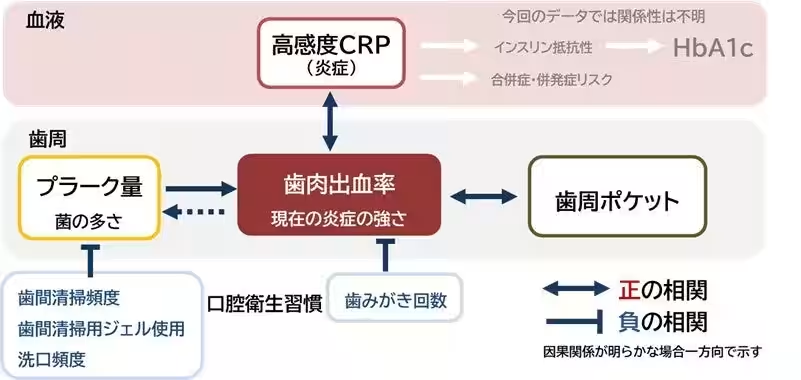
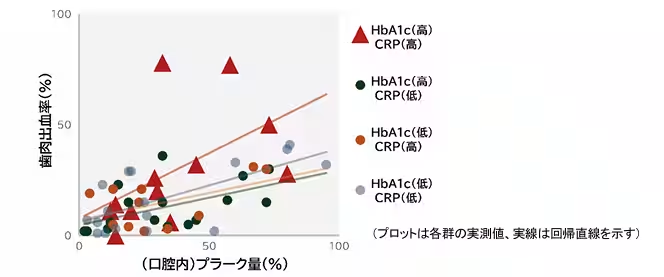
The study observed complex interactions among these indicators. While a direct correlation between HbA1c and gum health wasn't established, clear associations between gum bleeding and hs-CRP levels emerged. The research utilized a generalized linear model to assess these relationships and found that higher blood sugar and systemic inflammation were contributing factors to increased gum bleeding, further reinforcing the importance of effective plaque control.
A breakdown based on various combinations of blood indicators showed all groups demonstrated increased gum bleeding rates with higher plaque amounts. Notably, the group with elevated HbA1c and hs-CRP indicated a pronounced correlation, confirming the impact of combined systemic conditions on local oral health outcomes.
Implementing Practical Changes
As these findings are being disseminated, the Senri Dental Clinic has begun developing protocols for individualized care in managing gum disease among diabetic patients. The focus is on regular assessments of blood indicators to establish appropriate plaque control goals, ensuring an informed and collaborative approach to patient treatment, which encourages active participation in their oral care maintenance.
Dr. Hideki Suzuki, the clinic's director, emphasizes the importance of clear communication and shared objectives in long-term care relationships, outlining that this personalized framework not only fosters accountability among patients but also enhances overall treatment efficacy.
About Sunstar Group
Founded in 1977, the Sunstar Group aims to contribute to the well-being and longevity of individuals through a comprehensive approach to oral care. The organization is committed to harnessing research findings to enhance the health and quality of life of patients, linking oral health management with broader health outcomes.
As campaigns continue through initiatives designed to educate patients on the significance of oral health in overall wellness, the organization remains dedicated to delivering quality information and services that extend health spans in the face of changing demographics and health challenges.



Topics Health)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.