

Okayama University Discovers Key Molecules in iMCD Pathology to Advance Cure Development
Significant Discovery in Idiopathic Multicentric Castleman Disease (iMCD)
A research team from Okayama University has made a momentous breakthrough in understanding Idiopathic Multicentric Castleman Disease (iMCD), particularly the IPL subtype prevalent among Japanese patients. iMCD is a complex and rare disorder characterized by symptoms like lymph node swelling, fever, anemia, and fatigue. The research was published in the prestigious journal 'Haematologica' on September 11, 2025.
Understanding iMCD-IPL and its Challenges
Among the various forms of iMCD, the iMCD-IPL subtype is noted for its significant proliferation of IL-6, a molecule known to cause inflammation. While treatments like IL-6 inhibitors have shown efficacy in reducing symptoms, they merely serve as palliative measures rather than curative solutions. The absence of a complete cure necessitates lifelong treatment for patients, which poses a significant challenge.
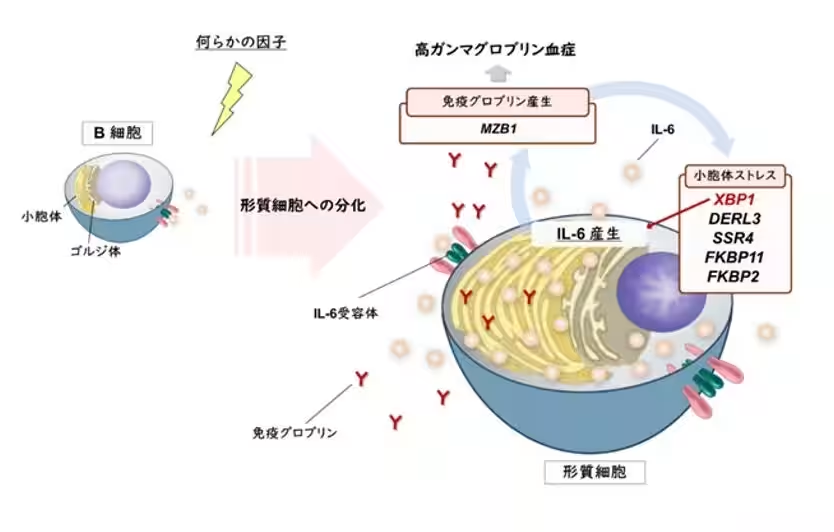
Dr. Asami Nishikori, an assistant professor at Okayama University's School of Health Sciences, together with her research colleagues, conducted genetic and protein expression analyses on patients with iMCD. They discovered that the origin of IL-6 production varies depending on the disease subtype. Specifically, they identified that certain genes are overactive in iMCD-IPL, leading to excessive IL-6 production.
Implications of the Research
This groundbreaking finding sheds light on the underlying mechanisms of iMCD and has the potential to pave the way for developing a definitive treatment. The team is optimistic that this research will not only enhance the understanding of the disease’s pathology but also catalyze the pursuit of a complete cure in the future.
“We are eager to deepen the understanding of this still largely enigmatic disease,” said Dr. Nishikori. “Through our findings, we hope to contribute to the development of a cure that will ultimately benefit those suffering from iMCD.”
Future Directions
The research was supported by significant funding sources, including the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science and the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. The team plans to continue their investigations into the genetic factors leading to iMCD, aiming to leverage this knowledge towards patient care.
With the increasing complexity and diversity of diseases like iMCD, ground-breaking research is essential. The implications of the findings at Okayama University represent an important stride in the journey toward understanding and curing a condition that has thus far eluded comprehensive treatment options.
For more detailed insights into the study, you can access the full research paper here.
This discovery represents a vital step not just for Okayama University, but also for the global medical community as we strive to transform the landscape of treatment for rare diseases like iMCD.







Topics Health)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.