

Obayashi and Aisin Begin Practical Testing of Perovskite Solar Cells
Obayashi and Aisin's Innovative Solar Power Initiative
In a significant step towards sustainable energy solutions, Obayashi Corporation, headquartered in Minato-ku, Tokyo, and Aisin Corporation, located in Kariya, Aichi Prefecture, have launched a joint project focused on the practical implementation of perovskite solar cells at the Obayashi Technical Research Institute in Kiyose, Tokyo. This project marks a crucial milestone in the advancement of renewable energy technology in Japan, where the focus on achieving carbon neutrality by 2050 is intensifying.
Background of the Experiment
The pressing need for expanding renewable energy sources is paramount, especially with solar power expected to become a key provider of electricity. In Japan, conventional silicon solar cells have been the primary technology; however, the challenges associated with securing installation space and achieving high efficiency make it necessary to explore alternatives. The emergence of perovskite solar cells, featured for their lightweight, flexible, and compact nature, offers a promising solution to these challenges.
Perovskite solar cells utilize iodine as a primary material, which can be sourced locally in Japan, thereby reducing reliance on imported materials. The production process is simpler compared to traditional solar cells and offers the potential for cost-effective mass manufacturing. However, while perovskite solar cells hold considerable promise, they do face obstacles, including issues related to efficiency and durability when benchmarked against silicon solar cells.
Aisin has been actively involved in researching organic solar cells for over two decades, leveraging this expertise to develop high-efficiency perovskite solar cells. Their unique design incorporates thin glass to enhance durability, maintaining the focus on maximizing energy production.
Details of the Experiment
1. Development of an Easily Replaceable Fastener System
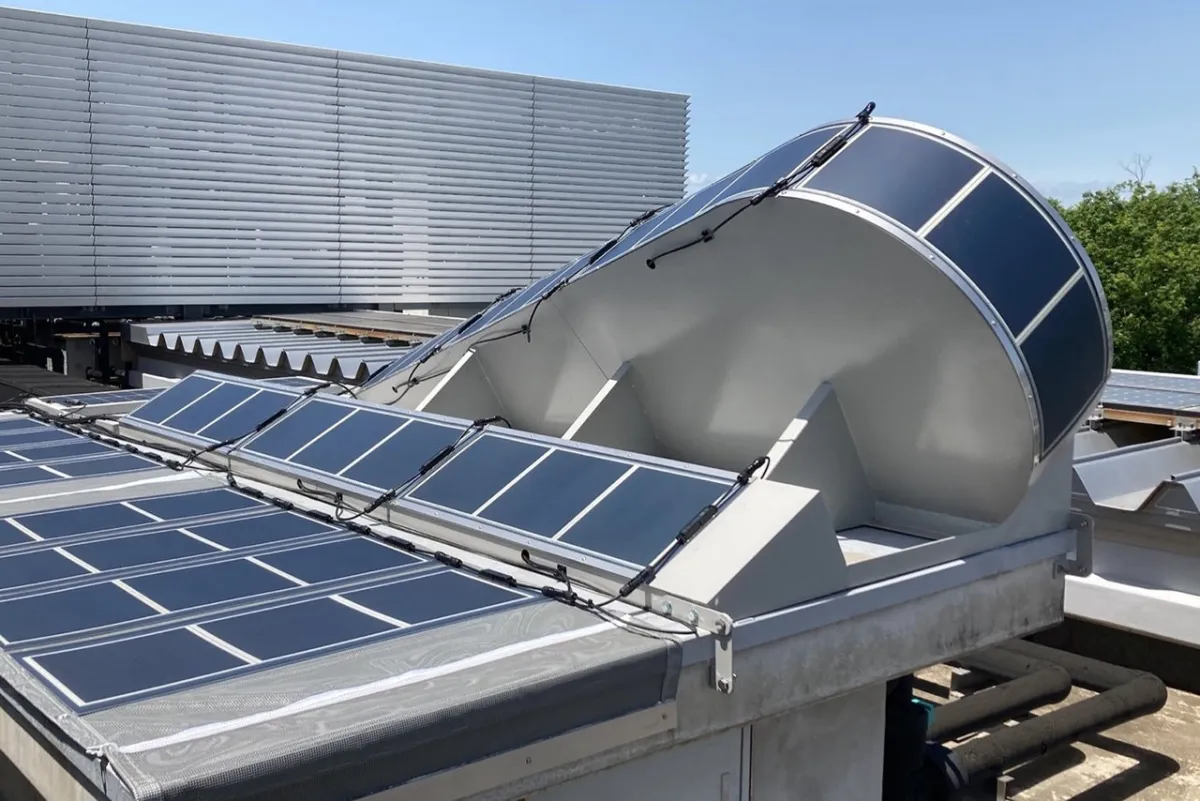
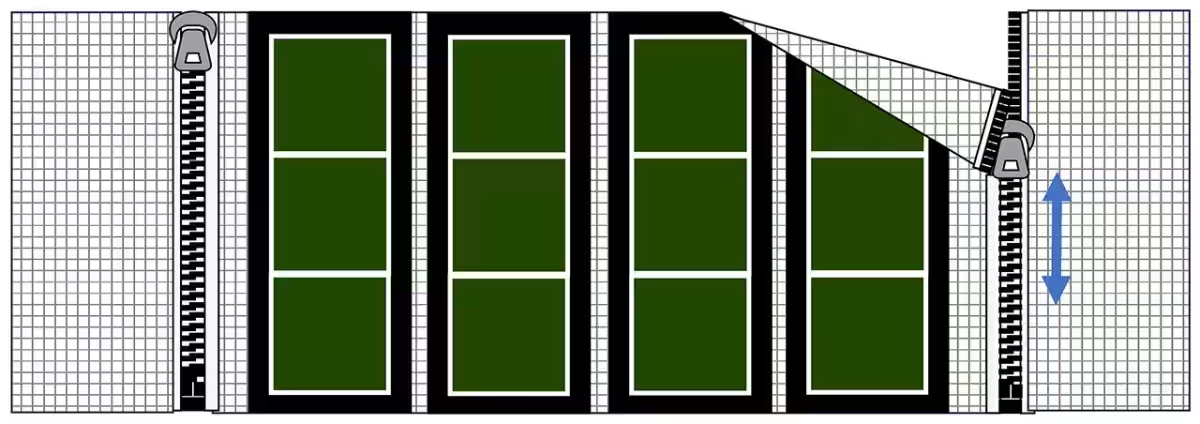
An essential aspect of integrating perovskite solar cells into existing buildings is the ability to easily swap out the batteries, even when the building is in use. The experimental approach includes the creation of a fastener-based removal system, which was successfully installed on the roof of the Obayashi Technical Research Institute.
This system employs a sheet with integrated perovskite solar cells that are attached to a mesh sheet secured at specific intervals by fasteners. This breathable mesh material, coupled with high-weather resistance fasteners, enables extensive areas to be linked conveniently while allowing individual segments to be replaced as needed. The superior maintainability of this installation method presents a significant advancement for long-term solar energy solutions.
2. Optimizing Annual Energy Production
The orientation and angle of installation greatly influence the energy output of solar panels. In Japan, the optimal setup is typically a 30-degree angle facing south; however, this requires a wide, unobstructed area, which is often limited in urban environments. To tackle this, the lightweight and flexible design of perovskite solar cells can be adapted to maximize energy production in confined spaces.
By simulating various configurations, the team at Obayashi developed a method that allows for the installation of more solar cells, increasing the total energy yield per area by over 20%, despite a slight drop in individual cell efficiency. Future evaluations will include comparative assessments of energy output and aging for perovskite cells.
3. Path Forward
The insights gained from this practical testing will fuel the rapid advancement of perovskite solar cell technology. This collaboration between Obayashi and Aisin aims to facilitate the integration of these cells into a variety of structures, including commercial buildings, factories, and infrastructure, thereby contributing to Japan's renewable energy initiatives and the overarching goal of achieving carbon neutrality.
This experiment not only signifies a leap in solar technology but also paves the way for a greener, more sustainable future in Japan.
Note: Perovskite solar cells are a leading-edge technology utilizing a unique crystal structure, while Aisin's research efforts are backed by significant funding from Japan's New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO).



Topics Environment)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.