
Deel Unveils Global Survey on AI's Impact on Work and Hiring Practices
Deel's Global Survey on AI and Employment
Deel, the comprehensive HR and payroll platform headquartered in California, recently conducted a groundbreaking survey titled "AI at Work: The Role of AI in the Global Workforce" in collaboration with IDC. This survey spans 22 global markets and focuses on how AI adoption is fundamentally transforming job roles and talent development approaches in organizations around the world.
Key Findings of the Survey
Recruitment Impact
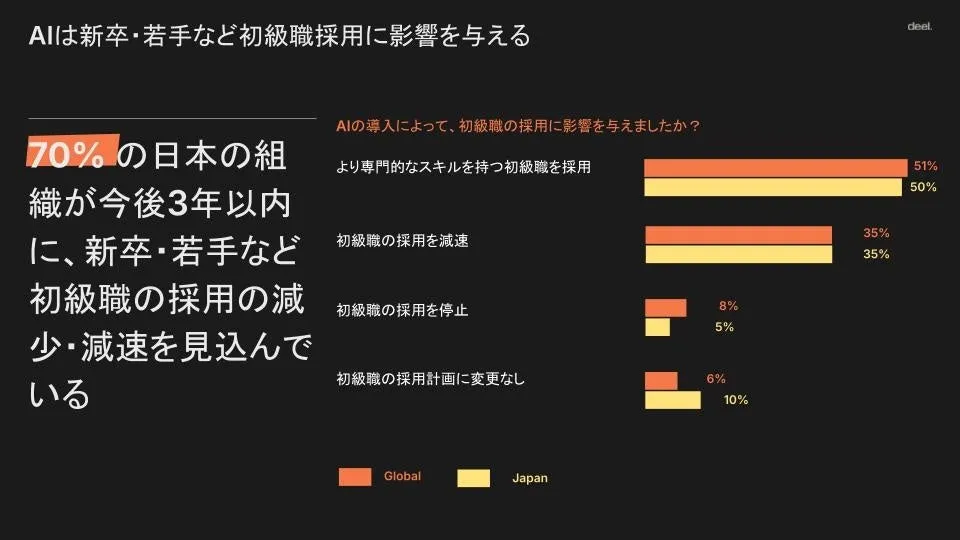
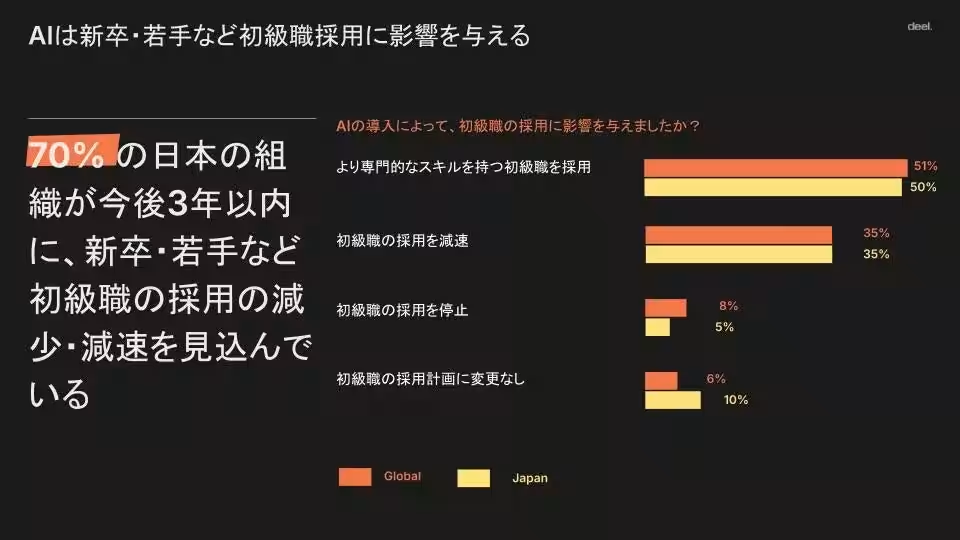
One of the most striking findings from the survey reveals that 70% of Japanese companies expect to slow down new graduate hiring within the next three years, exceeding the global average. Almost all companies in Japan (99%) have begun implementing AI, with a notable 64% utilizing AI in the recruitment process, significantly higher than the global average of 52%.
Job Transformation
The survey highlights that 48% of organizations in Japan are modifying their employees' work styles, while 24% have restructured roles largely or entirely as a result of AI-driven changes. This indicates a significant shift in how work is approached within organizations.
Challenges in Talent Development
A staggering 73% of Japanese firms express concerns about the difficulties in hiring and developing future leaders, while 72% report a decrease in on-the-job training opportunities. This reflects a pressing need for innovation in leadership training methodologies amidst rapid technological advancements.
Reskilling Initiatives
In Japan, 68% of companies have initiated AI training programs. However, the primary challenge identified for fostering reskilling development is the limited employee engagement, with 53% of respondents citing this as a barrier.
Changing Skill Demands
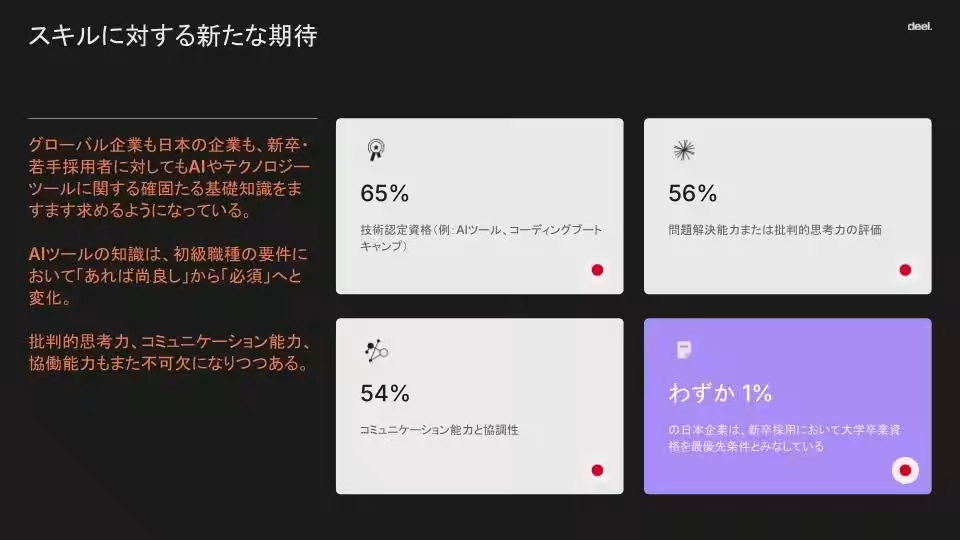
Interestingly, employers are prioritizing technical certifications (65%), problem-solving and critical thinking skills (56%), and communication and collaboration skills (54%) in new hires, while only 1% of firms require a college degree as a mandatory criterion.
Competition for AI Talent
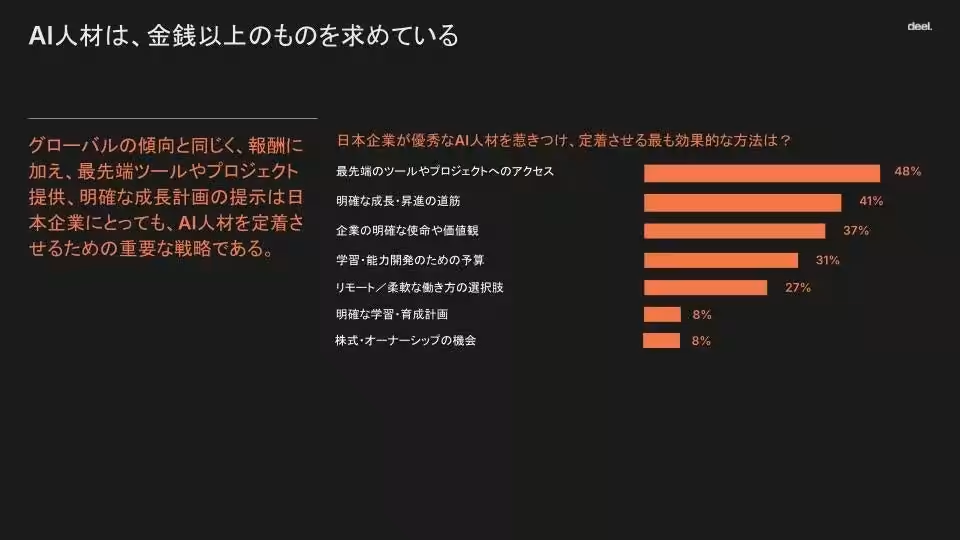
The survey indicates that 44% of Japanese companies are offering salaries that are at least 25% higher than comparable technical roles to attract top AI talent. Additional incentives such as access to cutting-edge tools (48%) and clear career paths (41%) are also being provided to retain talent.
AI Governance
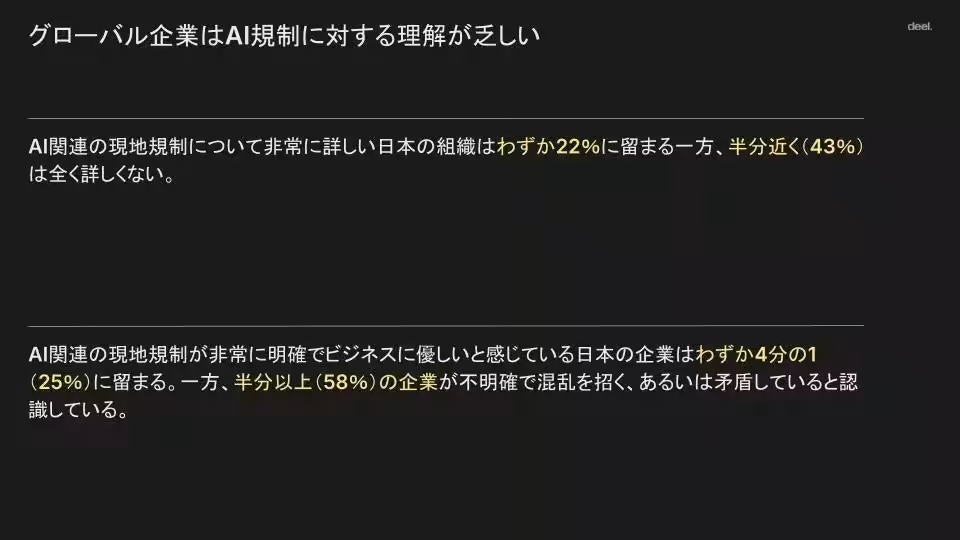
On the governance front, only 21% of Japanese firms feel they are well-informed about local AI regulations. However, 30% have adopted formal policies guiding the use of AI tools by employees, the highest rate compared to other markets.
The Expansion of AI Adoption and Its Impact on Talent Development
Across the surveyed markets, nearly all organizations (99%) have adopted AI, with about 70% moving beyond trial phases into full-scale integration. Notably, 66% of global firms anticipate reducing new graduate hiring over the next three years, with significant impacts seen in sectors such as media (53%), retail (51%), and healthcare (46%). Japan's 70% projecting similar hiring trends indicates a heightened awareness of the challenges posed by AI advancements.
Opportunities Amidst Challenges
While the hiring of new graduates is set to decelerate due to AI's influence, Japanese companies are grappling with substantial challenges in developing talent pipelines for future leaders.
- - Difficulty in Hiring and Developing Future Leaders: 72% of firms express concerns (global average: 71%).
- - Reduced On-the-Job Learning Opportunities for Young Employees: 72% report challenges in this area (global average: 69%).
Leading businesses recognize the need to balance productivity with talent development by redesigning roles, reskilling teams, and fostering a culture of continuous learning.
Business Role Redefinition due to AI
As AI integration deepens, workplace roles are being significantly revamped globally. Survey findings indicate that 91% of global companies have undergone role modifications or eliminations, with over a third (34%) implementing major organizational restructuring to align with AI integration. In Japan, while 48% are changing work styles, only 24% have conducted cross-functional or company-wide reorganizations, which falls short of the global average of 34%.
Global Trends in Job Transformation
Countries with the most eliminations and integrations include New Zealand (53%), Argentina (53%), and the United States (50%), while China reflects a different approach, with only 11% proceeding to eliminate roles, focusing instead on redesign (79%) bolstered by government-led skill development initiatives.
As routine tasks are increasingly automated through AI, human roles are transitioning to strategic decision-making, AI management, and creative problem-solving. The integration of business design with talent development becomes vital for future resilience.
Investment in AI Training: Progress with Challenges
To adapt to AI's influence, approximately 67% of organizations globally are investing in AI-related training and educational programs aimed at upskilling employees. Japan's 68% match underscores the growing acceptance of AI training. However, common operational challenges persist, including limited employee engagement (57%), budget constraints (51%), and a shortage of specialized trainers (45%). Only 3% have established cross-functional teams to oversee AI reskilling initiatives.
A significant number of Japanese firms also report limited engagement (53%) and budget constraints (51%) as primary barriers to effective reskilling efforts. Furthermore, the lack of clear accountability for AI reskilling remains a concern, with a notable 24% not knowing who is responsible for these initiatives.
Shifting Focus from Academic Credentials to Skill-Based Hiring
In the pursuit of new talent, there is a growing global trend towards valuing practical experience and skills over formal academic credentials. Only about 5% of global firms require a degree, with Japan reflecting an even lower figure of 1%. The survey identifies three key skills increasingly sought after in new hires:
- - Technical Certifications and Qualifications relevant to AI tools (66%)
- - Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking Skills (59%)
- - Communication and Collaboration Abilities (51%)
In Japan, companies also favor candidates with technical certifications (65%), problem-solving skills (56%), and strong communication capabilities (54%). The shift underscores a clear movement from academic qualification emphasis to practical skill assessment.
Challenges in Securing AI Talent and Compensation Issues
Despite the momentum for AI adoption, global firms face significant challenges in this area. The survey shows that nearly half (48%) of companies attribute delays in AI integration to legacy systems, with 43% noting a shortage of skilled AI professionals as a major hurdle. To remain competitive, about 50% of employers plan to offer AI specialists salaries higher than equivalent technical roles by 25% to 100%. This trend is particularly pronounced in the Asia Pacific region, with higher premiums noted in countries like South Korea (25%), India (22%), and New Zealand (21%). In Japan, 43% of companies cite securing AI talent as a critical challenge, with only 44% offering 25% or more in salary increases.
As salary considerations evolve, 49% of companies globally highlight access to cutting-edge tools as essential for attracting and retaining AI talent, while 43% prioritize offering clear career paths. Similarly, in Japan, 48% are providing access to advanced tools, and 41% emphasize career advancement clarity, showcasing firms' commitment to cultivating an appealing work environment for skilled professionals.
Delays in AI Governance and Internal Policy Realities
While AI adoption accelerates, the establishment of governance frameworks is lagging worldwide. Only 16% of organizations feel very knowledgeable about their country's AI regulations, with fewer than 24% perceiving these regulations as clear and business-friendly. In Japan, only 22% of firms are familiar with local AI governance, pointing to an ongoing need for improvement. However, Japanese businesses are taking proactive steps in managing AI risk, as about 30% have implemented formal, enforceable policies for guiding employee AI tool usage—the highest rate compared globally.
Concluding Remarks from Industry Leaders
Nick Catino, Global Policy Lead at Deel, noted, “AI is no longer emerging; it is completely embedded in how we work and conduct business. The roles of entry-level jobs are changing, and the skills required of companies are similarly evolving. Both workers and businesses must adapt quickly, as this is no longer a matter of competitiveness but one of survival.”
Similarly, Dr. Chris Marshall from IDC highlighted the unprecedented pace at which AI is reshaping the workforce, stating that successful organizations need to connect automation with human-centered visions, invest in reskilling, redefine opportunities for entry-level positions, and ensure governance evolves alongside innovation.
Ryo Nishihira, Country Manager at Deel Japan, emphasized, “AI is redefining Japan's working styles, recruitment practices, and global competitiveness. Major firms across industries are shifting from traditional academic credential systems to skill-based recruitment and a culture of continuous learning. This transformation accelerates productivity, creativity, and global competitiveness.”
Methodology
The survey was conducted by Deel in collaboration with IDC, engaging a total of 5,500 business leaders from organizations of various sizes and sectors, including banking, education, healthcare, technology, and more, across 22 global markets. The data collection took place in September 2025.
About Deel
Company Name: Deel Inc.
Headquarters: San Francisco, California, USA
CEO: Alex Bouaziz
Website: Deel
Deel is an all-in-one payroll and HR management platform designed for global teams. The platform integrates various HR functions, including HRIS, payroll processing, compliance, benefits management, performance tracking, and IT equipment management, catering to diverse work models across over 150 countries.


Topics Business Technology)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.