

JOLLYGOOD and Juntendo University Launch OSCE VR for Medical Students
OSCE VR: A Revolutionary Training Experience for Medical Students
In a significant collaboration between JOLLYGOOD Inc. and Juntendo University, a state-of-the-art VR tool known as "OSCE VR" is set to enhance the training of medical students preparing for the Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE). This new technology allows students to immerse themselves in realistic clinical scenarios, helping to refine their skills before they step into actual patient care settings.
Understanding OSCE
The OSCE, short for Objective Structured Clinical Examination, is a pivotal assessment in medical education designed to evaluate students' clinical competencies through practical examinations. It plays a crucial role as a final check before aspiring doctors begin their encounters with real patients.
However, many medical students face challenges when preparing for OSCE, often feeling overwhelmed by the exam's demands. They express concerns such as uncertainty regarding where to start and insufficient opportunities to practice the complete workflow of clinical examinations.
Addressing OSCE Preparation Challenges
Prior to participating in a preclinical OSCE, students undergo a form of assessment using simulated patients and medical simulations. These hands-on evaluations focus on the essential techniques of patient interaction and basic physical examination skills. Yet, traditional learning environments primarily rely on role-playing and two-dimensional materials, limiting students' opportunities for realistic, repetitive practice.
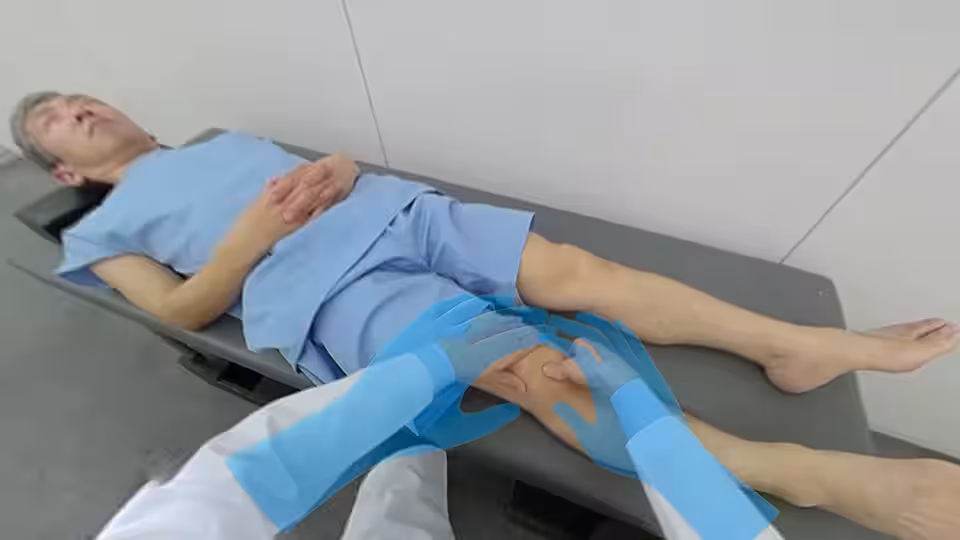
Recognizing these challenges, the OSCE VR was developed with guidance from esteemed faculty at Juntendo University. The immersive VR experience mirrors real-life examination scenarios, enabling students to visualize and engage with the examination process fully. Additionally, the inclusion of hand-tracking technology allows users to see their own hands in the VR space, creating a unique learning experience where students can physically replicate the flow of examinations.
Features of OSCE VR
The OSCE VR platform offers a series of meticulously designed training sessions encompassing critical elements of clinical interactions and physical assessments. The training is organized into three comprehensive stages:
1. Basic Module: Students learn examination protocols through audio-guided instructions.
2. Application Module: Provides an opportunity for students to repeat the basics while simulating an examination from a doctor's perspective.
3. Mock Examination Module: Allows students to practice under exam conditions, maintaining the same pace they would face in real assessments.
Moreover, the hand-tracking capability enhances the sense of immersion, allowing students to interact with the virtual environment more naturally.
Availability and Pricing
The OSCE VR experience will be offered through the VR application "JOLLYGOOD+," set to release on April 3, 2025, as part of its advanced courses aimed at medical students preparing for their examinations. The application is compatible with both Meta Quest and Apple iPads.
Pricing for the OSCE VR experience includes:
- - A monthly subscription of ¥5,500 (tax included)
- - An annual plan priced at ¥66,000 (tax included)
Users can make free membership registrations for trial access to some content and other VR offerings.
Expert Insights on OSCE VR Development
The development of OSCE VR has received mentorship from notable figures at Juntendo University, including Professor Toshio Naito and Associate Professor Hirotaka Mori. Both have emphasized the importance of acquiring basic examination skills before entering clinical practice.
Professor Naito stated, "OSCE training is indispensable for developing the necessary skills for patient interaction and physical exams, as each patient scenario is unique and requires varied approaches. The immersive environment VR creates is optimal for this type of training."
Meanwhile, Associate Professor Mori highlighted the focus on self-paced learning within OSCE VR. He aims to integrate AI technologies in future developments to further enhance the training program, allowing students to engage with virtual patients directly.
Professor Yushi Nishizaki commented on the noteworthy educational value of utilizing digital materials like OSCE VR during a transformative period in medical education, underscoring the necessity for efficient skills training.
Conclusion
JOLLYGOOD is poised to revolutionize medical education through innovative VR solutions, not only in healthcare but also in various sectors facing workforce challenges such as manufacturing, logistics, and retail. Companies interested in collaborating for DX implementation and AI initiatives are encouraged to reach out for partnerships.
For further inquiries, please contact:
- - Tel: 03-4455-2694
- - Email: [email protected]






Topics Health)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.