
Exploring Japan's Average Life Expectancy and Biological Ageing Insights
Understanding Japan's Life Expectancy Statistics and Their Implications
On July 25, 2025, Japan's Ministry of Health revealed the latest figures regarding the average lifespan of its citizens. Although we are living in an era marked by longer life expectancy, the real aspiration for many of us is to age in good health and with vitality. Achieving this goal hinges significantly on daily habits such as nutrition and exercise.
Recent research has begun to investigate the interplay between lifestyle changes and health, especially through the lens of epigenetics—the study of how genes can be controlled by environmental factors rather than solely by inherited genetic code. Epigenetic changes can be influenced positively or negatively by lifestyle choices, meaning habits established early on can have persistent effects that are hard to reverse, especially if unhealthy patterns persist over time.
Imagine epigenetics as a sticky note attached to your genetic material—a note that can indicate when and how genes express themselves. Though these notes can be added or removed depending on our lifestyle choices, the marks left by persistent habits can lead to health complications that are difficult to address. Fortunately, scientific evidence suggests that addressing these influences early on can help restore better health outcomes.
Survey Findings on Regrets Regarding Lifestyle Choices
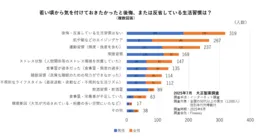
According to a survey conducted in June 2025 by Taisho Pharmaceutical, involving 1,000 participants aged 50 or older, over 30% claimed they do not regret any unhealthy habits from their past. However, the leading areas of regret included:
- - Skincare and Hair Ageing Care (267 respondents)
- - Exercise Frequency and Intensity (237 respondents)
- - Smoking Habits (169 respondents)
- - Ignoring Stress from Relationships (147 respondents)
- - Overeating (135 respondents)
Understanding how lifestyle impacts health can be better elucidated through epigenetics, as it demonstrates a clearer correlation between habits and biological ageing. I had the opportunity to discuss insights from Dr. Sawako Hibino, an expert in age management who serves as a scientific advisor to the EpiClock® Test at Rhelixa, to understand which actions are recommended from an epigenetic standpoint.
The Science of Lifestyle Impacts on Genetics
Recent innovations in technology allow researchers to assess how lifestyle choices affect genes, which is where the EpiClock® Test plays a crucial role. This advanced biological age test can analyze the impact of diet, exercise, sleep, and stress on our genetics. Dr. Hibino emphasized that our DNA is inherently set to promote health, but prolonged poor habits can create significant epigenetic changes that disrupt this functioning. Imagine a faulty switch that governs gene expression—where genes that should be repairing cells or fighting inflammation are silenced, while those promoting inflammation may be turned on excessively.
Research indicates that specific nutrients and lifestyle modifications can effectively “rewrite” these epigenetic influences—what is termed epigenetic reprogramming. As studies continue to explore various nutrients' roles in this context, evidence increasingly supports the idea that a Mediterranean diet, regular aerobic exercise, and high-quality sleep correlate with a younger epigenetic age.
Sustaining Health Through Dietary Choices
Identifying nutrients that correctly regulate genetic functions opens avenues for moderating the speed of ageing through our diets. Fundamental to achieving longevity is a balanced diet. Among the healthiest eating patterns, the Mediterranean diet stands out—it has been vigorously endorsed by researchers as a preventive measure against ageing. This diet mainly consists of seafood, olive oil, nuts, vegetables, fruits, and whole grains while minimizing red meats and processed foods.
Rich in healthy fats, dietary fibers, and diverse polyphenols, the Mediterranean diet is crucial for reducing cellular inflammation and oxidative stress—key contributors to the ageing process. For instance, significant clinical studies conducted in Spain highlight the benefits of frequent seafood consumption and limited red processed meats in lowering cardiovascular disease risks.
Focusing on ingredients like taurine, abundant in seafood, can help stabilize cell osmosis, support the autonomic nervous system, and exhibit strong antioxidant properties. Experiments on middle-aged mice have shown its capability to prevent bone density loss, improve muscle strength and metabolism, and even enhance cognitive function, providing conclusive evidence of its role in extending healthy lifespan.
Moreover, beauty-related compounds like L-cysteine and glutathione bolster the body's antioxidant environment while promoting cellular turnover and detoxification. These nutrients are not only available as supplements but are also naturally found in foods such as liver, broccoli, and avocados.
In addition, olive oil's antioxidant properties stem from its polyphenols and oleic acid, contributing to cellular longevity. Nuts—especially walnuts and almonds—are rich in Vitamin E and magnesium, which are associated with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits. Likewise, vegetables and fruits rich in Vitamin C, carotenoids, and folate contribute to cellular repair and immune strengthening.
Engaging regularly with these dietary choices can construct a solid foundation for maintaining a youthful biological age. Moving forward, there's anticipation for personalized nutrition guidance based on individual epigenetic assessments that could optimize dietary habits for longevity.
Three Lifestyle Habits for Positive Epigenetic Influence
Beyond diet, lifestyle habits are crucial for their epigenetic impacts. It’s posited that certain practices can significantly contribute to managing gene switches beneficially. Here are three essential habits to consider:
1. Regular Exercise: Walking approximately 10,000 steps daily can help mitigate telomere shortening and effectively reduce biological age.
2. Quality Sleep: Maintaining optimal sleeping conditions and a warm bath can favor deeper sleep cycles bolstered by the parasympathetic nervous system.
3. Stress Management: Creating a stress-free environment and intentionally engaging in enjoyable activities can positively affect one's mental health and, in turn, one's epigenetic status.
Conclusion
Genetic factors play a role in longevity, accounting for an estimated 25-30%, while lifestyle factors and environments account for the remaining 70-75%. Thus, addressing lifestyle and dietary choices early stands as a pivotal step toward youthful longevity.
For detailed insights on the EpiClock® Test, visit Rhelixa's website.

Topics Health)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.