

BlueMeme and Kyushu University Unveil Advanced Genome Analysis Technology Using Quantum AI
Pioneering Genome Analysis with Quantum AI
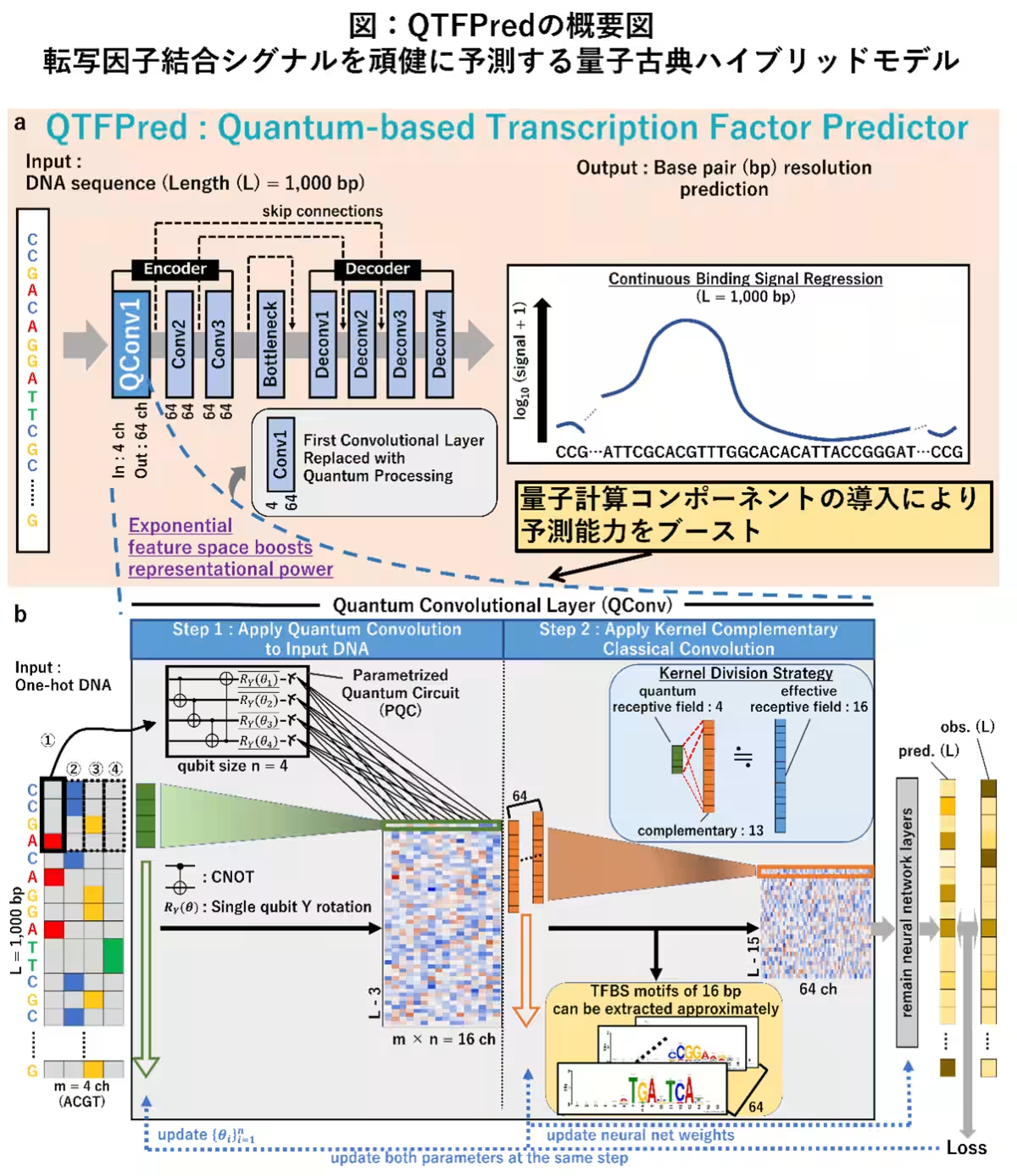
In a remarkable advancement for genomic research, 株式会社BlueMeme has collaborated with Kyushu University to develop QTFPred (Quantum-based Transcription Factor Predictor), a sophisticated technology leveraging quantum AI for genome analysis. This groundbreaking research will be published in the prestigious journal Briefings in Bioinformatics on November 26, 2025.
Background and Objectives
Transcription factors (TFs), essential molecules that regulate gene activity, play pivotal roles in understanding life phenomena, disease research, and drug discovery. However, the challenge arises due to insufficient experimental data on many TFs, making it difficult for conventional AI methods to conduct accurate analyses. This lack of data leads to decreased prediction accuracy, which hinders progress in drug development and personalized medicine.
To address these challenges, the joint research team employed quantum machine learning, a fusion of quantum computing principles and AI, to achieve high-precision gene control predictions even with limited data. By harnessing the characteristics of quantum bits (qubits), such as superposition and entanglement, the researchers captured intricate information structures that traditional AI models could not decipher, achieving unprecedented analysis precision despite data limitations.
Summary of Research Findings
1. Development of a New AI Model: The team designed the unique AI model QTFPred, which integrates quantum computing mechanisms, enabling high-precision prediction of binding patterns even for TFs with limited experimental data.
2. Superiority Over Conventional AI: Tests conducted using publicly available human cell data demonstrated that QTFPred consistently achieved higher predictive accuracy across almost all tasks compared to existing AI models. The model proved capable of delivering stable prediction performance even with minimal training data, showcasing its readiness for real-world applications in research settings.
3. Discovery of Cooperative Binding Patterns: The analyses revealed the mechanisms by which multiple transcription factors cooperatively bind, deepening our understanding of biological phenomena and opening new avenues for drug discovery research.
International Recognition
This innovative achievement has garnered significant attention, having been accepted as a poster presentation at the American Society of Human Genetics (ASHG 2025) conference held in Boston, USA, in October 2025. The journal Briefings in Bioinformatics, considered a leading publication in bioinformatics (Impact Factor: 7.7), further validates the global importance of this research outcome.
Future Directions
Both BlueMeme and Kyushu University are committed to advancing research and development in the following areas:
- - Expanding Application Areas: Including chromatin analyses (ATAC-seq) and disease-related genomic regions.
- - Validation Using Quantum Computers: Aiming for future large-scale analyses.
- - Integration into Drug Discovery and Personalized Medicine: Exploring applications for predicting disease risks and identifying target molecules.
BlueMeme aspires to continue fostering innovation in life sciences and medical fields through the societal implementation of cutting-edge technologies, including quantum AI.
Comments from Key Researchers
Professor Masaru Nagasaki from Kyushu University commented, "Accurately predicting where transcription factors bind to DNA is crucial for understanding gene functions and disease mechanisms. However, obtaining sufficient experimental data for these factors, particularly in tissue-specific cells, has been challenging. Our research showcased a new approach that leverages quantum computing characteristics to overcome this obstacle. Although quantum machine learning is still in its developmental stages, we believe this represents a significant step toward practical applications."
Taichi Matsubara, a researcher at BlueMeme, added, "Quantum computing enables processing more information simultaneously than traditional technologies through the principle of superposition. We successfully demonstrated the utility of our quantum-integrated model, QTFPred, in practical genomic data analysis. While currently implementing GPU simulations, the future availability of actual quantum computers will allow us to analyze more extensive and complex biological systems. We are poised to accelerate research toward the societal implementation of quantum AI, focusing on drug discovery and personalized medicine applications."
Publication Information
- - Journal: Briefings in Bioinformatics (Oxford University Press)
- - Paper Title: QTFPred: Robust High-Performance Quantum Machine Learning Modeling that Predicts Main and Cooperative TF Bindings with Base Resolution
- - Publication Date: November 26, 2025
- - Lead Author: Taichi Matsubara
- - Corresponding Author: Masaru Nagasaki
- - Co-authors: Sōsuke Machida (BlueMeme), Makoto Matsuoka (BlueMeme), among others
- - DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbaf604
About BlueMeme
Founded in 2012, BlueMeme has been at the forefront of introducing the low-code development platform, OutSystems, in Japan. By October 2025, the company has successfully implemented low-code products in over 180 companies, delivering more than 5,000 services utilizing low-code methods, and training over 6,200 OutSystems developers. Recognized as Asia's first premier partner of OutSystems, BlueMeme employs its unique development framework, AGILE-DX, to facilitate effective agile and low-code operations, striving to enhance the international competitiveness of Japanese businesses through disruptive transformation driven by next-generation information system development.

Topics Health)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.