

Current Insights on COVID-19 Infection and Healthcare in Okayama University and Its Community
Overview of COVID-19 Situation in Okayama
As of April 24, 2025, Okayama University has compiled relevant data regarding the COVID-19 infection rates and healthcare provisions available in Okayama Prefecture. This analysis is being enriched with commentary from specialists within the community, with the goal of offering a clearer understanding of the current health landscape. It is important to provide regular updates on this matter, and a weekly review is planned for ongoing monitoring.
The presented data summarizes patient report counts and healthcare capacity as made available publicly on the Okayama Prefectural website. Additionally, it draws insights from a comprehensive review of the monitoring items by the Tokyo metropolitan government. Due to the ease of restrictions announced by the WHO regarding the pandemic, Japan is seeing a gradual return to normal life. However, it remains critical for the community to understand the existing infection status and healthcare infrastructure to bolster preventative measures in everyday life.
Infection Status as of April 24, 2025
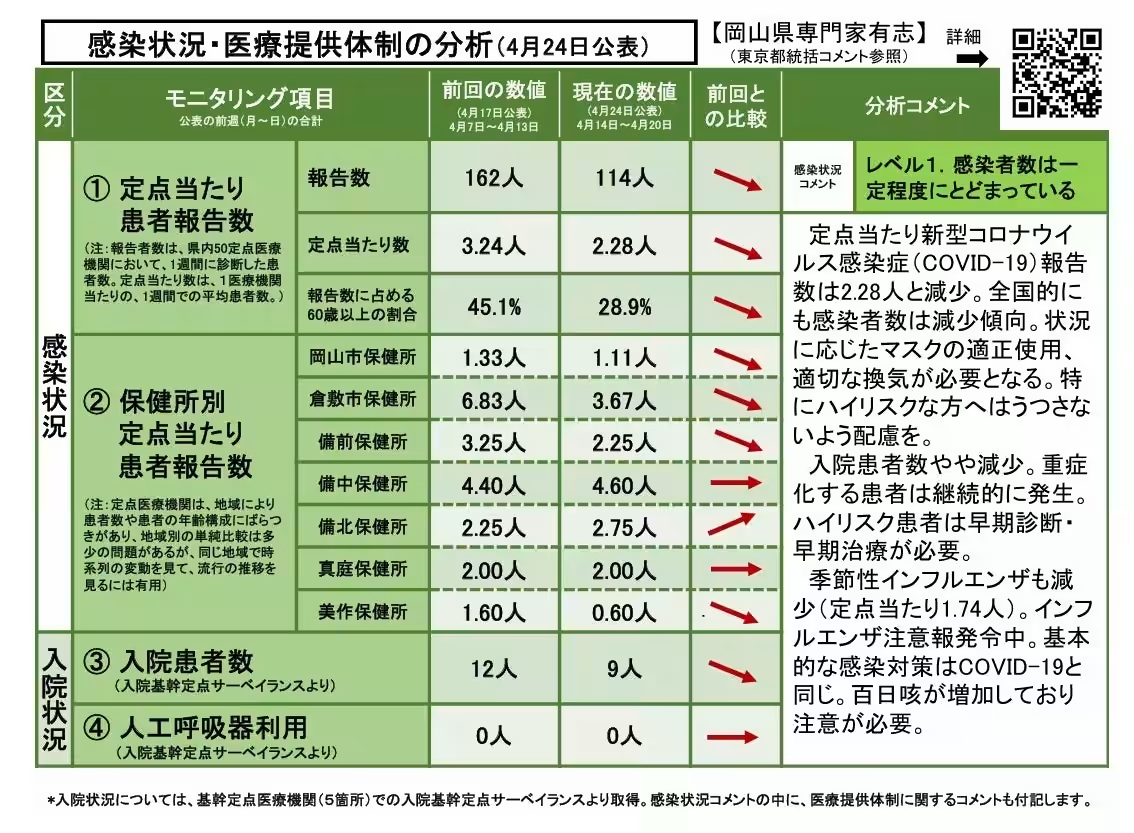
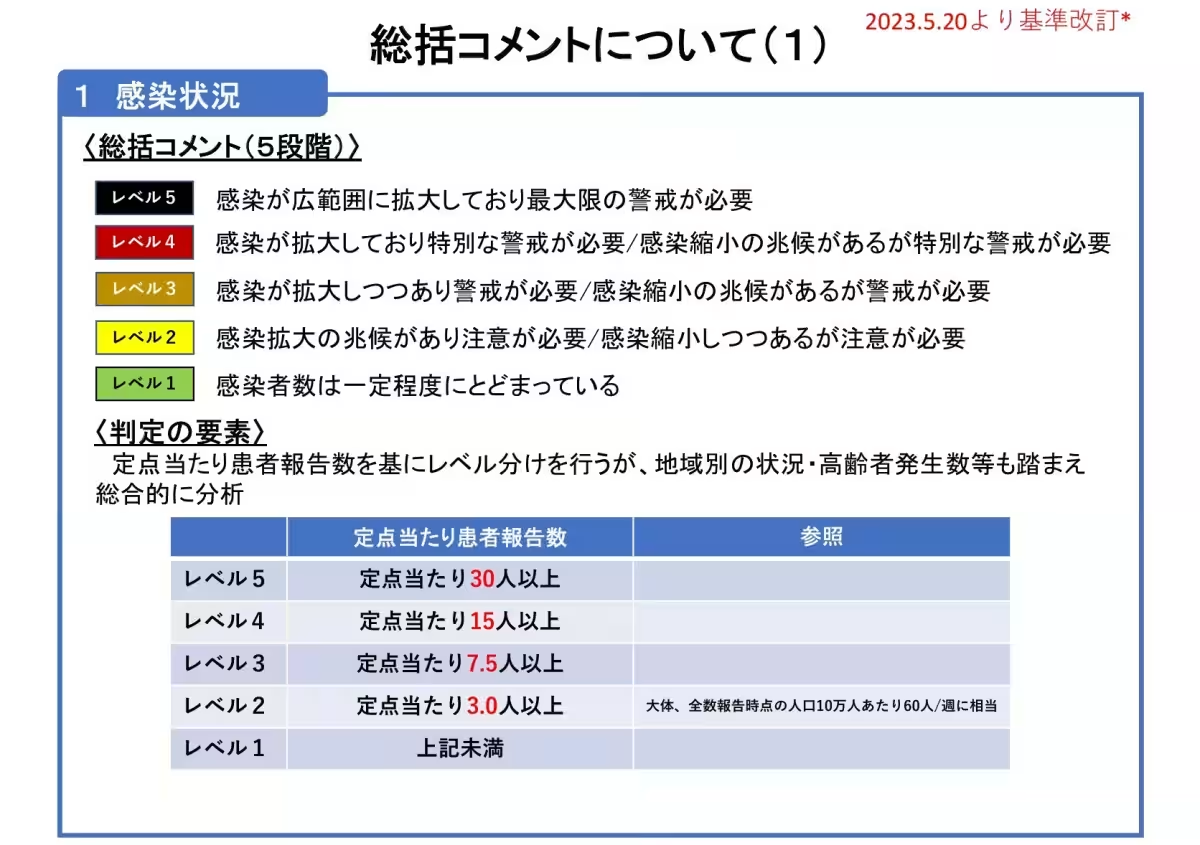
Currently, the infection level in Okayama Prefecture is rated at Level 1, indicating that the number of COVID-19 cases is being maintained at a stable rate. Reports indicate a reduction in cases, with a recorded rate of 2.28 individuals diagnosed per designated observation point. This trend reflects a national decline in infections as well.
It is essential for individuals to continue using face masks appropriately and ensuring proper ventilation, especially considering the ongoing concern for high-risk groups.
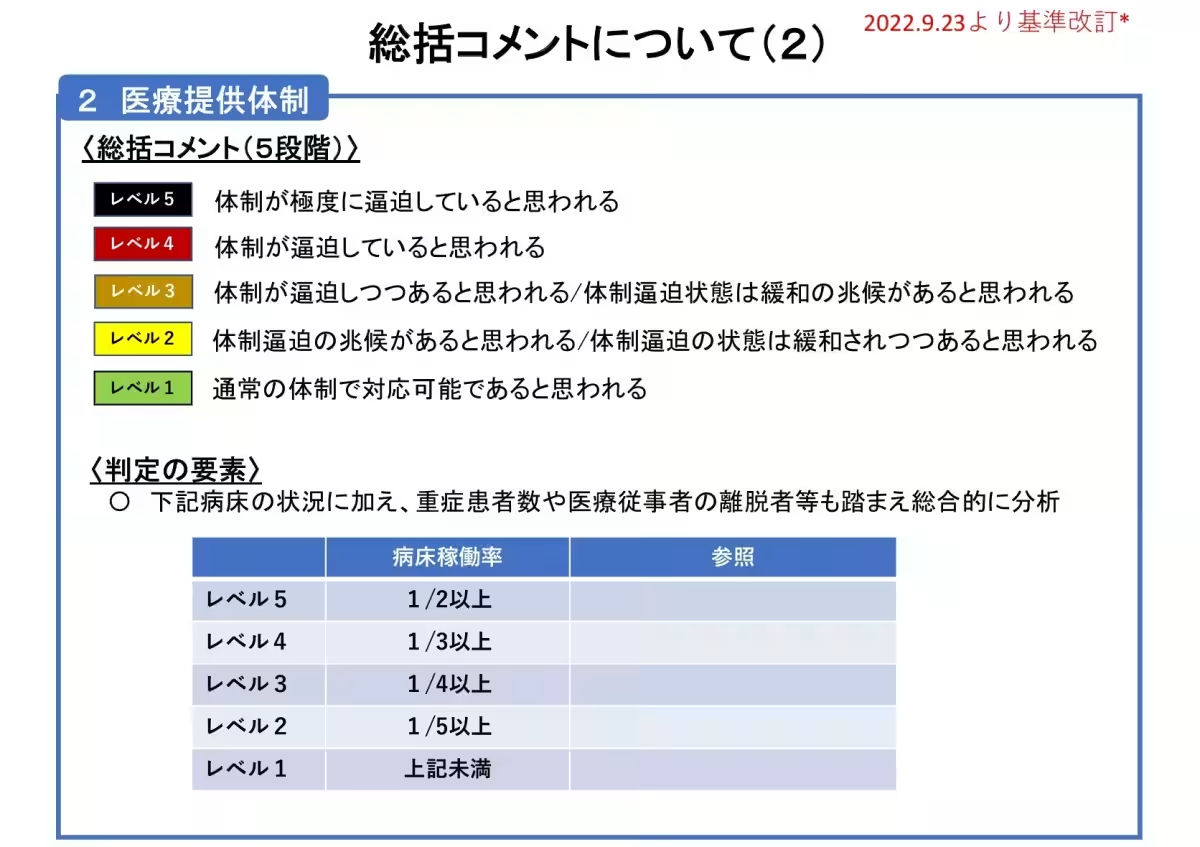
Hospitalization and Treatment Resources
While there has been a slight drop in the number of hospitalized patients, cases of severe illness continue to emerge. This highlights the need for early diagnosis and prompt treatment, especially for high-risk individuals. Furthermore, seasonal influenza cases are also on the decline, currently at an observation rate of 1.74 cases per point. Despite this, an influenza warning is still in effect, necessitating identical precautions as applied to COVID-19. Another area of growing concern is the reported increase in whooping cough cases, indicating a need for continued vigilance.
This data comes from a collection of observed reports curated by a group of experts, including notable contributions from professionals at Okayama University. Some key figures contributing to this analysis include Takashi Yorito from the Department of Epidemiology and Hygiene, Eitai Hagiya from Okayama University Hospital, and Koji Fujita from Tsuyama Central Hospital, among others. Their collaborative effort aims to highlight and address not only the current infection trajectory but also the necessary healthcare strategies in combating the spread of COVID-19 and associated illnesses.
In summary, the data cultivated from Okayama University's analysis serves a dual purpose: it acts as a valuable resource for understanding ongoing COVID-19 trends and urges the community toward effective infection-prevention measures. The public is encouraged to follow these insights closely and utilize them to bolster personal safety practices. Continued information dissemination will remain a priority, reflecting the evolving nature of the pandemic and its repercussions.
For more detailed insights, the community can refer to additional resource links provided by Okayama University and local health authorities. This commitment not only fosters transparency regarding public health data but reinforces community cohesion in facing ongoing health challenges together.








Topics Health)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.