
Innovative 4D-Printed Vascular Stent Expands Automatically at Body Temperature
Introduction
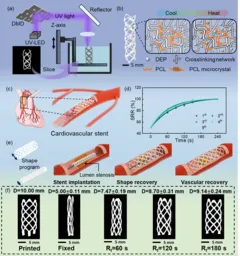
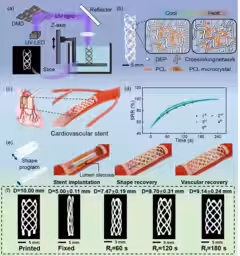
In the realm of medical devices, stents are vital in treating vascular diseases where blood vessels narrow. Traditionally, these stents required heating or complex manipulation to function, posing a notable burden for both patients and medical professionals. Recent research led by Professor Shinjiro Umezu of Waseda University and Dr. Kayo Hirose from Tokyo University Hospital has yielded a revolutionary vascular stent that expands automatically at body temperature (37°C). Using advanced 4D printing technology, this stent eliminates the need for external heating, promising to transform conventional vascular treatments.
Design and Mechanism
The newly developed stent maintains a compact, folded shape when cooled, making it easy to transport to the target site within the body. Once it reaches the desired location, it naturally expands to its pre-defined shape at body temperature, effectively supporting the blood vessel from the inside. This innovative design reduces the risk of tissue damage associated with high-temperature methods previously used.
4D printing technology allows for the customization of stents tailored to the unique shapes of individual patients' blood vessels. This adaptability can potentially minimize displacement and excessive pressure on the vessels, leading to safer outcomes.
Safety and Testing
Animal studies have confirmed both the safety and functionality of the stent in a living environment, advancing it through preliminary non-clinical stages for vascular treatments. The automatic deployment mechanism simplifies the stent placement process, contributing to shorter therapy times and reducing complications related to complicated procedures.
Historical Context
Historically, vascular stents, whether made of metals or polymers, have been widely employed to restore blood flow in cases of vascular stenosis worldwide. However, traditional methods posed significant burdens—requiring not only precise mechanical intervention but also posed risks of thermal damage to surrounding tissues.
Advancements in shape-memory materials and 3D printing techniques have opened new avenues for developing medical devices that can alter their forms within the body. Yet, instances demonstrating operation safely at body temperature have been rare until now.
Significance of Recent Development
The implications of this new stent design are profound. By eliminating the need for external heating devices, it simplifies procedures and reduces the overall risks associated with installation. This not only eases the burden on medical practitioners but also aligns with the patient-centric approach of modern healthcare, focusing on minimally invasive treatments that enhance recovery and reduce postoperative discomfort.
The capability to design stents based on individual vascular anatomy is a significant advancement toward personalized medicine. As health populations grow, especially among the elderly, having adaptable medical technology to meet diverse needs becomes increasingly vital.
Future Impact and Challenges
While this research marks a critical achievement in stent technology, further evaluation and development toward clinical application are necessary. Current testing has primarily been limited to animal studies, necessitating comprehensive testing in human contexts to ascertain long-term stability and performance in varying vascular conditions.
Additionally, stent requirements differ based on several factors such as the site and nature of the disease, which underscores the need for optimization in design to meet specific clinical challenges. Assessing factors like durability and degradation will also play a crucial role in further development.
The future envisions this temperature-sensitive design paradigm, alongside 4D printing, potentially being applied across other medical devices, enhancing the landscape of healthcare technology that responds dynamically to internal body environments. Such innovations herald a promising shift toward more compassionate, efficient patient care worldwide.
Research Authors' Commitment
This transformative research stems from a shared desire to forge safer, more effective vascular treatment options. With promising developments in stent technology, the goal is to alleviate patient burdens while expanding the options available in medical treatment strategies. Continuous collaboration and real-world input will propel these advancements forward.
Conclusion
By harnessing body temperature as a trigger for automatic deployment, this innovative vascular stent not only reduces the complexity of the procedure but also promises to enhance overall safety for patients. The pioneering efforts of Shinjiro Umezu and his team pave the way for future breakthroughs in personalized medical devices, respecting the intricate needs of patients and optimizing the potential for superior outcomes in healthcare.
Topics Health)









【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.