
Impact of Metabo Health Check System on Working-age Individuals in Japan Revealed
Introduction
The rapidly aging population in Japan has raised concerns about the increasing healthcare costs associated with lifestyle-related diseases such as diabetes and hypertension. To address these challenges, the Metabo Health Check system, officially known as the Specific Health Checkups and Guidance, was introduced in 2008. This system focuses on the prevention and early detection of lifestyle diseases.
Overview of the Research
A research team from Waseda University, which includes experts such as Masato Oikawa, Haruko Noguchi, and Akira Kawamura, in conjunction with Toshi Hide Awatani from Kochi University of Technology, conducted an analysis examining the impact of the Metabo Health Check system on the health and lifestyle behaviors of working-aged individuals enrolled in the National Health Insurance (NHI). The study particularly emphasized the correlation between municipal financial efforts and health outcomes.
Key Findings
Reduction in Disease Prevalence
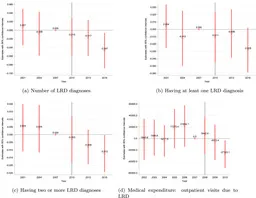
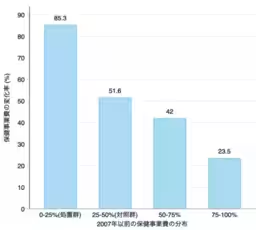
The results indicate that municipalities that invested more in health programs experienced a 10.4% reduction in the incidence of lifestyle-related diseases among NHI members. Furthermore, the proportion of individuals suffering from multiple diseases decreased by a remarkable 35.8%. This suggests that financial commitment to public health can yield significant health benefits.
Economic Impact
In terms of economic efficacy, the research estimates that the reduction in healthcare costs associated with lifestyle diseases is approximately nine times greater than the costs incurred due to the implementation of the Metabo Health Check system. This underscores the financial viability of investing in health promotion programs.
Behavioral Changes
The analysis also found positive shifts in health behaviors among participants. There was a notable increase in the number of individuals walking over 8,000 steps daily, a decrease in smoking rates, and reduced alcohol consumption. This illustrates the program's role in encouraging healthier lifestyle choices among participants.
Inequality in Health Improvements
However, the findings also highlighted a concerning trend: the health improvements were predominantly observed in economically stable households, such as self-employed individuals and homeowners. Conversely, unemployed individuals and those living in rental apartments did not show significant health enhancements. This points towards existing health disparities that need to be addressed.
Background and Methodology
The Need for the Study
Despite widespread health check-up programs in many nations, previous research primarily focused on employed individuals in corporate settings. There has been limited exploration concerning those who are self-employed or unemployed regarding the effectiveness of health interventions. The introduction of the Metabo Health Check was intended to standardize health check-ups and provide municipalities with incentives to improve NHI member health outcomes.
Analytical Approach
The study applied a dosed Difference-in-Differences (DID) estimation technique to evaluate the causal effects of the Metabo Health Check program on health status and behaviors among NHI enrollees. It utilized data from large-scale national surveys, including the Basic Survey on Living Conditions, to support its findings.
Conclusion
The research published in the "Journal of Health Economics" demonstrates that the Metabo Health Check system significantly contributes to improved health outcomes among working-aged individuals under the National Health Insurance scheme. Despite these advancements, there remains a pressing need to focus on vulnerable populations who are not benefiting from such health programs. Policymakers are encouraged to design strategies that facilitate equal access to health improvement resources for all socioeconomic groups.
Future Directions
Moving forward, it is vital to explore the reasons behind the lack of engagement from economically disadvantaged groups and to enhance outreach efforts to raise awareness about the importance of regular health check-ups. The insights gained from this study offer invaluable considerations for shaping the future of Japan’s social security policies, ensuring that they inclusively support all citizens intending to foster healthier communities.


Topics Health)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.