
AI-Driven Cell Mapping to Accurately Predict Drug Efficacy and Side Effects
Revolutionizing Drug Discovery with AI-Driven Cell Mapping
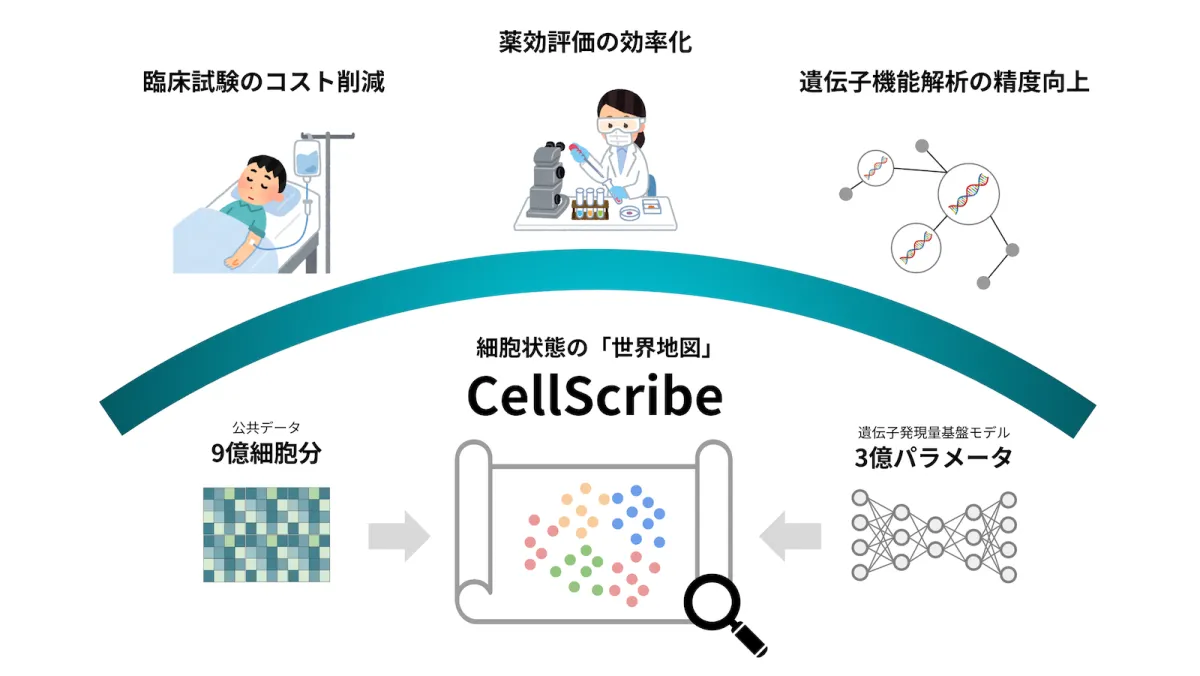
In a breakthrough that promises to reshape the future of drug discovery, the Humanome Institute has unveiled its latest innovation: CellScribe. This state-of-the-art model utilizes single-cell gene expression data to construct a detailed map of cellular responses to medications, allowing for precise predictions of both therapeutic effects and potential side effects. Here’s a closer look at how this technology is set to expedite the often lengthy and costly process of bringing new drugs to market.
The Challenge in Drug Discovery
Developing a new drug typically requires over a decade of research and expenditures exceeding 100 billion yen. This long journey becomes even more complicated with the rise of novel modalities like mRNA and monoclonal antibody therapies. These drugs usually operate through mechanisms that differ significantly from existing treatments, resulting in a lack of relevant prior experiments, which complicates the prediction of their impacts on living organisms.
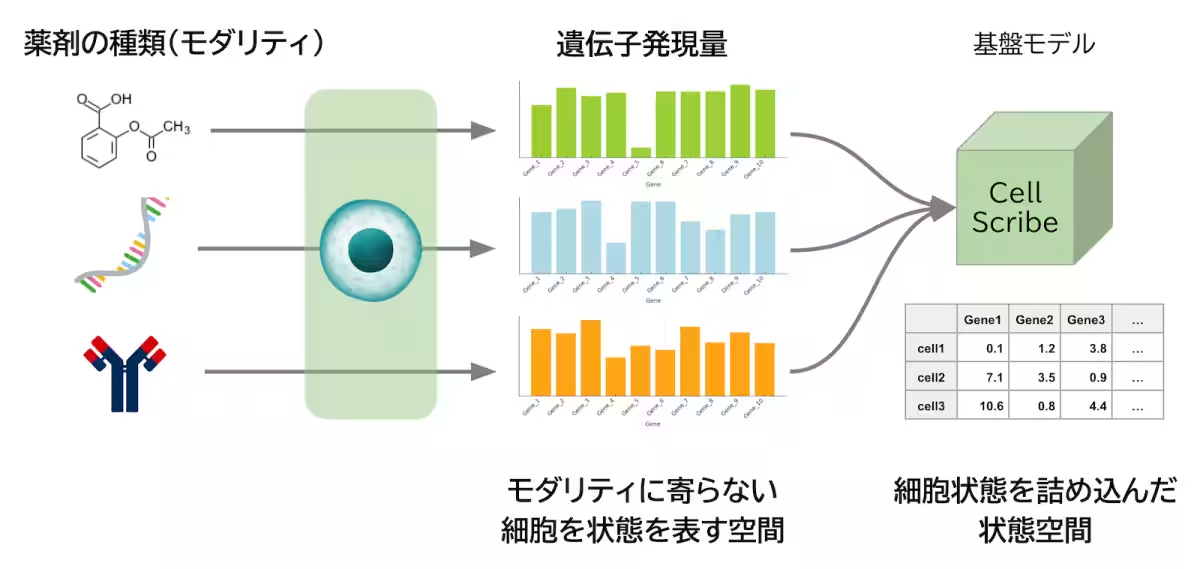
Recent advancements in single-cell analysis techniques have emerged as a powerful aid in tackling these challenges. By allowing researchers to observe the expression levels of individual genes within cells, this technology can offer a granular understanding of cellular responses to drugs. However, the vast and intricate datasets produced present another hurdle for researchers seeking to glean actionable insights; thus, there was a pressing need for a robust analytical foundation to handle such complex information.
The Solution: CellScribe
In response to these challenges, the Humanome Institute has developed CellScribe, a foundation model specifically designed to analyze gene expression data obtained from single cells with both high efficiency and accuracy. This model is essentially like a world map of cellular responses, integrating diverse cellular information to forecast the characteristics and trends within experimental datasets obtained by users.
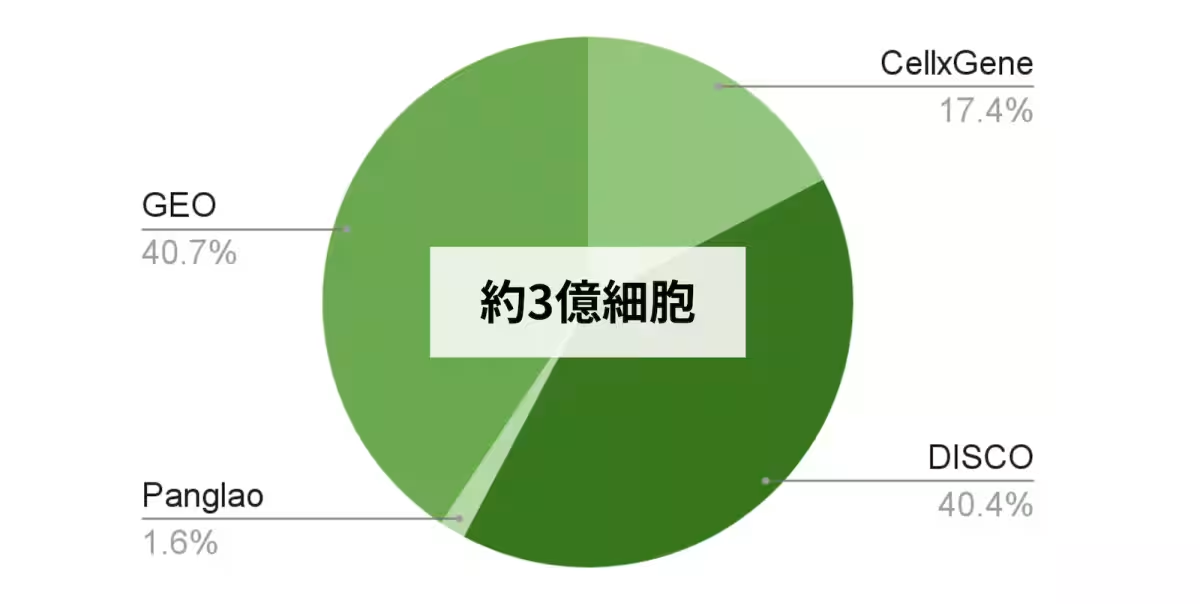
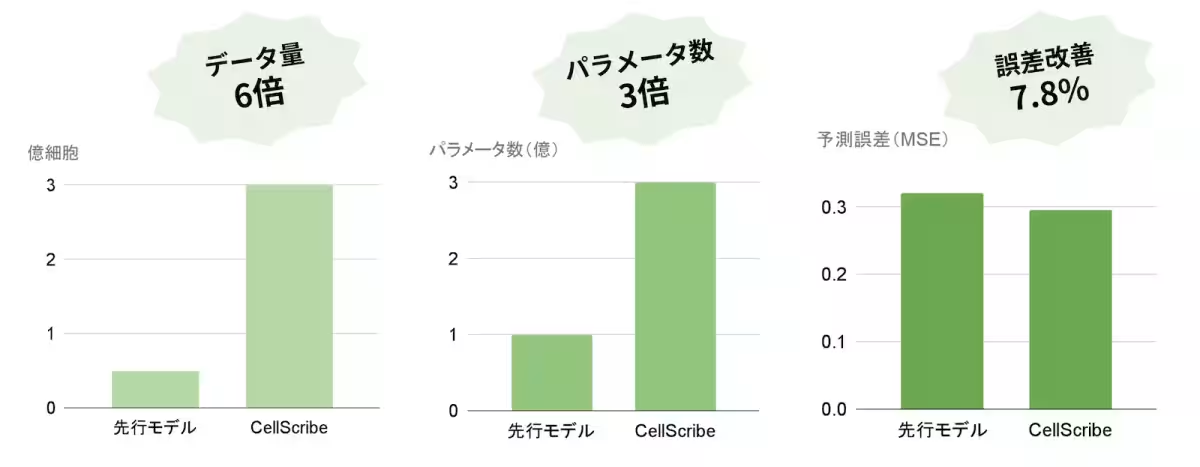
To build this groundbreaking model, CellScribe leverages data from approximately 900 million cells—far exceeding previous research efforts. This remarkable feat is accomplished through the integration of data from four publicly available databases, including CellxGene, embedding a total of 300 million parameters into the model. With this extensive dataset, the model has achieved a remarkable reduction of about 7.8% in prediction error, outperforming previous variations such as the asymmetric encoder-decoder model known as scFoundation.
Incredible Precision
CellScribe has demonstrated exceptional reliability in predicting gene expression profiles, achieving an average mean squared error (MSE) of 0.295 as of April 19, 2025, showcasing its predictive accuracy when compared to its predecessors. This enhanced precision enables users not only to interpret the specific characteristics of data but also to identify previously overlooked routes and promising targets for drug discovery.
Future of Drug Discovery with AI
The implications of CellScribe extend far beyond theoretical applications; it signifies a tangible advancement in pharmaceutical research. With plans to collaborate closely with pharmaceutical companies, academic institutions, and biotech startups, the Humanome Institute is dedicated to enhancing the efficiency and success rates of drug development. Future expansions will also encompass the integration of non-single-cell experimental data, broadening the scope and enhancing the model's versatility in various applications.
Acknowledgements
The development of this groundbreaking technology has received support from the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI) and the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) under the Generative AI Accelerator Challenge (GENIAC) project, aimed at advancing generative AI capabilities.
For those interested in practical applications of CellScribe, the model's samples and corresponding code are available on the Humanome Institute's GitHub repository, further democratizing access to this revolutionary technology.
In conclusion, as the Humanome Institute continues to refine CellScribe and push the boundaries of AI in life sciences, we stand on the cusp of a new era in drug discovery, where the once daunting task of bringing new therapies to the market can become more manageable and efficient. By leveraging sophisticated AI tools like CellScribe, researchers will be better equipped to tackle the complexities of human health and disease, opening up possibilities for the development of innovative and effective medical treatments.
Topics Health)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.