
Significant Rise in Male Parental Leave Rates and Decreased Gender Wage Gap in Japan
Significant Rise in Male Parental Leave Rates and Decreased Gender Wage Gap in Japan
A recent study conducted by the Japan Productivity Center has unveiled some encouraging trends regarding parental leave for men and gender wage disparity among Japan's top listed companies. As per the survey published on August 1st, 2023, the rate at which men are taking parental leave has seen a significant increase, now exceeding 60%. This marks a potent shift from just 33.5% two years ago, climbing to 48.8% last year, and now reaching an impressive 62.9%.
Key Findings from the Survey
The survey compiled data from 1,104 companies listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange, specifically examining their disclosures relating to human capital and diversity-based parameters as mandated by Japanese government regulations. Here are the notable insights:
1. Female Management Representation
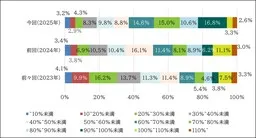
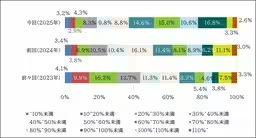
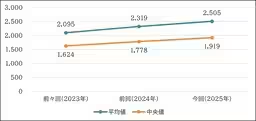
Despite a persistent challenge, the percentages of women in management positions have shown a decrease in the number of companies where this figure remains below 5%. Currently, 40.6% of companies fall into this category, down from 46.0% last year and 48.2% the year before. Conversely, the average female management representation has slightly increased to 9.1%.
2. Increasing Male Parental Leave Rates
The dramatic increase in male parental leave uptake is a clear indicator of changing workplace norms. This trend evidences an improvement in participating sectors, where the percentage of companies with male parental leave rates above 60% has jumped significantly. The gap between different industries appears to be narrowing, indicating a widespread acknowledgment of the importance of parental leave for sustainability in workplaces.
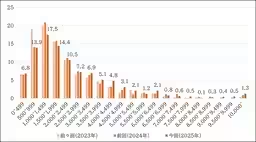
3. Gender Wage Gap Improvements
When analyzing wage disparity, the average pay gap between men and women was reported at 72.0%. This is a slight improvement from last year's figure of 71.4%. Most notably, the largest share of companies is categorized within the range of 70-75%, showing that many are beginning to address the wage imbalance.
4. Rise in Reporting on Human Capital
Moreover, the report revealed a marked increase—about 19.6%—in the volume of disclosures regarding human capital practices within company reports compared to two years previous, highlighting a growing acknowledgment of the importance of this issue among companies.
5. Insights on DX-Driven Companies
Interestingly, companies that focus on digital transformation (DX) tend to exhibit a smaller gender wage gap. Approximately 43.3% of companies reported mentioning DE in their disclosures and showed a higher male parental leave uptake.
Conclusion
The progressing landscape depicted in this report portrays a shift toward more inclusive practices within Japanese workplaces. As businesses adapt to new regulations and apparent cultural changes, the increasing numbers of men taking parental leave, the rising percentage of women in management roles, and the gradual closing of the gender wage gap are promising indicators of Japan's evolution toward gender equality in the corporate sector. For a complete examination of the survey results and additional data, please visit the Japan Productivity Center's research website here.
Topics People & Culture)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.