

Research on Inhibition of Lipid Peroxidation by Grape Extract to be Presented at European Dermatology Conference
The POLA Innovation Center, a division of POLA Inc., based in Shinagawa, Tokyo, has made significant advances in researching the effects of a specific grape extract, known as the lateral shoot extract from the new grape cultivar 'Shinku'. This research has unveiled its potential to inhibit ultraviolet (UV) light-induced lipid peroxidation. The findings will be presented at the 54th European Society for Dermatological Research Conference, to be held in Belgium from September 10 to 13, 2025.
The study involves a collaborative effort between POLA's scientists and Keiko Murota, a professor at the Department of Life Science, Shimane University. The paper, titled Inhibition of Ultraviolet-induced Lipid Peroxidation by Lateral Shoot Extract of 'Shinku’, a New Red Grape Cultivar Developed in Shimane Prefecture, Japan, details the method and results of their experiments.
The process involved extracting the lateral shoots of the Shinku grape, a cultivar developed through cross-breeding Benihara and Shine Muscat, which are notable for their large, red berries sustainably produced in Shimane Prefecture. These lateral shoots are often discarded during grape cultivation, particularly after pruning from autumn to winter or during excessive shoot thinning in spring and summer, leading to significant waste. However, the extract from these shoots has shown remarkable potential in skincare applications.
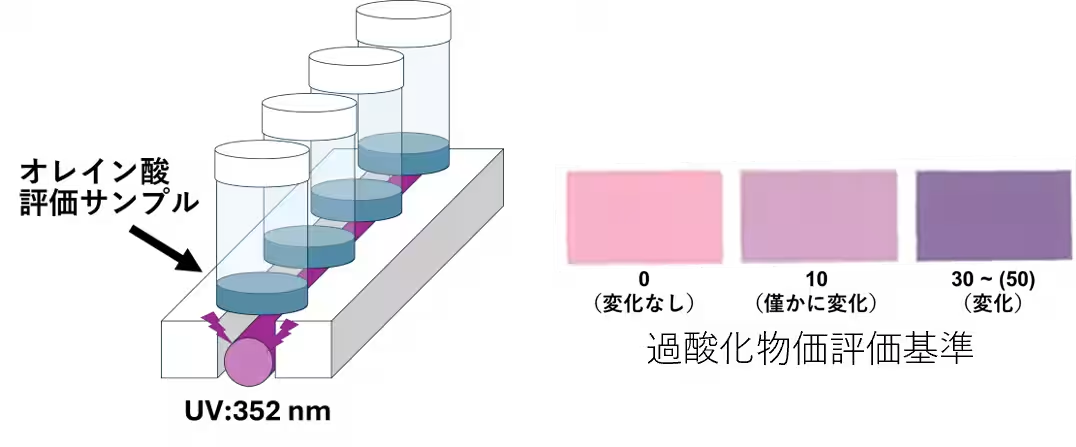
Lipid peroxidation occurs when fatty acids react with reactive oxygen species, commonly exacerbated by UV exposure. This oxidative process leads to the formation of harmful peroxidized lipids, which can adversely affect skin health. The research demonstrated that peroxidized lipids compromise the skin's barrier function and may contribute to various skin issues, including inflammation, dullness, and enlarged pores. The inclusion of the lateral shoot extract alongside oleic acid (a major component of sebum) revealed a significant inhibition of the lipid peroxidation process following UV exposure.
In the study, the researchers assessed the peroxide value of oleic acid after UV irradiation. The results show a marked increase in peroxide levels following UV exposure, indicating accelerated oxidation. However, when lateral shoot extract was applied, a noticeable reduction in this increase was observed, suggesting the extract's potent protective capability against oxidative stress on the skin. The graphical representation illustrates the comparative effects, with the extract denoted by a distinctive color marking its efficacy.
The success of this study is significant not only for POLA but also for the broader dermatological and cosmetic industry, emphasizing the potential of using discarded agricultural byproducts in skincare formulations. The findings reinforce the scientific merit of utilizing grape byproducts, offering a sustainable route toward enhancing skin health while minimizing waste.
The opportunity to present at the European Society for Dermatological Research conference underscores the recognition of this work on an international scale, highlighting the study's unique contributions to dermatological science. With global interest in sustainability and innovative skincare solutions, the findings of this research could pave the way for future product development in the cosmetic sector. By harnessing the benefits of the Shinku grape's byproducts, POLA solidifies its commitment to both environmental sustainability and cutting-edge scientific research.



Research Overview
The study involves a collaborative effort between POLA's scientists and Keiko Murota, a professor at the Department of Life Science, Shimane University. The paper, titled Inhibition of Ultraviolet-induced Lipid Peroxidation by Lateral Shoot Extract of 'Shinku’, a New Red Grape Cultivar Developed in Shimane Prefecture, Japan, details the method and results of their experiments.
The process involved extracting the lateral shoots of the Shinku grape, a cultivar developed through cross-breeding Benihara and Shine Muscat, which are notable for their large, red berries sustainably produced in Shimane Prefecture. These lateral shoots are often discarded during grape cultivation, particularly after pruning from autumn to winter or during excessive shoot thinning in spring and summer, leading to significant waste. However, the extract from these shoots has shown remarkable potential in skincare applications.
The Importance of Lipid Peroxidation
Lipid peroxidation occurs when fatty acids react with reactive oxygen species, commonly exacerbated by UV exposure. This oxidative process leads to the formation of harmful peroxidized lipids, which can adversely affect skin health. The research demonstrated that peroxidized lipids compromise the skin's barrier function and may contribute to various skin issues, including inflammation, dullness, and enlarged pores. The inclusion of the lateral shoot extract alongside oleic acid (a major component of sebum) revealed a significant inhibition of the lipid peroxidation process following UV exposure.
Experimental Results
In the study, the researchers assessed the peroxide value of oleic acid after UV irradiation. The results show a marked increase in peroxide levels following UV exposure, indicating accelerated oxidation. However, when lateral shoot extract was applied, a noticeable reduction in this increase was observed, suggesting the extract's potent protective capability against oxidative stress on the skin. The graphical representation illustrates the comparative effects, with the extract denoted by a distinctive color marking its efficacy.
Implications of the Findings
The success of this study is significant not only for POLA but also for the broader dermatological and cosmetic industry, emphasizing the potential of using discarded agricultural byproducts in skincare formulations. The findings reinforce the scientific merit of utilizing grape byproducts, offering a sustainable route toward enhancing skin health while minimizing waste.
Conclusion
The opportunity to present at the European Society for Dermatological Research conference underscores the recognition of this work on an international scale, highlighting the study's unique contributions to dermatological science. With global interest in sustainability and innovative skincare solutions, the findings of this research could pave the way for future product development in the cosmetic sector. By harnessing the benefits of the Shinku grape's byproducts, POLA solidifies its commitment to both environmental sustainability and cutting-edge scientific research.




Topics Health)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.