
Discovery of CTDNEP1 Gene Offers Hope in Slowing Pancreatic Cancer Progression
The Promising Role of CTDNEP1 Gene in Combating Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic cancer, often referred to as the “silent killer,” is one of the most lethal forms of cancer, primarily due to late diagnosis and limited treatment options. Recent research from the Tokyo University of Science highlights a significant breakthrough in the fight against this aggressive disease: the identification of the CTDNEP1 gene as a potential tumor suppressor.
The Groundbreaking Research
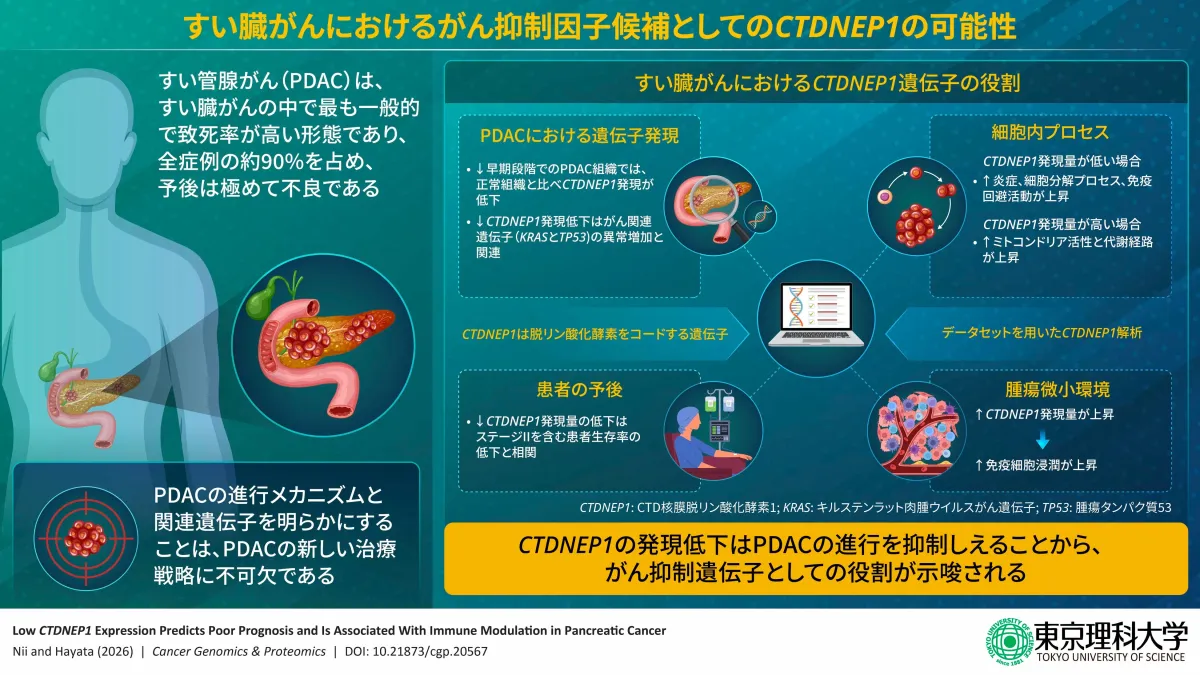
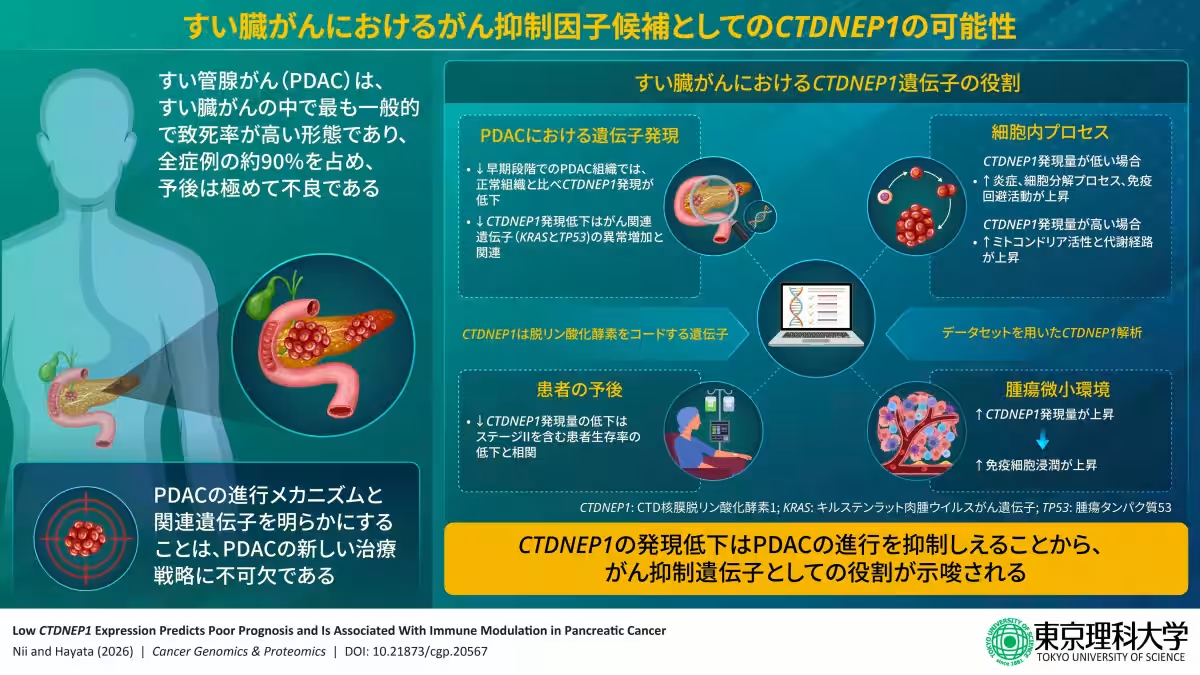
Led by Professor Tadayoshi Hayata and doctoral candidate Mayuka Nii, the study revealed that CTDNEP1, known for its critical involvement in bone metabolism, also plays a crucial role in inhibiting pancreatic cancer progression. This gene's expression levels in pancreatic cancer tissue were found to be significantly lower compared to normal tissue, correlating with poorer patient prognoses, thereby highlighting its potential as a biomarker for predicting patient outcomes.
Using genetic data from pancreatic cancer patients, the team discovered that those with low CTDNEP1 expression had lower survival rates. Notably, CTDNEP1 levels were closely associated with the infiltration of immune cells into the tumor, suggesting that it not only affects cancer growth but also influences the tumor's immune environment.
Implications for Early Diagnosis and Treatment
This groundbreaking study opens new avenues for early diagnosis and therapeutic interventions. The research emphasizes the need for developing new biomarker tools to assist in the early identification of pancreatic cancer, a task that has been a challenge due to the disease’s subtle symptoms in its early stages. The findings suggest that CTDNEP1 could serve as a target for new treatment strategies, offering hope in a field with limited options.
The study utilized comprehensive data from The Cancer Genome Atlas, analyzing gene expression, survival rates, and genetic mutations from a substantial sample of pancreatic cancer patients (n=177). It concluded that not only was CTDNEP1 expression reduced across various cancer types, but the decrease was particularly notable in pancreatic cancer from the earliest stages of the disease.
Understanding the Mechanisms
The mechanisms by which CTDNEP1 operates are still under investigation. It was previously known for its roles in regulating cellular functions and signaling pathways essential for maintaining various organ functions, including bone and kidney health. The connection to pancreatic cancer demonstrates the need for further research to elucidate CTDNEP1's exact role in cancer pathology.
Additionally, when examining the metabolic pathways stimulated by CTDNEP1, the study indicated that higher expression levels were associated with immune processes, promoting a favorable environment for the body's immune response to combat the tumor.
As pancreatic cancer continues to be a challenging disease to treat, ongoing research on CTDNEP1 could lead to innovative methods of diagnosis and therapy. This study underscores a critical step towards understanding not just the cancer itself but the complex interplay between cancer progression and the immune system.
Future Directions
Looking forward, the research team plans to conduct further experiments to clarify how CTDNEP1 influences pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and metastasis. They aim to discover factors that regulate CTDNEP1 expression, potentially uncovering new therapeutic targets. Professor Hayata has dedicated nearly two decades to understanding CTDNEP1, and reflects on the personal impact of pancreatic cancer through his own experiences with friends who have succumbed to the disease.
“I hope this research contributes to developing new early detection methods and treatment strategies for pancreatic cancer,” said Professor Hayata.
As research progresses, the potential for CTDNEP1 to serve as a promising prognostic biomarker or therapeutic target in pancreatic cancer represents a beacon of hope amid the challenges faced in treating this notoriously difficult cancer. The scientific community eagerly anticipates the continued investigations that may one day lead to viable solutions for patients suffering from this aggressive form of cancer.
Conclusion
The study findings published online in the journal Cancer Genomics & Proteomics underline the importance of understanding the genetic factors involved in pancreatic cancer. With new insights into CTDNEP1, there’s potential not only for improved diagnostic capabilities but also for more effective treatment strategies that may ultimately offer a lifeline to those affected by this formidable illness.
Topics Health)









【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.