

Collaboration Between Nagoya, Okayama, and Juntendo Universities for Medical Research Advancement
Collaborative Medical Research Advancements
In the realm of healthcare, groundbreaking advancements require robust collaboration among institutions. A promising initiative has emerged from the union of Nagoya University, Okayama University, and Juntendo University, making strides towards addressing some of Japan's most pressing health concerns. At the forefront of this initiative is the AMED (Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development) Medical Research Support Program, which has selected this joint endeavor for the fiscal year 2025, allowing these institutions to create an integrated platform for medical research.
Key Highlights of the Initiative
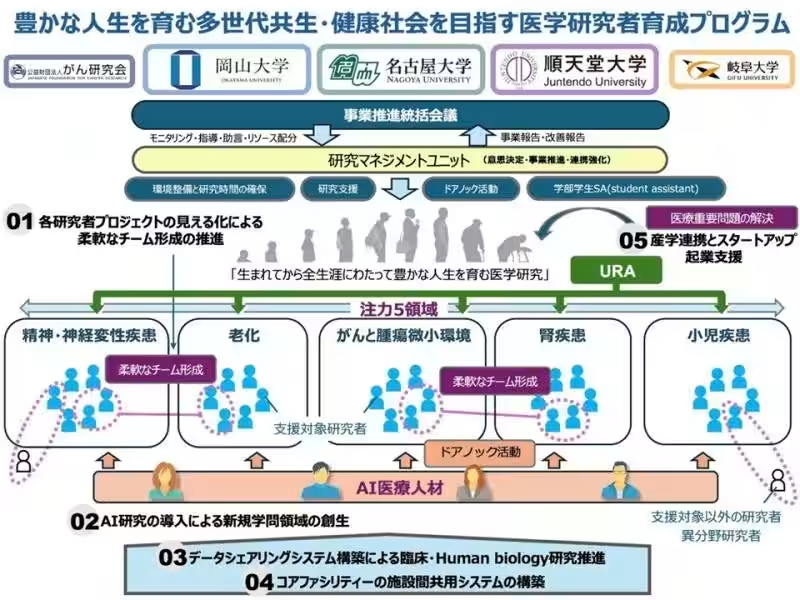
This collaborative effort is anchored in the creation of a strong joint research framework among the three universities, classified as centers for innovative medical technology under AMED. By fusing the unique characteristics of national and private universities, the program aims to accelerate research in critical priority areas. The strategic use of artificial intelligence and large-scale medical data is emphasized, promoting a data-driven research approach that can lead to significant breakthroughs in healthcare.
One of the most innovative aspects of this program is its focus on enabling researchers to dedicate more time to their studies. This is achieved through substantial reforms aimed at creating a conducive research environment. The goal is to allow young medical researchers to immerse themselves in pioneering and challenging studies without distractions.
Overview of the Program
The jointly suggested project, titled 'Developing a Multigenerational and Healthy Society That Nurtures a Rich Life,' aims to cultivate an environment where younger researchers can thrive. This initiative is especially timely, addressing the urgent challenges posed by Japan's declining birth rate and rapidly aging society. The collaboration between these three universities is meant to leverage each institution's strengths, facilitating a supportive atmosphere for young medical researchers focused on innovative studies.
The leadership of this project is headed by Professor Masahisa Katsuno, who serves as the Dean of the Graduate School of Medicine at Nagoya University. The program will run from October 1, 2025, to March 31, 2028, and is structured to establish a new system where experienced researchers and clinical practitioners work together to support the younger generation in their research endeavors. This model is envisioned to set a precedent that could shape the future of medical research and academia-industry collaboration in Japan.
Stakeholders and Responsibilities
The management of this ambitious project has designated Professor Masahisa Katsuno from Nagoya University as the lead representative, alongside key personnel from Okayama University and Juntendo University. For Okayama University, Professor Jun Wada, Dean of the Medical School, will oversee the responsible execution of the project, while Professor Kazuhisa Takahashi from Juntendo University will handle the university's roles in the initiative.
This program will serve as a model for fostering relationships between industry and academia and will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of medical research in Japan.
Contact and Further Information
For more information, updates, and inquiries related to the program, please reach out to the respective administrative offices of the involved universities. Here are the contact details:
- - Nagoya University: General Affairs Office, Faculty of Medicine - Tel: 052-744-2040
- - Okayama University: General Affairs Division, Public Relations Office - Tel: 086-251-7292
- - Juntendo University: General Affairs Division - Tel: 03-5802-1006
The collaboration between these esteemed institutions is a significant move towards enhancing Japan's medical research landscape, promising to nurture talent and foster a healthier society through extensive research and cooperation.





Topics Health)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.