

Exploring the Utilization of Image and Video Data in AI Development: Key Insights from PIXTA's 2025 Research Study
Exploring the Utilization of Image and Video Data in AI Development: Key Insights from PIXTA's 2025 Research Study
In an ever-evolving digital landscape, understanding the dynamics of data sourcing for AI development has become increasingly critical. PIXTA, a leading online marketplace for photos, illustrations, videos, and music materials based in Shibuya, Tokyo, recently conducted a survey named "AI Utilization of Image and Video Data in Development 2025". This research aimed to unveil the current trends and challenges surrounding the sourcing of image and video data for machine learning.
The survey, conducted from March 14th to March 15th, 2025, with 226 active respondents, revealed some striking insights into the motivations and obstacles connected with the utilization of open datasets and proprietary data collection.
Key Findings
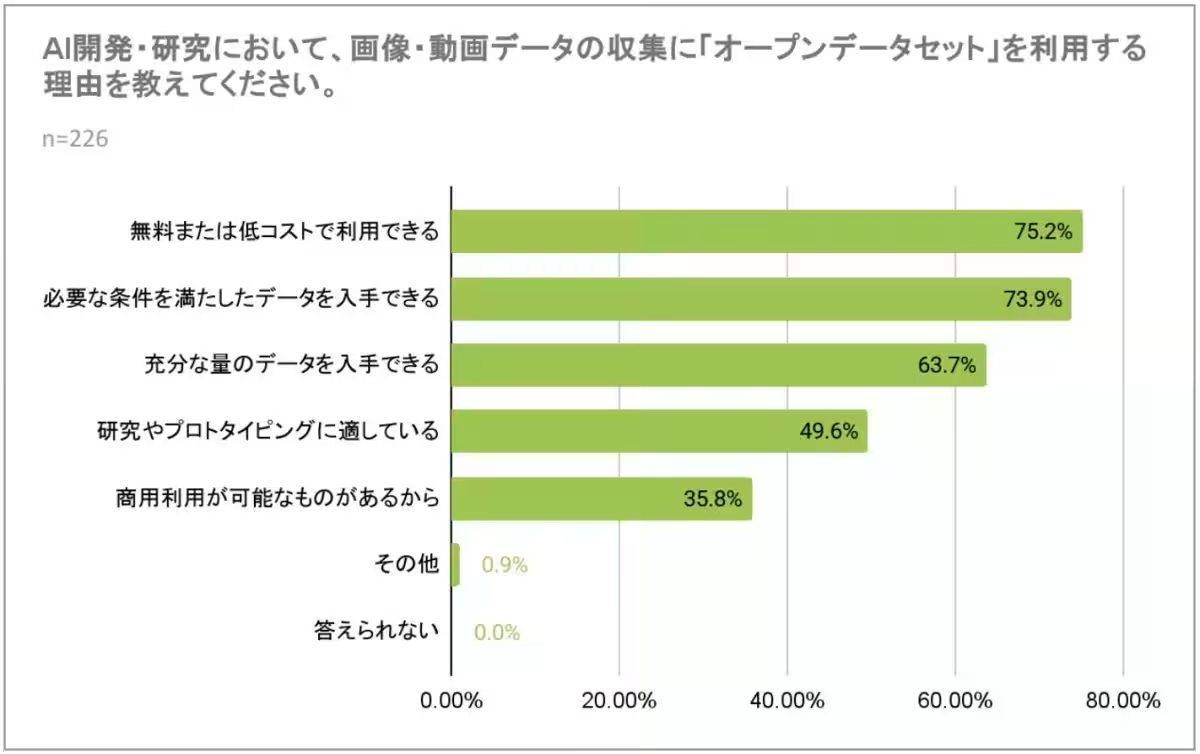
1. Motivations for Using Open Datasets: About 75.2% of respondents cited cost-effectiveness as a primary reason for relying on open datasets. The ability to meet specific criteria and access a significant volume of necessary data were also important factors, with 73.9% and 63.7% of respondents respectively agreeing with these motivations.
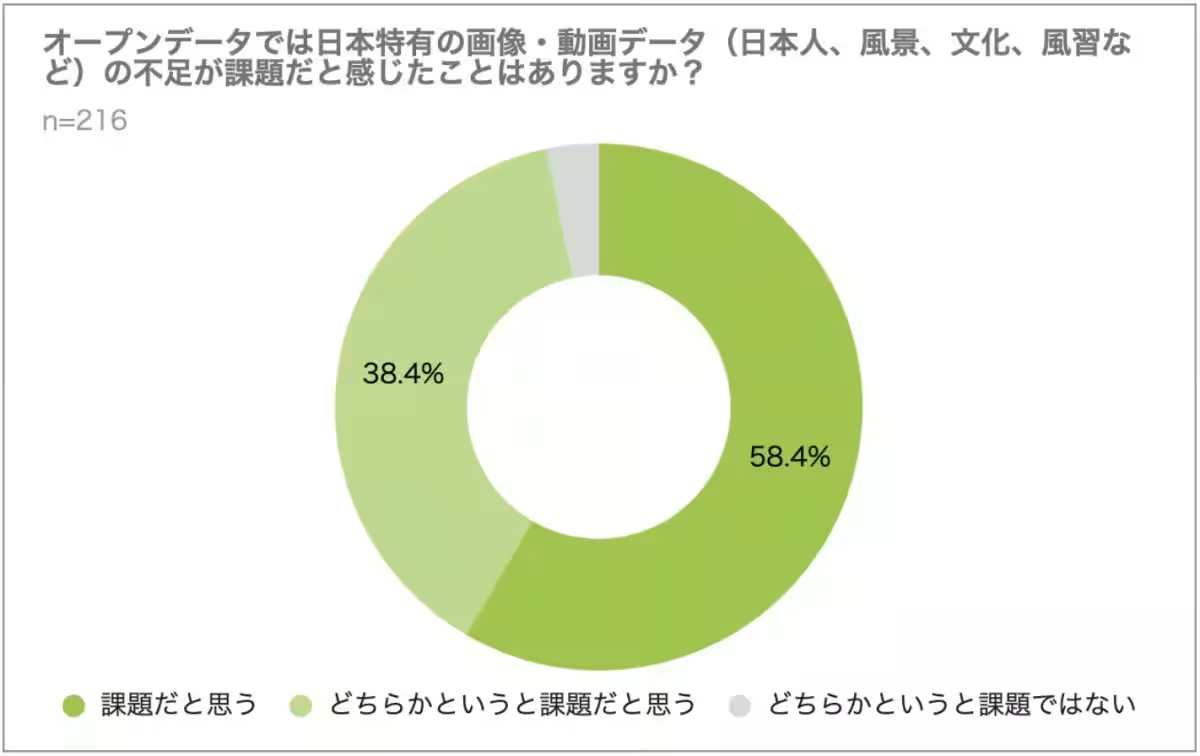
2. Challenges of Open Datasets: Despite the appeal of free datasets, the glaring challenge remains the biased data content. Approximately 65.5% of respondents acknowledged that they encounter biases in the data, with around 90% emphasizing a shortage of unique Japanese data, particularly reflecting the nation’s cultural and environmental specifics.
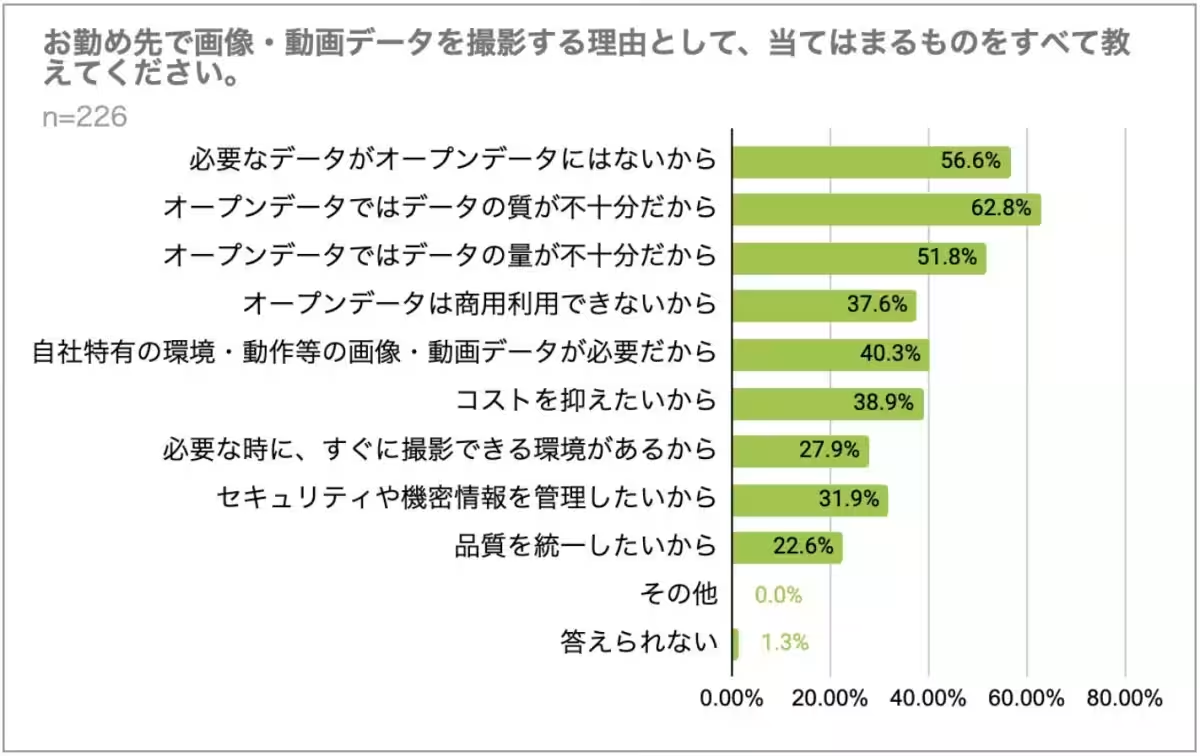
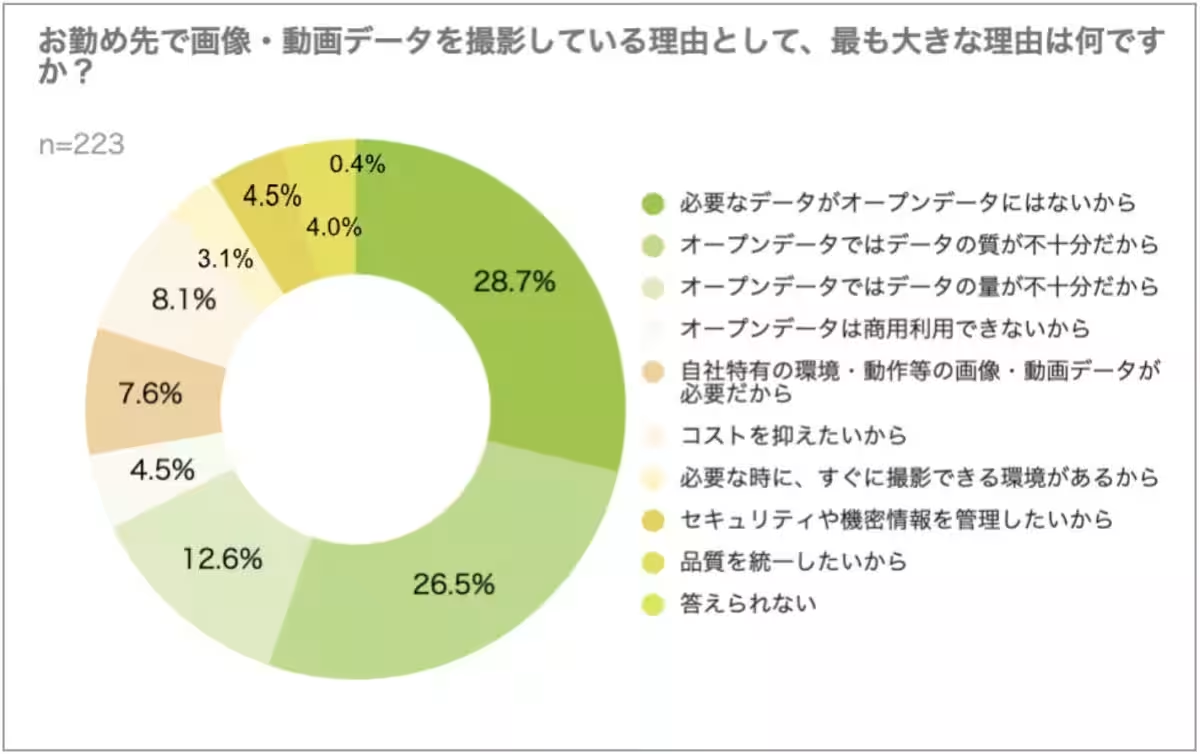
3. Self-collection of Data: A common strategy for mitigating the issues with open data is the self-collection of images and videos. Respondents noted that they feel compelled to capture their visuals because existing open data sources might not meet their quality or specificity needs. This is evident as 62.8% claimed that the quality of open data is insufficient. Participants also enjoyed the flexibility of acquiring data that aligns with their unique project needs, which open datasets often lack.
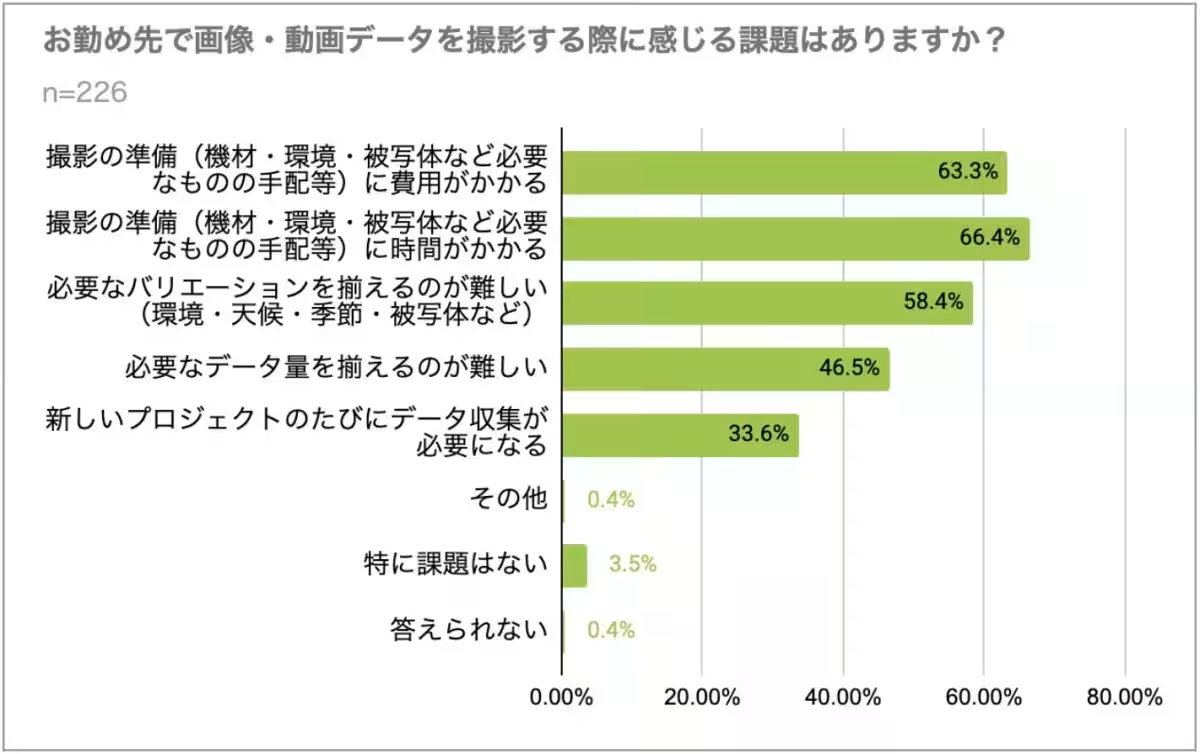
4. Self-collection Challenges: However, the self-collection process introduces its own set of hurdles. Respondents highlighted that acquisition processes often demand significant time and resources with 66.4% citing the preparation time, and 63.3% concerned about the financial implications surrounding the setup and execution of shoots.
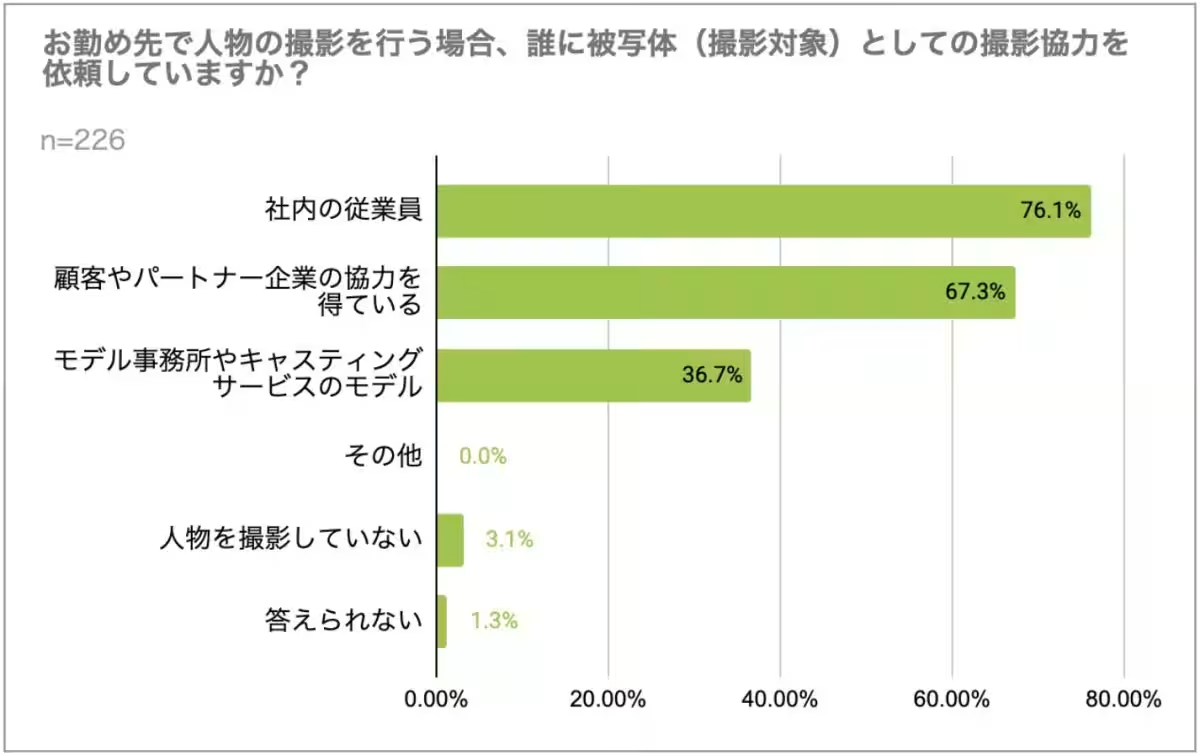
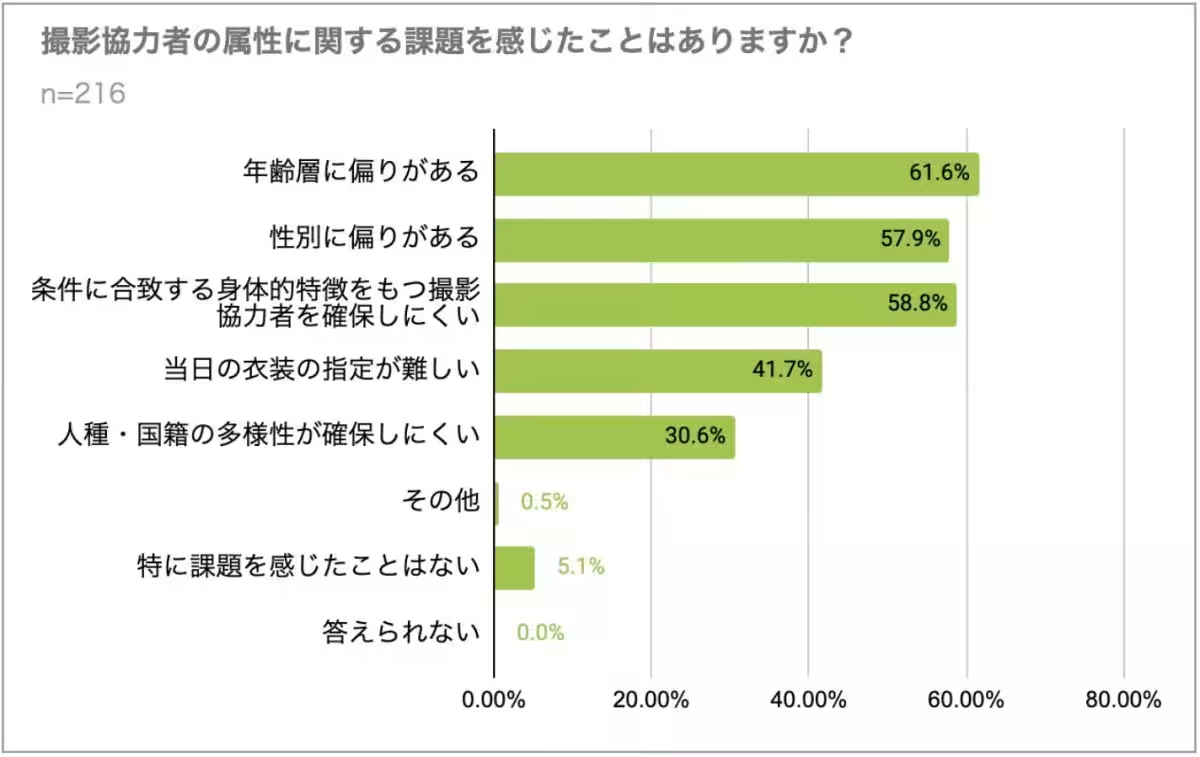
5. Shifting Focus to Quality and Variety: To overcome issues regarding image diversity, many organizations predominantly rely on their employees for assistance in shooting data, forming about 76.1% of gathering teams. However, a notable 61.6% recognized an age and gender bias among these helpers, which raises questions about the representational quality of the resultant data.
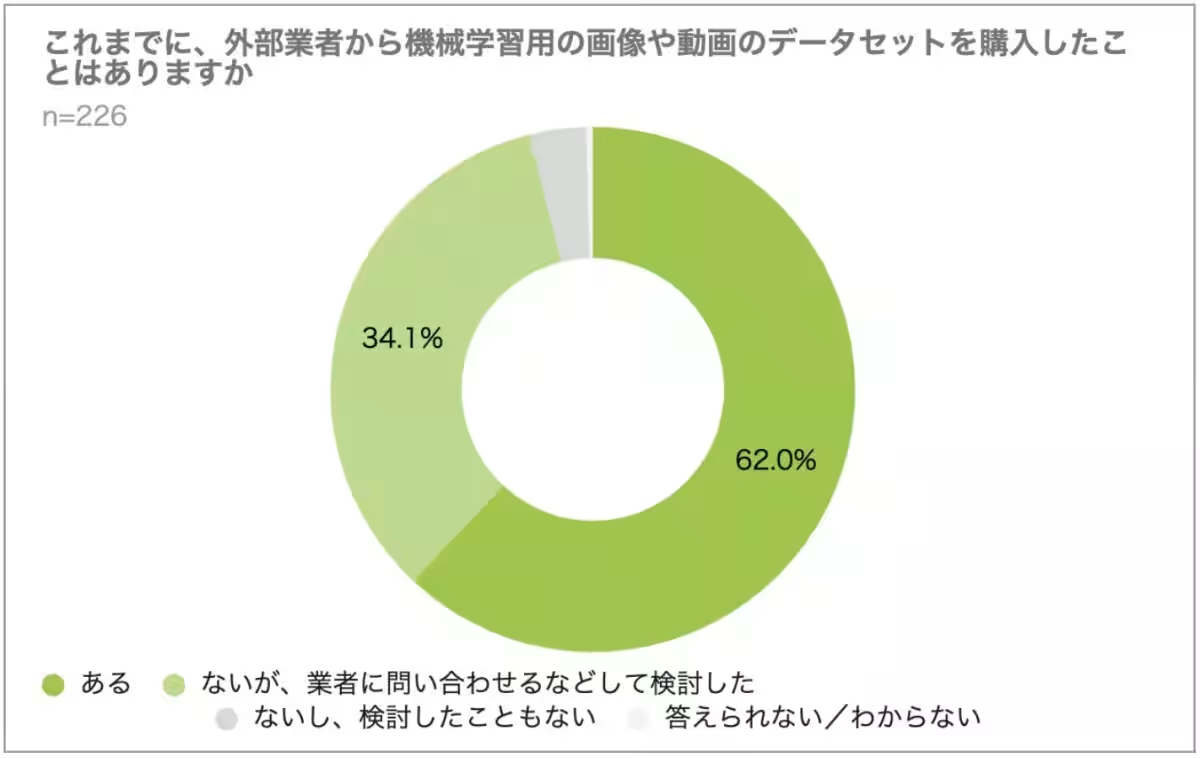
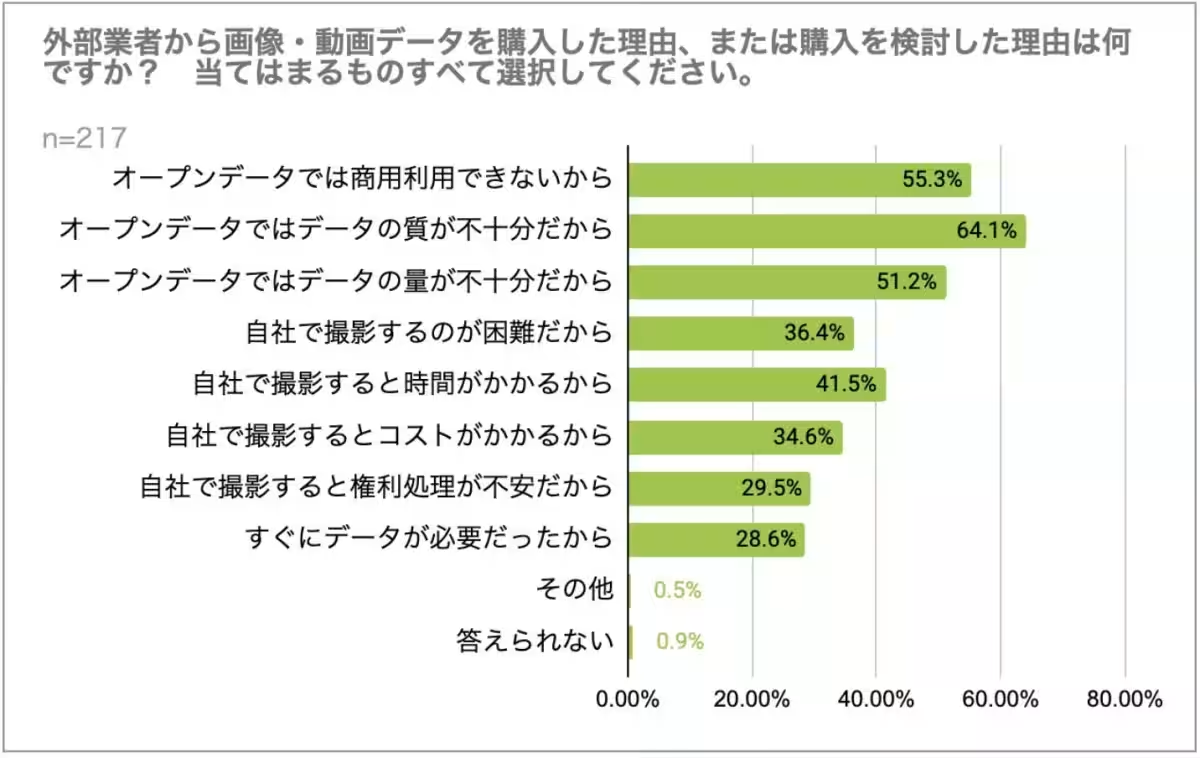
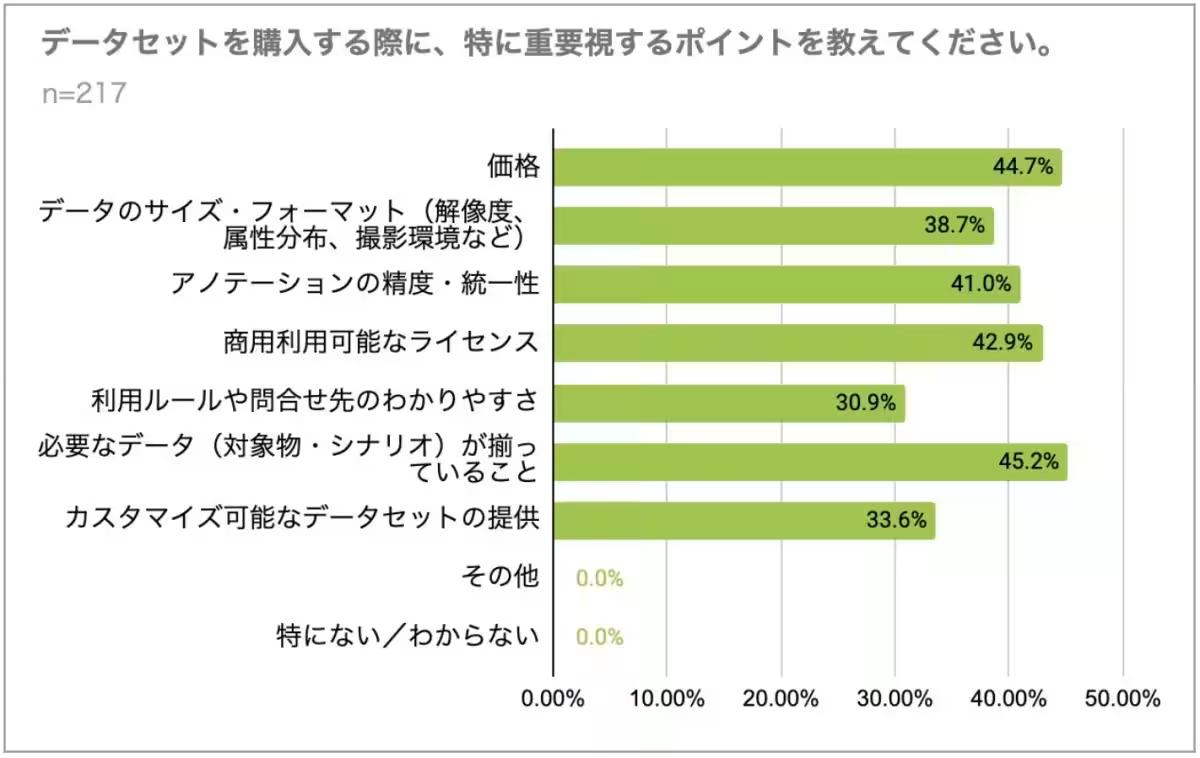
6. Interest in Purchasing Datasets: More than 90% of the respondents showed interest in purchasing datasets, primarily to address the quality and commercial usability of the data—64.1% emphasized that the lack of sufficient quality from open datasets is a significant motivator for team onboarding of pay-for data.
Conclusion
The findings from PIXTA’s survey underscore a critical understanding of image and video data's role in AI development. While open data provides initial cost savings, the need for high-quality, culturally appropriate datasets is undeniable. This creates an opportunity for companies to explore hybrid strategies that incorporate both open data utilization and proprietary image gathering to enhance their data diversity and relevance.
PIXTA’s machine learning data provision service presents a compelling solution, combining extensive libraries of Japanese imagery and advanced annotation techniques, assisting developers in overcoming common data quality barriers. As the digital image economy continues to evolve, understanding the nuances of data sourcing will be essential for innovation and practical application in AI systems.




Topics Business Technology)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.