

Exploring the Future of Solar Power: Integrated Solar Cells in Urban Building Materials
In a bold move towards carbon neutrality, the Tokyo Port Authority has embarked on a groundbreaking project to implement integrated solar power building materials using advanced solar cells. This initiative aligns with their "Tokyo Bay Carbon Neutral Strategy," aiming to facilitate a leading-edge decarbonization effort across the region.
Recently, a collaborative agreement was established between the Tokyo Port Authority, Toshiba Energy Systems Corporation, YKK AP Corporation, Kandenko Co. Ltd., and the Tokyo Teleport Center, marking a significant step in this sustainable journey. The launch of this venture, commencing on August 5, will take place at the Telecom Center building in Odaiba, part of the Tokyo Bay area, where the practical implementation of next-generation solar cells will be closely examined.
The focus of this verification project is to assess the performance and practicality of these building-integrated solar power window units equipped with next-gen solar cells, known as perovskite solar cells. These innovative cells offer several advantages over conventional silicon solar cells, making them a promising choice for urban environments. For example, their lightweight and flexible nature allows for a broader range of installation sites, enabling greater adaptability in diverse infrastructures.
Notably, the development of manufacturing technology may lead to mass production and lower manufacturing costs, further enhancing the competitiveness of these solar cells compared to traditional options. This effort is particularly significant in Japan, where roughly 30% of the global iodine supply – a crucial material for perovskite cells – is sourced domestically.
The verification will take place in an existing structure, allowing for real-world data collection and analysis, which is integral to determining the feasibility of widespread adoption of this technology in urban building practices. The testing period is set to run until January 20 of the next year, providing ample time to gather insights on energy production effectiveness and heat management through the use of heat-reflective glass in the windows.
Ultimately, the Tokyo Port Authority aims to propel technological development towards the practical application of next-gen solar cells. This initiative is expected to make significant contributions to creating a decarbonized society and ensuring stable energy supplies, necessary elements for a sustainable future in urban environments.
Through rigorous testing and evaluation, the project seeks to demonstrate that the integration of advanced solar technology into the fabric of urban architecture can foster an energy-efficient ecosystem while simultaneously addressing critical environmental challenges. As cities continue to grow, innovative solutions like this will be vital in shaping the urban landscape for generations to come, paving the way for a greener and more sustainable urban future.

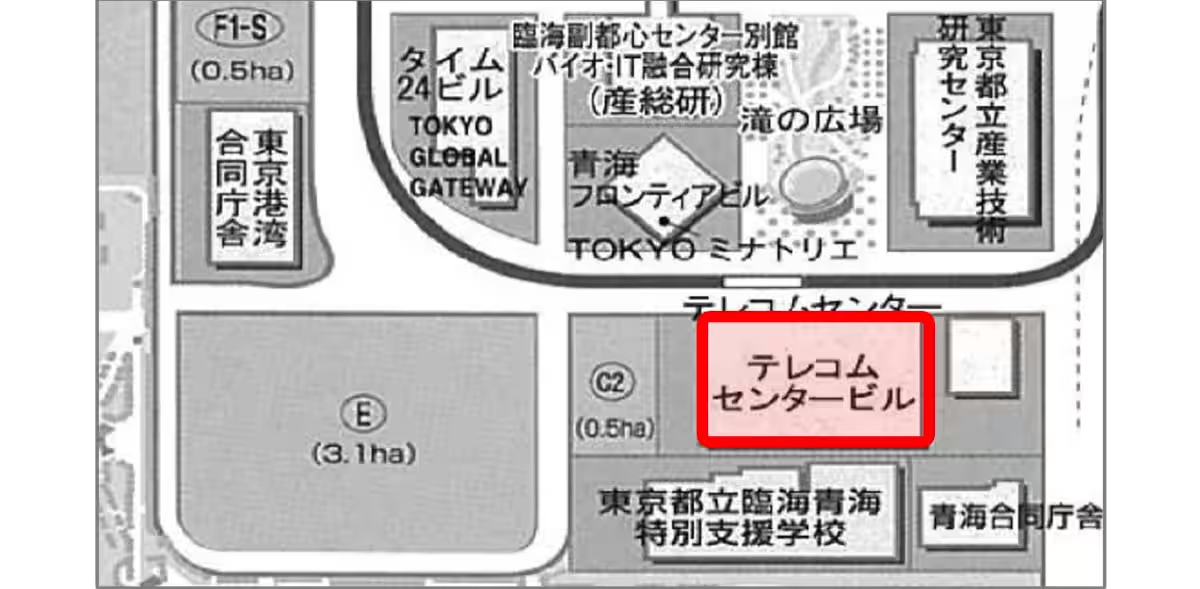
Recently, a collaborative agreement was established between the Tokyo Port Authority, Toshiba Energy Systems Corporation, YKK AP Corporation, Kandenko Co. Ltd., and the Tokyo Teleport Center, marking a significant step in this sustainable journey. The launch of this venture, commencing on August 5, will take place at the Telecom Center building in Odaiba, part of the Tokyo Bay area, where the practical implementation of next-generation solar cells will be closely examined.
The focus of this verification project is to assess the performance and practicality of these building-integrated solar power window units equipped with next-gen solar cells, known as perovskite solar cells. These innovative cells offer several advantages over conventional silicon solar cells, making them a promising choice for urban environments. For example, their lightweight and flexible nature allows for a broader range of installation sites, enabling greater adaptability in diverse infrastructures.
Notably, the development of manufacturing technology may lead to mass production and lower manufacturing costs, further enhancing the competitiveness of these solar cells compared to traditional options. This effort is particularly significant in Japan, where roughly 30% of the global iodine supply – a crucial material for perovskite cells – is sourced domestically.
The verification will take place in an existing structure, allowing for real-world data collection and analysis, which is integral to determining the feasibility of widespread adoption of this technology in urban building practices. The testing period is set to run until January 20 of the next year, providing ample time to gather insights on energy production effectiveness and heat management through the use of heat-reflective glass in the windows.
Ultimately, the Tokyo Port Authority aims to propel technological development towards the practical application of next-gen solar cells. This initiative is expected to make significant contributions to creating a decarbonized society and ensuring stable energy supplies, necessary elements for a sustainable future in urban environments.
Through rigorous testing and evaluation, the project seeks to demonstrate that the integration of advanced solar technology into the fabric of urban architecture can foster an energy-efficient ecosystem while simultaneously addressing critical environmental challenges. As cities continue to grow, innovative solutions like this will be vital in shaping the urban landscape for generations to come, paving the way for a greener and more sustainable urban future.



Topics Environment)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.