
Exploring the Challenges Faced by Diabetes Patients in Blood Glucose Monitoring
Exploring the Challenges Faced by Diabetes Patients in Blood Glucose Monitoring
In the realm of diabetes management, regular blood glucose monitoring is crucial for maintaining health, yet it comes fraught with various challenges. A recent study conducted by LOOK TEC Co., Ltd., involving 1,022 participants, including Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes patients, gestational diabetes patients, and internal medicine doctors, sheds light on the difficulties encountered in this routine task and the potential for non-invasive monitoring devices.
The Need for Regular Monitoring and Its Associated Challenges
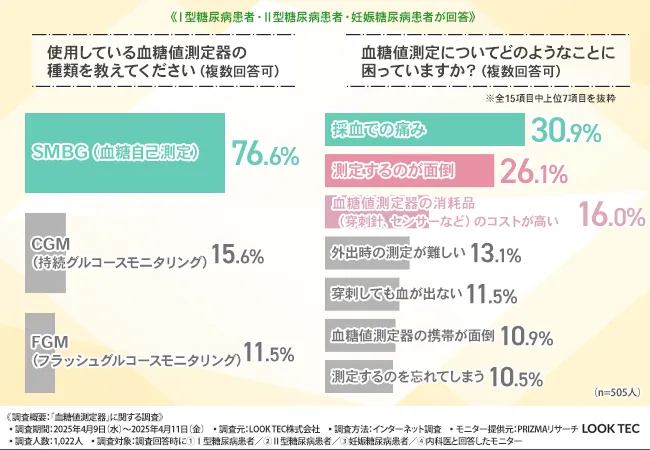
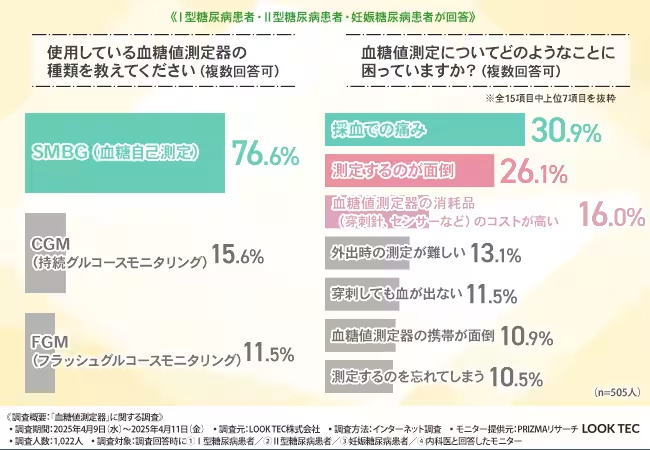
Diabetes patients often rely on regular monitoring to track their blood glucose levels effectively. However, the process is not without its drawbacks. The survey revealed that the predominant method utilized by patients is Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose (SMBG), comprising 76.6% of responses, followed by Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) at 15.6%, and Flash Glucose Monitoring (FGM) at 11.5%. Despite the advancement of technology, SMBG remains the most prevalent method due to its long-standing presence.
The participants cited several challenges associated with blood glucose monitoring. Notably, 30.9% of respondents highlighted pain during blood sampling as a major issue, while 26.1% mentioned the inconvenience of the process, and 16.0% identified the high cost of consumables as a concern. The psychological stress associated with routine monitoring and the financial burden associated with the high cost of consumables are significant barriers to effective diabetes management.
Demand for Non-Invasive Solutions
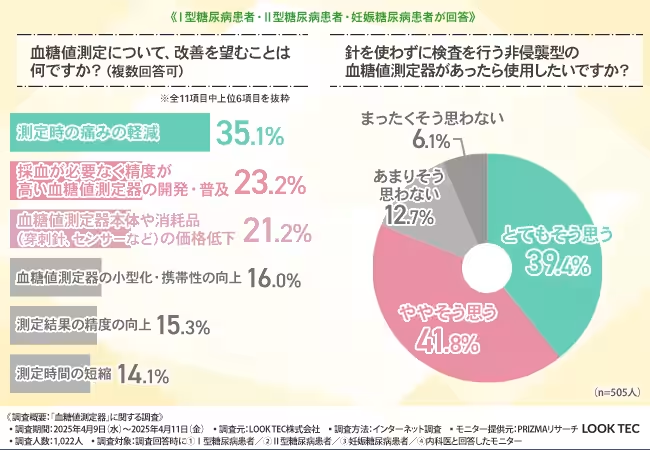
When asked about desired improvements in blood glucose monitoring, a significant majority expressed a desire for pain reduction during testing (35.1%) and the development of accurate, needle-free devices (23.2%). The findings underscore a clear demand for innovations that can alleviate the discomfort and challenges tied to current monitoring methods.
An impressive 81.2% of participants indicated that they would be willing to use a non-invasive blood glucose monitoring device if made available. This highlights the importance of reducing physical discomfort and mental stress linked with regular glucose testing. The idea of eliminating the need for needles resonates powerfully with patients as it not only lessens physical burden but also addresses psychological hurdles.
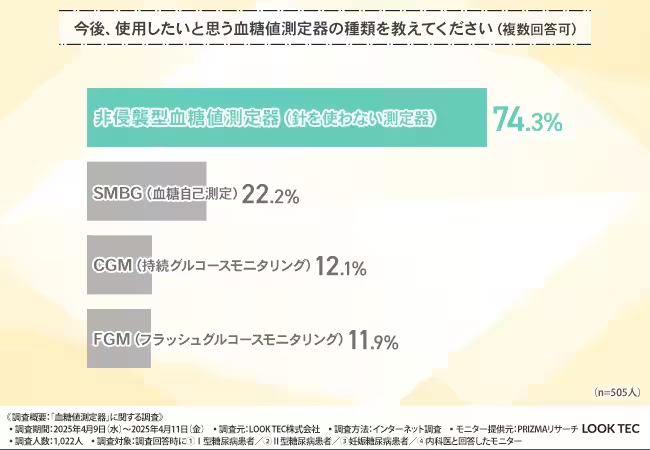
In terms of future preferences, 74.3% indicated a preference for non-invasive blood glucose meters, solidifying the trend towards a less intrusive approach to monitoring.
Insights from Internal Medicine Doctors
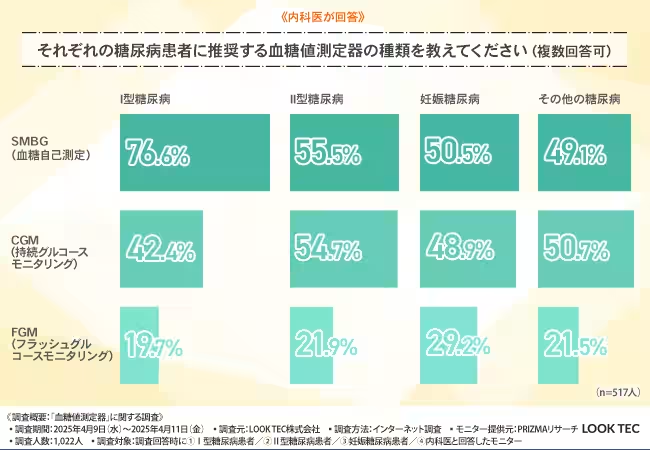
While patients largely favor non-invasive devices, the perspectives of internal medicine doctors play a vital role in understanding the dynamics of blood glucose monitoring. The doctors surveyed were asked about the devices they recommend for diabetes patients. For Type 1 diabetes patients, 80% recommended SMBG, given its reliability. However, for patients with other forms of diabetes, there was a more balanced support for both SMBG and CGM, suggesting that the choice of device often varies based on individual patient needs and treatment plans.
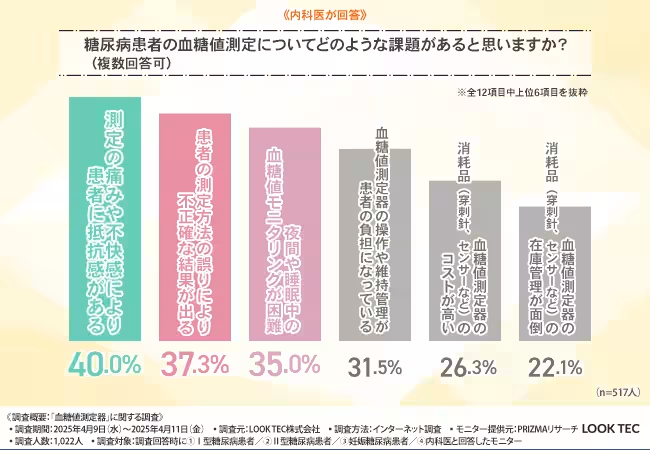
Doctors also noted several key challenges that they perceive exist in blood glucose monitoring. These included patient resistance stemming from pain or discomfort during testing (40.0%), inaccuracies due to improper measurement techniques (37.3%), and difficulties in monitoring glucose levels during night or sleep hours (35.0%).
The Future of Blood Glucose Monitoring
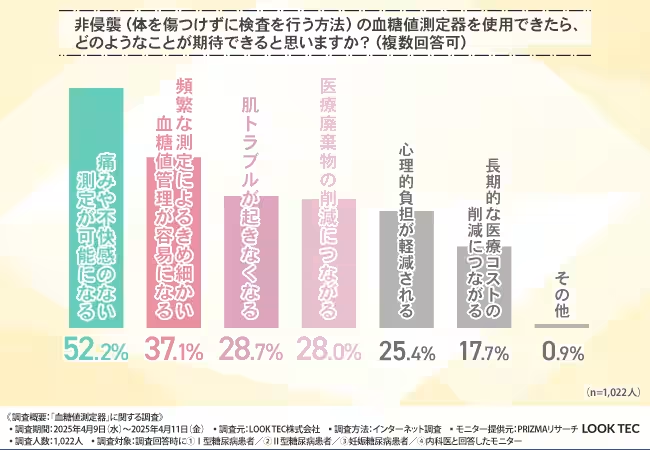
The survey concluded with anticipations regarding non-invasive blood glucose monitoring. Over 52.2% of internal medicine professionals believe that non-invasive methods could potentially eliminate pain and discomfort, while 37.1% noted that frequent measurements would allow for better day-to-day blood glucose management. Furthermore, 28.0% acknowledged that it could lead to reduced medical waste, aligning with wider environmental considerations in healthcare.
These insights highlight a profound opportunity for advancements in diabetes management. Addressing the multifaceted challenges patients encounter not only enhances personal health but could also lead to broader societal benefits. Emphasizing non-invasive solutions might indeed forge a new standard in diabetes care, ultimately improving the quality of life for patients and easing the burden on healthcare providers.
Conclusion: The Path Forward
This survey vividly illustrates the existing issues within blood glucose monitoring for diabetes patients. The call for non-invasive devices is not merely a matter of convenience; it reflects a pressing need for innovations that take into account both physical and psychological factors in daily management. As developers aim to meet these needs, it will be essential for them to listen to both the voices of patients and healthcare professionals alike, fostering a new era of diabetes care that prioritizes both efficacy and ease of use.
Topics Health)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.