

Analysis of Infection Rates and Healthcare Systems in Okayama Prefecture as of August 2025
Overview of COVID-19 Infection and Healthcare Analysis in Okayama Prefecture as of August 4, 2025
As of August 4, 2025, the Okayama University has actively monitored and reported on the COVID-19 situation within Okayama Prefecture, compiling data available on the prefectural government's website. Experts in the field, associated with Okayama University, have provided insightful comments to enhance the understanding of this evolving public health phenomenon. The analysis will be updated weekly to reflect the most current information.
The COVID-19 pandemic, declared over by the World Health Organization, has seen Japan gradually return to normalcy. However, understanding the specific situation regarding infections and healthcare systems in Okayama has become increasingly important. The data provided serves both as a reference for public health measures and as guidance for daily life, with an emphasis on preventive strategies.
Infection Trends and Healthcare System
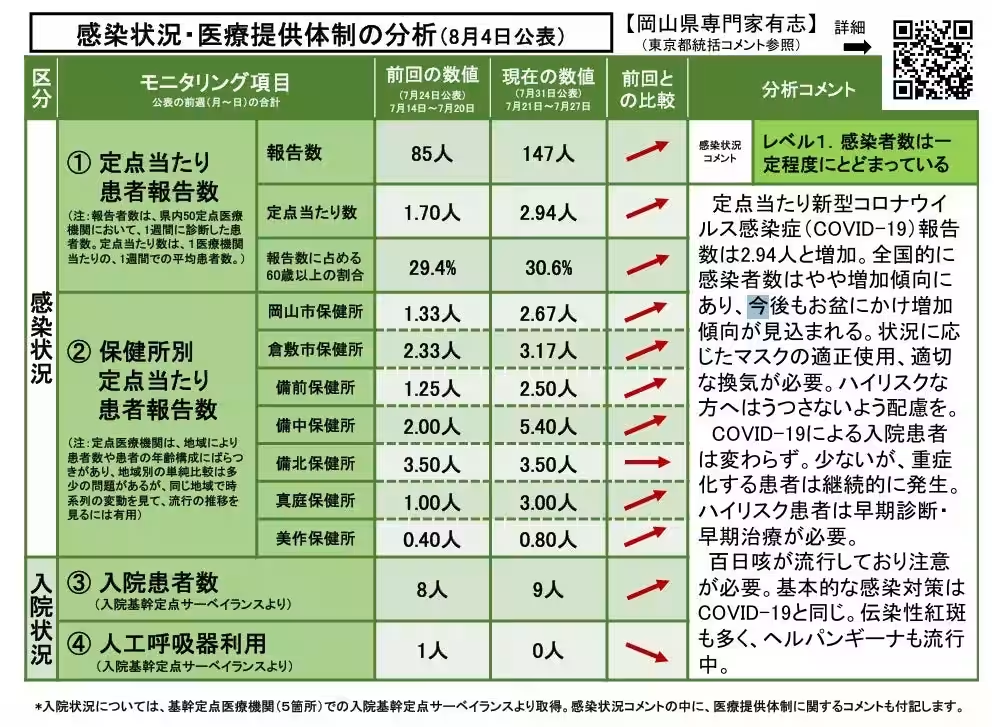
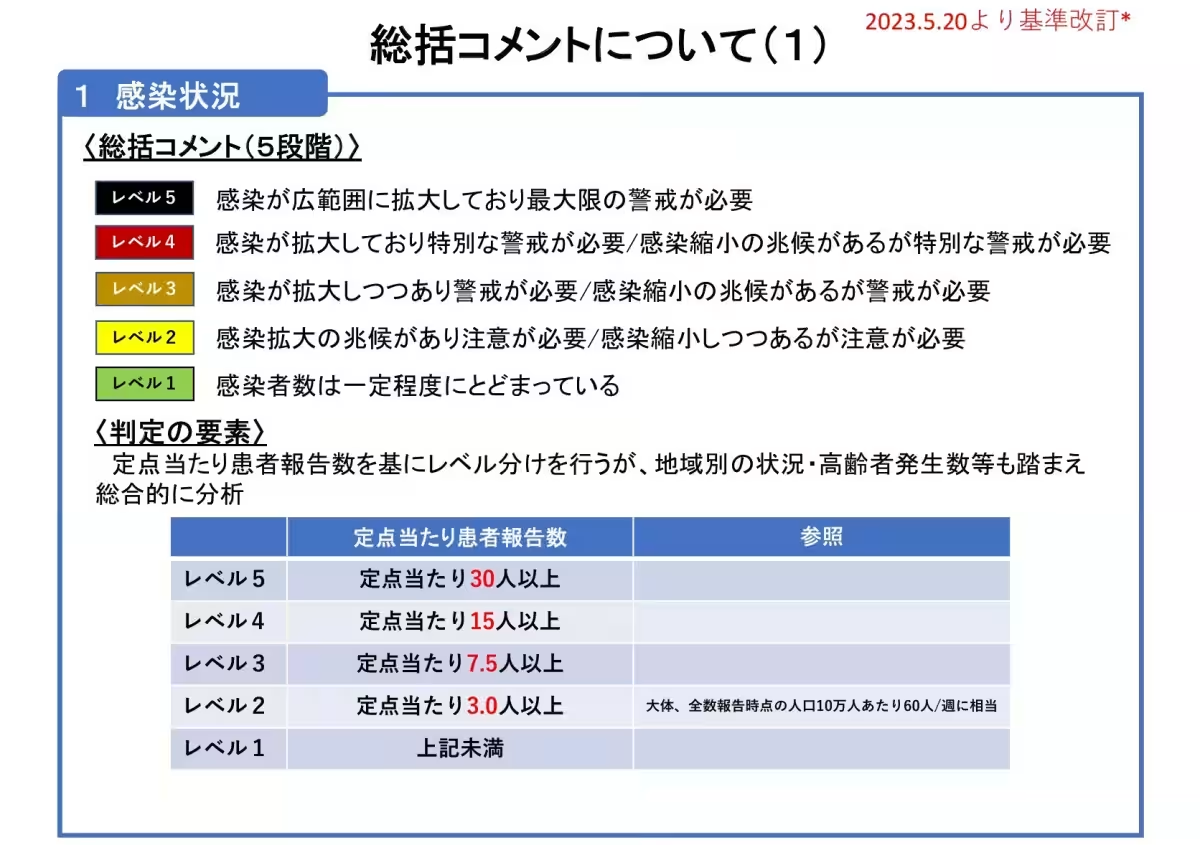
According to the latest report, the COVID-19 infection number per designated monitoring point has increased to 2.94, indicating a slight upward trend. Nationwide, cases are rising modestly, with expectations for continued increases as the summer holiday season, commonly referred to as Obon in Japan, approaches. Effective measures such as appropriate mask-wearing and ventilation are recommended, especially to protect those at higher risk from severe illness.
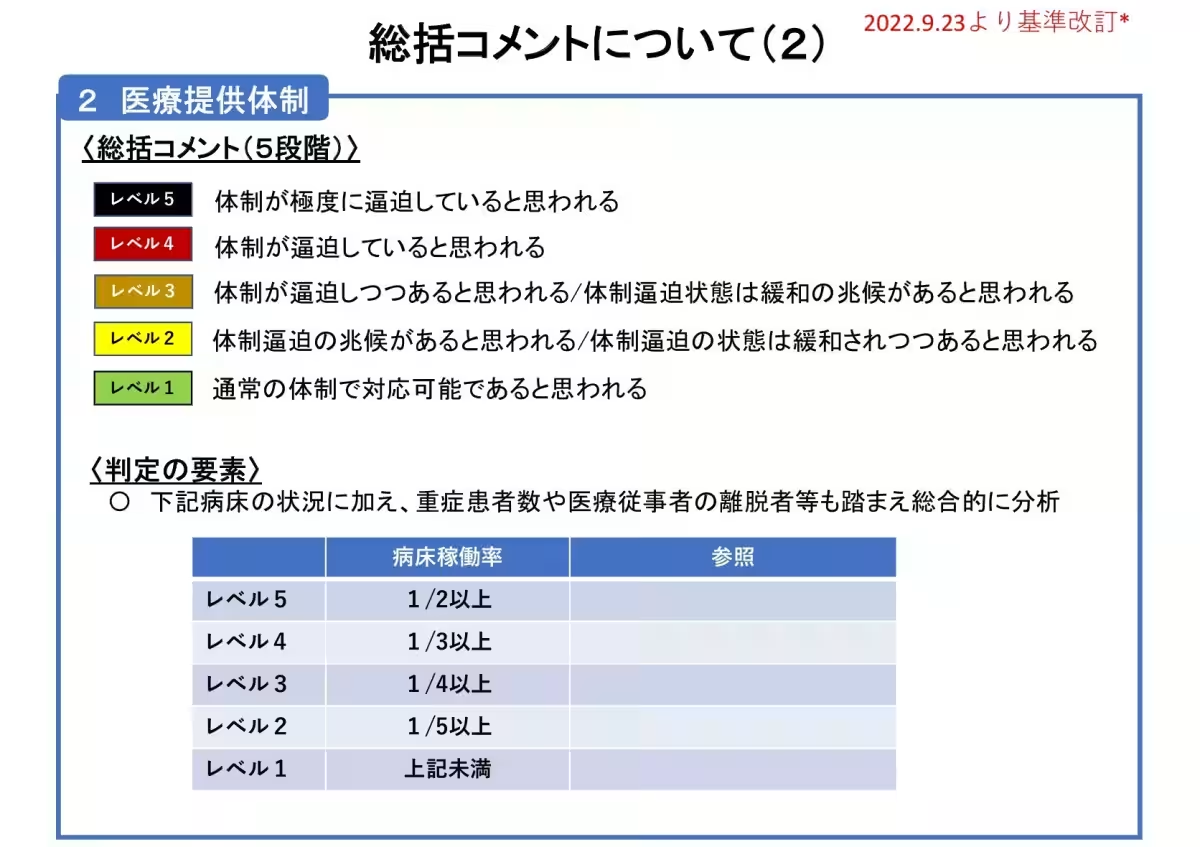
Currently, the number of hospitalized patients due to COVID-19 remains low; however, some high-risk patients continue to experience severe health complications. Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment for these patients are crucial. Notably, whooping cough is also on the rise, necessitating vigilance similar to COVID-19 preventive actions. Other ailments such as infectious erythema and hand-foot-and-mouth disease are also reported in the region, which highlights the need for ongoing vigilance against infections.
The Okayama University team, which includes notable experts such as Professor Takashi Yorito from Okayama University’s Graduate School of Medicine, Dentistry, and Pharmaceutical Sciences, and Dr. Hidehiro Hagiya from Okayama University Hospital, emphasizes the importance of accurate data collection, analysis, and timely communication to public health agencies and the community.
Weekly Updates
In alignment with the data presentation practices employed in Tokyo and other metropolitan areas, the Okayama Prefecture analysis is structured for easy understanding. Each report includes essential insights that can assist residents in comprehending the local healthcare landscape and the necessary precautions to take in their everyday lives, especially regarding COVID-19.
Regular updates provide the basis for a sustained dialogue surrounding infection prevention and foster a collective response to public health challenges. The collaboration between various healthcare professionals ensures a multifaceted approach to managing ongoing health threats.
For further information, please refer to the detailed reports and updates available through the following links:
The continuous flow of information and expert commentary aims to serve the community effectively, aiding public understanding of health risks associated with ongoing infectious disease patterns. Residents are encouraged to stay informed and adopt the necessary precautions to protect themselves and their families.
Conclusion
The situation in Okayama Prefecture illustrates the dynamic nature of the pandemic and highlights the importance of responsive healthcare strategies. The commitment of healthcare professionals, researchers, and educational institutions like Okayama University plays a vital role in effectively navigating these challenging times.








Topics Health)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.