
Transforming English Learning: The Impact of AI Collaboration on Student Outcomes
The Role of AI in Revolutionizing English Learning
In recent years, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in education has gained significant attention, especially in language acquisition. A remarkable advancement has been made by Mirai Translation Corp, which has collaborated with Ritsumeikan University to implement an AI-assisted English learning program. With over 900,000 users, their cloud-based AI translation system aims to enhance students' learning experiences through tools like FLaT, significantly impacting the quality of their English writing.
Study Overview
Starting in the autumn semester of 2022, this initiative harnessed AI technology to support approximately 5,000 undergraduate and graduate students at Ritsumeikan University. The focus was to explore how collaboration with AI influences learning processes and outcomes, as well as the psychological aspects of students. In 2024, they conducted two significant surveys targeting different student groups:
1. Undergraduate students in their first and second year, focusing on foundational skill development.
2. Graduate students delving deeper into specialized fields.
The findings were recently shared at the 2025 PC Conference held at Kagoshima University, where the relevance of AI in educational methodologies was discussed.
Research Highlights
Survey 1: The Impact of AI on English Composition
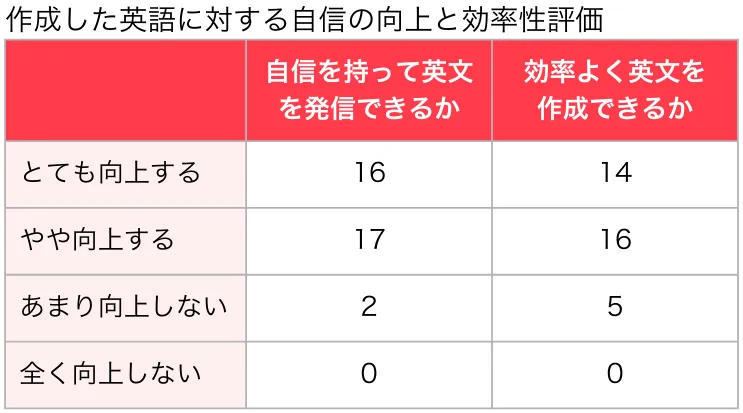
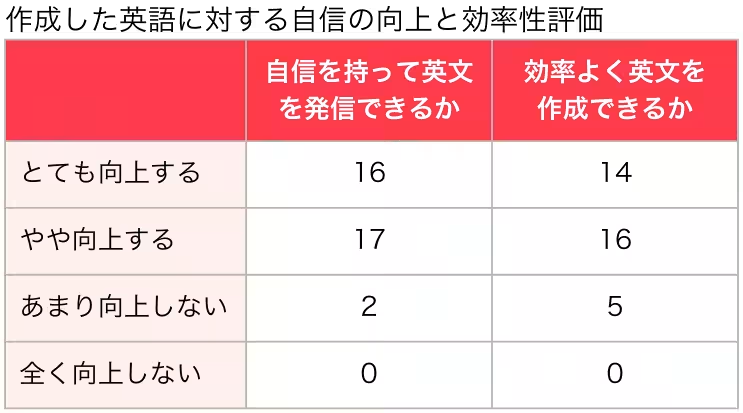
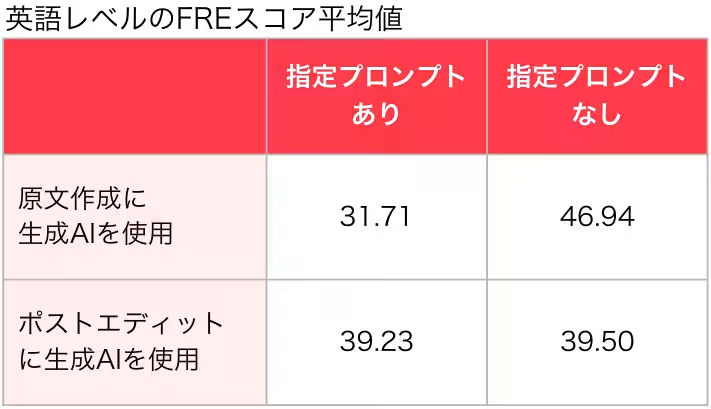
The first survey revealed noticeable differences based on how AI was utilized during English composition tasks. By generating Japanese texts and then applying AI translation, students experienced reduced completion times and enhanced writing quality, indicated by higher FRE scores.
Utilizing generative AI for post-editing didn’t show a direct effect on the quality of English output; however, it significantly boosted students' confidence. Even though it required additional time for post-editing, the willingness of students to invest that time reflected their desire to improve their writing quality.
Survey 2: Transforming Translations into Personal Voice
In the second survey involving graduate students, they leveraged AI-generated outputs to rework translations into their unique expressions. This process included pre-editing and post-editing with the AI serving as a collaborative partner, allowing students to refine their translations to reflect their expertise and personal insights.
It was fascinating to see how students chose their own final expressions while relying on AI for suggestions, demonstrating their growth in developing a personal voice in their academic work.
Implications for AI Collaboration in Education
The research underscores that the method of AI implementation can lead to distinct learning outcomes. The timing and type of AI utilized contribute to both the efficiency and improvement of textual quality, along with fostering student confidence. Moreover, students transforming AI-generated content into their own work showcases a deeper cognitive engagement than previously assumed, contradicting concerns about AI stunting intellectual growth.
To cultivate such productive learning experiences, simply integrating AI tools or teaching usage techniques is insufficient. Educators must design tasks relevant to students' interests and fields, encouraging them to incorporate their viewpoints into AI suggestions, thus enhancing the quality of their outputs.
Future Prospects
Mirai Translation plans to continue its collaborative research with Ritsumeikan University, further delving into educational methodologies that promote critical thinking and expression through AI partnerships. They aspire to remain a supportive technological partner in higher education, contributing to the advancement of this transformative approach in learning.
A special thanks to all involved from Ritsumeikan University without whose support this research could not have been achieved.
Research Background and Methods
AI translation and generative AI are based on the neural network “Transformer” model, but they differ in machine learning techniques and data training. The research aims to explore how these tools affect accuracy and psychology in language tasks among students. The methodology included a quantitative analysis of first- and second-year students and a qualitative analysis involving graduate students, focusing on their collaborative processes with AI throughout translation tasks.
By synthesizing these findings, this study highlights the promise of AI in fostering a more engaging and effective learning environment for students, paving the way for future advancements in educational technology.
Topics Other)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.