
Groundbreaking Achievement in Quantum Communication: Entanglement Swapping via Single Photons
Breakthrough in Quantum Communication
The National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT) has achieved a groundbreaking milestone by successfully demonstrating quantum entanglement swapping using sum-frequency generation between single photons. This marks the first time such a protocol has been applied globally, heralding a new era in quantum communication.
The Significance of the Achievement
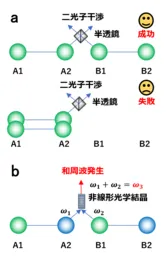
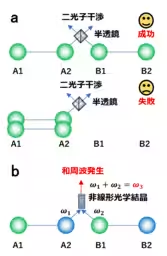
This achievement is significant for various reasons. Quantum entanglement is a fundamental element in the field of quantum information processing, facilitating secure communication and operations in quantum computing. In previous research, entanglement swapping typically utilized two-photon interference; however, that method had limitations regarding measurement processes that could reduce fidelity. Now, with NICT's high-performance technology, researchers overcame those hurdles using sum-frequency generation.
Quantum entanglement by single photons holds enormous potential. The use of nonlinear optical effects applied to single photons is a theoretical foundation for elevating quantum communication protocols but previously faced challenges in practical application due to low signal and high noise ratios. The newly integrated technologies employed by NICT created enormous improvements in these critical areas.
Components of the Research
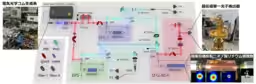
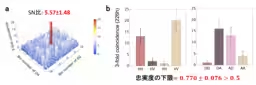
The research capitalized on several high-level techniques: ultra-fast quantum entangled light sources, low-noise superconducting single-photon detectors, and high-efficiency nonlinear optical crystals. These innovative elements enabled the successful confirmation of high signal-to-noise ratios when using sum-frequency generation among single photons.
These advancements resulted in the ability to confirm strong quantum entanglement without destroying the produced photonic pairs, thereby enhancing the feasibility of long-distance quantum key distribution and higher-fidelity operations.
Future Prospects
As quantum technologies continue to evolve, the implications of this research pave the way for the miniaturization and efficiency enhancement of optical quantum computing circuits. It is anticipated that further improvements in the signal-to-noise ratio will lead to greater capabilities in quantum protocols. Moreover, this could potentially lead to new and revolutionary nonlinear optical devices that capitalize on these findings.
This work foreshadows significant advancements in the field, as demonstrated through its publication in the esteemed journal Nature Communications on October 7, 2025.
Research Contributors
The successful outcomes of this groundbreaking work were made possible by an accomplished team of researchers, including Yoshiaki Tsujimoto, Kentaro Wakui, and others from the Future ICT Research Institute and Electromagnetic Waves Research Institute. Their synergy and expertise played a pivotal role in achieving this remarkable milestone.
Conclusion
In summary, NICT's successful demonstration of quantum entanglement swapping using single-photon techniques is a major leap forward in quantum communication. Not only does it validate theoretical protocols previously deemed difficult to realize, but it further opens up possibilities for enhanced quantum technologies that will shape the future of secure communication and computation.
This achievement joins the roster of pivotal advancements in quantum information science, holding promise for future innovations and applications. As researchers continue to refine these methods, the vision of an era dominated by quantum communication becomes an ever-closer reality.

Topics Consumer Technology)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.