
Check Point Research Reveals Most Active Malware of June 2025: AsyncRAT and FakeUpdates Dominate
In June 2025, Check Point Research released its latest Global Threat Index, shedding light on the most widespread malware threats globally. Among the findings, AsyncRAT, a Remote Access Trojan (RAT), now ranks as the third most prevalent malware. This malicious software exploits platforms like Discord to distribute harmful payloads, affirming its growing significance in the cyber threat landscape. Meanwhile, FakeUpdates continues to reign as the most widespread malware, affecting organizations worldwide.
Moreover, ransomware group Qilin has made headlines for targeting major enterprises, particularly in the healthcare and education sectors, adding to its notoriety within the realm of cybercrime.
As cybercriminal tactics become increasingly sophisticated, organizations must implement many-layered defense security solutions to proactively counter evolving threats. The June 2025 Global Threat Index underlines the urgency of adopting proactive measures to shield against cutting-edge sophisticated attacks.
Lotem Finkelstein, the Director of Threat Intelligence at Check Point, commented, "The emergence of AsyncRAT and the ongoing prevalence of FakeUpdates highlight the evolution of the complexities in cyberattacks. The rise of dominant ransomware groups like Qilin showcases a more targeted and sophisticated approach to data theft and encryption. Organizations must adopt real-time threat intelligence and comprehensive security strategies to defend effectively."
Key Findings:
1. AsyncRAT: Retaining a top position in threat rankings as of June 2025, AsyncRAT exploits trusted platforms to deliver payloads for data theft. With AsyncRAT, attackers can gain remote access and control over infected systems.
2. FakeUpdates: This downloader malware remains the most prevalent worldwide, linked to the hacking group Evil Corp, spreading through drive-by downloads to prompt users to install fake browser updates. It subsequently delivers various secondary payloads after infection.
3. RaaS (Ransomware as a Service) Group Qilin: This group continues targeting high-value sectors, especially healthcare and research organizations, using phishing emails to infiltrate networks and encrypt sensitive data.
In Japan, the leading malware in June was Androxgh0st, affecting 3.36% of businesses. Previously top-ranked FakeUpdates dropped to second place with a 1.81% impact, while AgentTesla climbed to the third spot with a 1.29% share.
Globally, FakeUpdates maintains its position as the most active malware, impacting 4% of organizations, followed by Androxgh0st at 3% and AsyncRAT at 2%.
Among the leading ransomware groups, Qilin stood out in June, accounting for 17% of reported attacks, followed by Akira at 9% and Play at 6%.
In mobile malware, Anubis leads with its ability to bypass multi-factor authentication and steal banking credentials, often distributed through malicious apps available on the Google Play Store. Following Anubis are AhMyth, an Android RAT disguised as legitimate apps, and Hydra, a banking Trojan requesting dangerous permissions to infiltrate banking applications.
In June, the education and research sector remained the most targeted globally, followed by government entities and telecommunications. These industries are particularly vulnerable due to their critical infrastructure and extensive user bases.
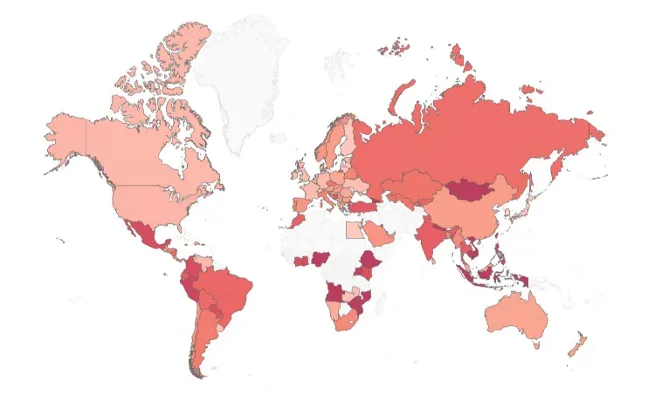
The global risk map indicates that malware activity is intensifying in regions such as Eastern Europe and Latin America, especially with infections related to FakeUpdates and Phorpiex. Asian countries like Nepal and Vietnam have seen increased attacks involving Remcos and AgentTesla, while Spain and France have reported surges in infections from Lumma info-stealer and Raspberry Robin.
In summary, the June 2025 Global Threat Index reveals a rising tide of multi-layered malware campaigns and the increasingly sophisticated tactics of groups like Qilin. While FakeUpdates remains a dominant threat, an urgent response to other malicious actors like AsyncRAT and Qilin ransomware is critical. Organizations in education, government, and telecommunications continue to face notable vulnerabilities, emphasizing the necessity for comprehensive and proactive security measures in the evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats.
For the full report and further insights on the June 2025 Global Threat Index, visit Check Point Research’s blog.
Moreover, ransomware group Qilin has made headlines for targeting major enterprises, particularly in the healthcare and education sectors, adding to its notoriety within the realm of cybercrime.
As cybercriminal tactics become increasingly sophisticated, organizations must implement many-layered defense security solutions to proactively counter evolving threats. The June 2025 Global Threat Index underlines the urgency of adopting proactive measures to shield against cutting-edge sophisticated attacks.
Lotem Finkelstein, the Director of Threat Intelligence at Check Point, commented, "The emergence of AsyncRAT and the ongoing prevalence of FakeUpdates highlight the evolution of the complexities in cyberattacks. The rise of dominant ransomware groups like Qilin showcases a more targeted and sophisticated approach to data theft and encryption. Organizations must adopt real-time threat intelligence and comprehensive security strategies to defend effectively."
Key Findings:
1. AsyncRAT: Retaining a top position in threat rankings as of June 2025, AsyncRAT exploits trusted platforms to deliver payloads for data theft. With AsyncRAT, attackers can gain remote access and control over infected systems.
2. FakeUpdates: This downloader malware remains the most prevalent worldwide, linked to the hacking group Evil Corp, spreading through drive-by downloads to prompt users to install fake browser updates. It subsequently delivers various secondary payloads after infection.
3. RaaS (Ransomware as a Service) Group Qilin: This group continues targeting high-value sectors, especially healthcare and research organizations, using phishing emails to infiltrate networks and encrypt sensitive data.
Domestic Malware Trends
In Japan, the leading malware in June was Androxgh0st, affecting 3.36% of businesses. Previously top-ranked FakeUpdates dropped to second place with a 1.81% impact, while AgentTesla climbed to the third spot with a 1.29% share.
- - Androxgh0st (3.36%): A Python-based malware scanning public .env files for sensitive login credentials related to AWS, Twilio, Office 365, and SendGrid services. By identifying Laravel-based websites via a botnet, it extracts confidential data, allowing attackers to deploy additional malware, establish backdoor connections, and exploit cloud resources for cryptocurrency mining.
- - FakeUpdates (1.81%): This malware targets users with fake browser update prompts and is associated with Evil Corp, spreading via drive-by downloads from infected websites.
- - AgentTesla (1.29%): A sophisticated RAT functioning as a keylogger and info stealer, it collects keystrokes, monitors system keyboards, captures screenshots, and extracts credentials through various software such as Google Chrome and Microsoft Outlook.
Global Malware Activity
Globally, FakeUpdates maintains its position as the most active malware, impacting 4% of organizations, followed by Androxgh0st at 3% and AsyncRAT at 2%.
Among the leading ransomware groups, Qilin stood out in June, accounting for 17% of reported attacks, followed by Akira at 9% and Play at 6%.
- - Qilin: A top ransomware group, Qilin focuses on large enterprises, especially in healthcare and education, constituting 17% of attacks in June 2025.
- - Akira: Emerging in early 2023, Akira represents 9% of ransomware activities, exploiting vulnerabilities at VPN endpoints.
- - Play: Continuing to pose a severe threat, Play is linked to 6% of ransomware incidents, targeting organizations via compromised valid accounts and unpatched vulnerabilities, including Fortinet SSL VPN.
Mobile Malware Insights
In mobile malware, Anubis leads with its ability to bypass multi-factor authentication and steal banking credentials, often distributed through malicious apps available on the Google Play Store. Following Anubis are AhMyth, an Android RAT disguised as legitimate apps, and Hydra, a banking Trojan requesting dangerous permissions to infiltrate banking applications.
Industry Threats
In June, the education and research sector remained the most targeted globally, followed by government entities and telecommunications. These industries are particularly vulnerable due to their critical infrastructure and extensive user bases.
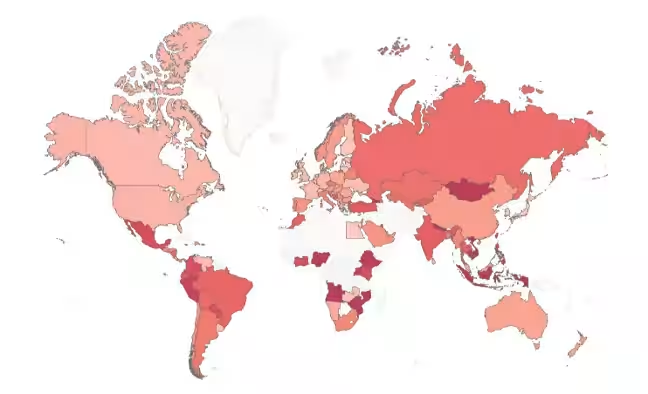
The global risk map indicates that malware activity is intensifying in regions such as Eastern Europe and Latin America, especially with infections related to FakeUpdates and Phorpiex. Asian countries like Nepal and Vietnam have seen increased attacks involving Remcos and AgentTesla, while Spain and France have reported surges in infections from Lumma info-stealer and Raspberry Robin.
In summary, the June 2025 Global Threat Index reveals a rising tide of multi-layered malware campaigns and the increasingly sophisticated tactics of groups like Qilin. While FakeUpdates remains a dominant threat, an urgent response to other malicious actors like AsyncRAT and Qilin ransomware is critical. Organizations in education, government, and telecommunications continue to face notable vulnerabilities, emphasizing the necessity for comprehensive and proactive security measures in the evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats.
For the full report and further insights on the June 2025 Global Threat Index, visit Check Point Research’s blog.

Topics Other)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.