

Analysis of Infection Trends and Medical Response in Okayama University as of December 2025
Analysis of Infection Trends and Medical Response
As of December 30, 2025, Okayama University has released an analysis regarding the COVID-19 infection status and healthcare response in Okayama Prefecture. Utilizing data published on the prefecture's official website about patient reports and healthcare provisions, the university has compiled relevant figures and provided insightful commentary from a group of experts in the region. Regular updates will be issued weekly to keep the public informed.
Notably, this report draws upon the analysis of the latest monitoring items from Tokyo's authorities, presenting a clear visual representation to aid understanding. With the World Health Organization declaring an end to the pandemic, and society gradually returning to normal, it remains essential for residents to stay informed about the infection status and preventive measures.
Current Infection Status and Medical Response
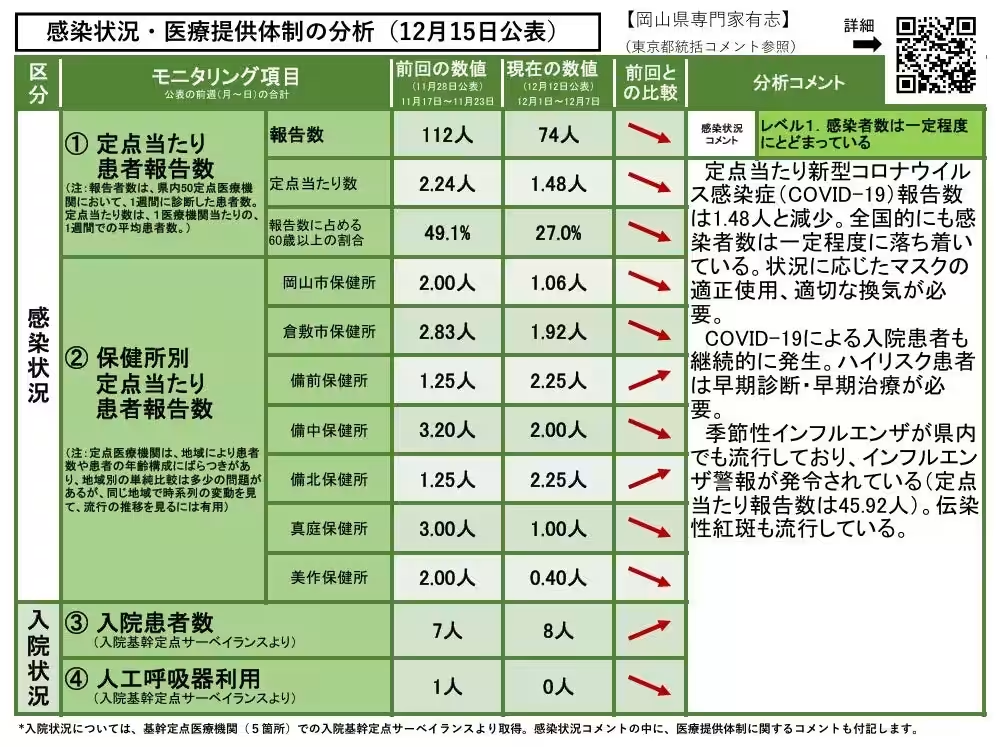
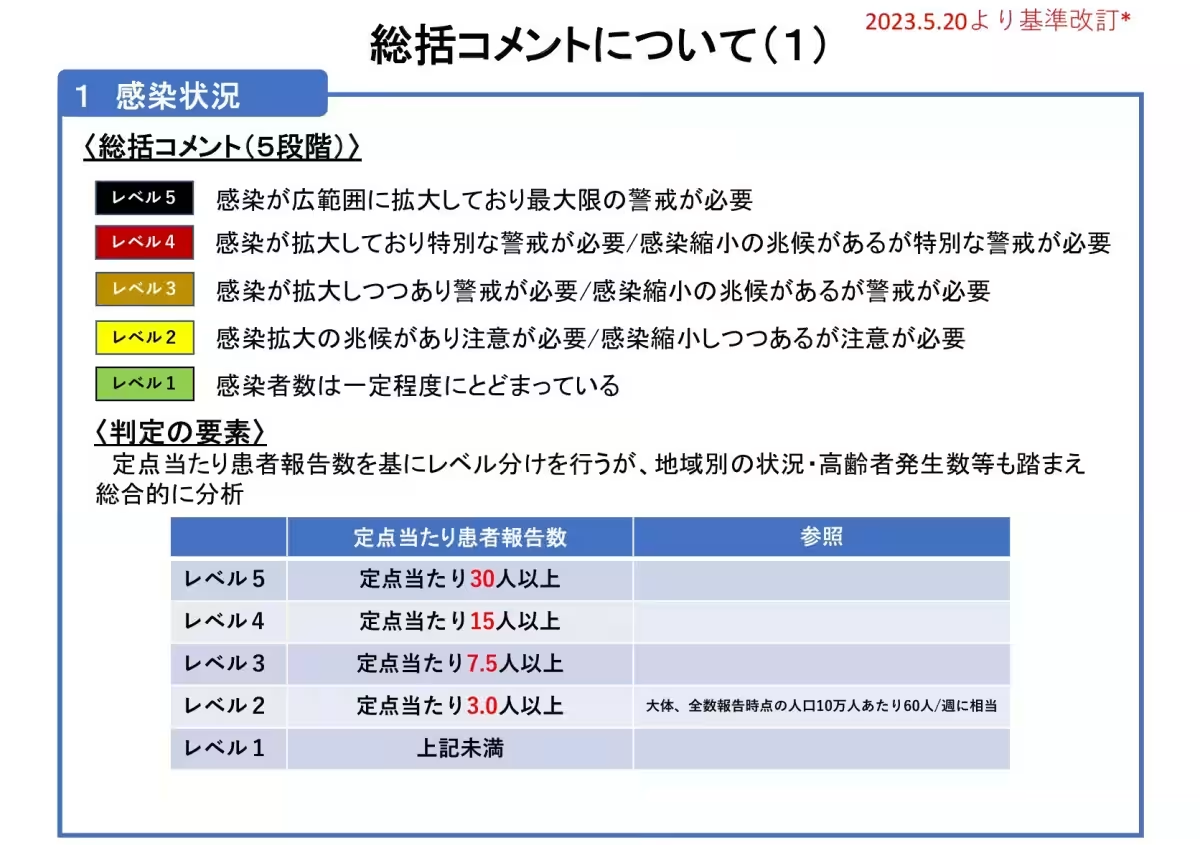
As of December 15, 2025, the analysis rates the infection level in Okayama Prefecture as Level 1, which indicates that the number of infections is remaining steady. The reported figure shows an average of 1.48 new COVID-19 cases per designated observation point, indicating a decrease in reported cases. This trend aligns with a national pattern where infections are also stabilizing.
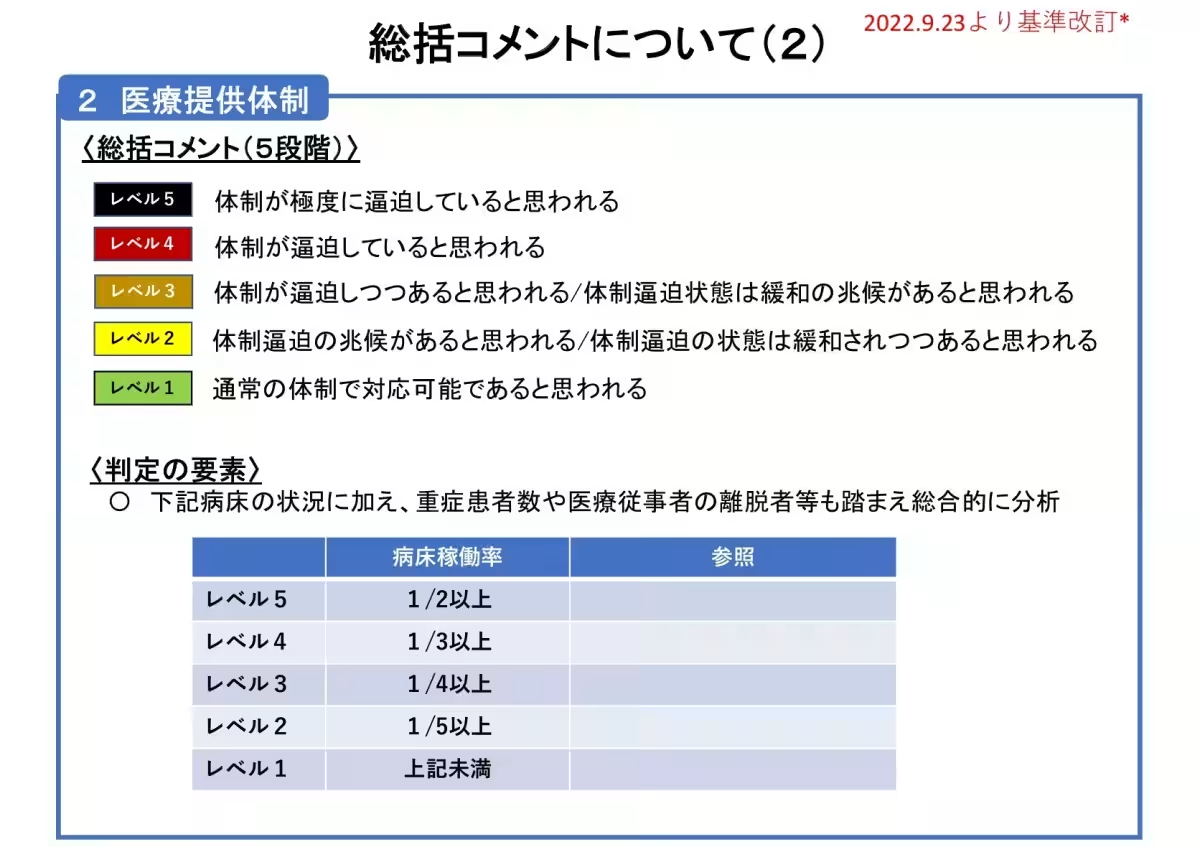
However, hospitalizations due to COVID-19 continue to occur, particularly among high-risk patients who require prompt diagnosis and treatment. The seasonal flu is also circulating within the prefecture, with an influenza alert issued, reporting a significant increase in cases at 45.92 per designated monitoring point. Additionally, cases of infectious erythema are on the rise.
In light of these circumstances, experts continue to emphasize the importance of appropriate mask usage and adequate ventilation in public spaces to mitigate the spread of the virus. The local healthcare system is actively engaged in monitoring and responding to these infection trends.
Expert Contributions
The commentary and analysis included in the report are provided by a dedicated group of experts from Okayama University. This group includes:
- - Takashi Rai, Professor at Okayama University's Graduate School of Medicine, Dentistry, and Pharmaceutical Sciences, specializing in epidemiology and public health.
- - Hidetaka Hagiya, Internal Medicine and General Practice specialist at Okayama University Hospital.
- - Koji Fujita from Tsuyama Central Hospital, specializing in Internal Medicine and Infectious Diseases.
- - Yasunori Ichimura from the National Center for Global Health and Medicine.
- - Daisuke Yoshioka from Kawasaki Medical University’s Department of Clinical Infectious Diseases.
The collaboration among these specialists aims to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the infection status and the overall healthcare response in Okayama. They hope the information provided serves as a resource for individuals and families in making informed decisions regarding their health and safety.
In conclusion, the ongoing analysis and reporting by Okayama University highlight the institution's commitment to public health and safety, particularly in navigating the challenges posed by COVID-19 and seasonal infections. Residents are encouraged to stay vigilant and adhere to recommended safety practices to protect themselves and their communities.
Additional Resources
For more information, individuals can access numerous references including earlier reports on infection trends and healthcare strategies, along with guidelines and updates from the Okayama University website. Continuous efforts to communicate relevant health data reflect the university's dedication to enhancing public safety through research and community engagement.
By staying informed and practicing appropriate preventive measures, the community can collectively work towards maintaining health and safety in the face of ongoing public health challenges.








Topics Health)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.