
The Rise of Cyber Attacks in 2025: Insights from the NICTER Observation Report
Overview of NICTER Observation Report 2025
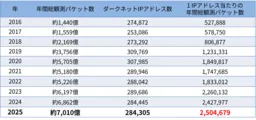
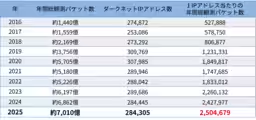
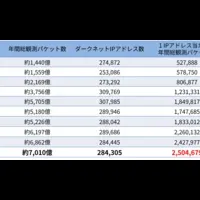
The National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT) has just released its latest findings in the NICTER Observation Report 2025. According to this report, a historic amount of cyber attack-related communications has been recorded since the beginning of dark web monitoring, totaling approximately 701 billion packets. This marks an increase of about 2.2% compared to the previous year. Despite only a minor rise in the packets observed per IP address, the pervasive level of exploration and preparatory attacks seen across the internet remains alarming.
Key Findings
Surge in Cyber Attack Communications
The data captured by NICT's large-scale dark web monitoring network reveals that the number of attack-related communications has reached unprecedented levels. The recording of about 701 billion packets in 2025 demonstrated a significant amount of activity, averaging around 2.5 million packets per IP address for the year.
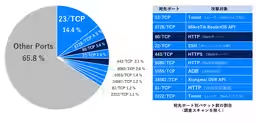
This uptick in communication highlights ongoing trends in internet scanning activities and preparatory steps for attacks, which are now standard operational procedures for many malicious actors. Approximately 55% of these packets were believed to be scanning communications, indicating that reconnaissance activities are still a major concern even as the percentage dropped slightly from the prior year.
Evolving IoT Threat Landscape
In recent years, attacks focused on Internet of Things (IoT) devices have escalated, diverging from the previously prevalent Mirai botnet. The NICTER report recognizes a significant rise in the number of IoT devices infected by alternative botnets. Notably, a bot known as RapperBot has reportedly compromised around 60,000 global devices by 2025. The report sheds light on the increasing sophistication of such threats, where the infected devices often go unnoticed by users, particularly household routers and surveillance equipment.
In a related note, following the indictment of RapperBot's operators by the U.S. Department of Justice in August 2025, communications from these attackers' command servers ceased, suggesting that law enforcement actions are having an impact.
DRDoS Attacks and Frequency Changes
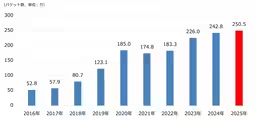
Distributed Reflective Denial of Service (DRDoS) attacks also showed a notable surge in 2025. Approximately 82.85 million such attacks were globally registered, including around 900,000 targeted at Japan alone. This signifies a significant rise from approximately 30.95 million global attacks in 2024, with winter carpet-bombing attacks becoming increasingly common. The data also suggests that fewer services are being exploited for these attacks, indicating a possible trend towards more streamlined and efficient attack methods.
Future Outlook
As the number of continually connected IoT devices continues to rise, experts predict that widespread scanning and IoT bot infections will remain persistent threats. NICT intends to leverage the insights garnered through NICTER's continuous observations to raise awareness about such threats within the community and guide appropriate countermeasures. Furthermore, through collaboration with CYNEX, a nexus point for academia, industry, and government in cybersecurity, NICT will bolster information sharing and research.
Related Links
For more information and detailed analysis, please visit the following resources:
The report not only highlights the escalation of cyber attacks but underscores the urgency of reinforcing cybersecurity measures across various sectors as we look to the future.

Topics Policy & Public Interest)









【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.