
Check Point Research Reveals Major Cyber Threats for September 2025
Major Cyber Threats Report for September 2025
Check Point Research (CPR), the threat intelligence division of Check Point Software Technologies, has unveiled its Global Threat Intelligence Report for September 2025. This report highlights significant trends and risks in the cyber threat landscape that organizations need to address.
Despite a slight decrease in the overall number of cyberattacks worldwide, ransomware attacks and data risks associated with generative AI have skyrocketed to unprecedented levels. On average, organizations faced approximately 1,900 cyberattacks weekly, which reflects a 4% decrease from August, yet signifies a 1% increase compared to the same month last year. Although total attack numbers appear stable, the evolving attack methodologies and rapidly expanding risks associated with generative AI indicate that the threat environment is becoming increasingly complex and dynamic.
Education and Research Sector Hit Hardest
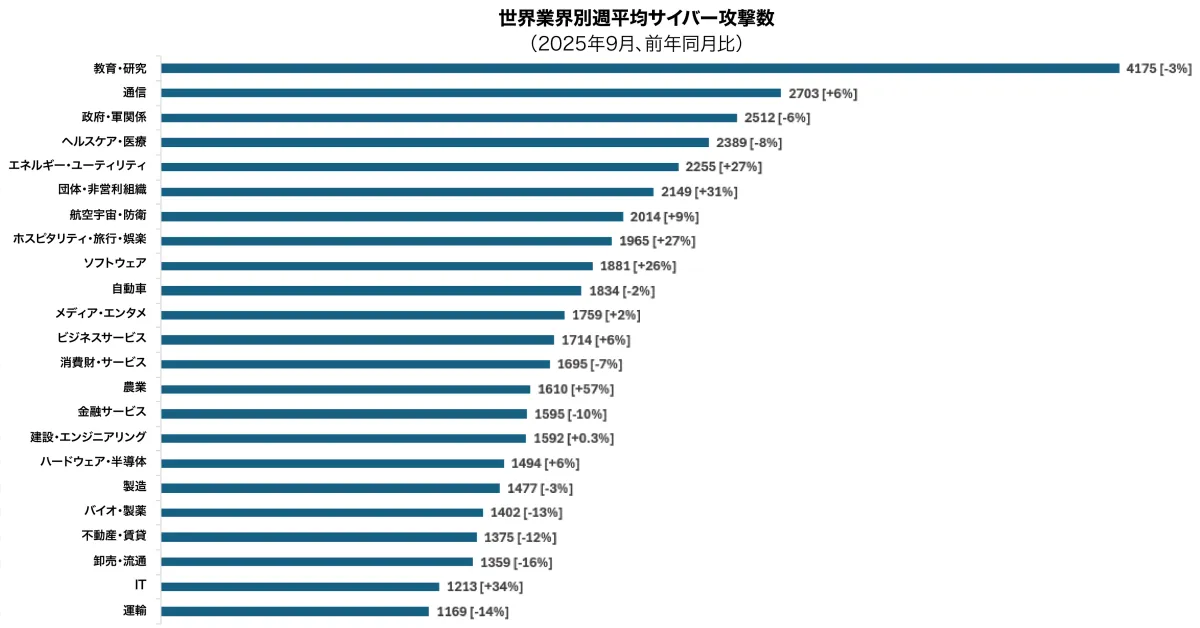
In September 2025, the education and research sector was the most targeted industry, suffering an average of 4,175 attacks per organization weekly. While this represents a 3% decrease year-over-year, it remains substantially higher than any other sector. The telecommunications industry followed, experiencing a 6% increase year-over-year with an average of 2,703 attacks weekly. Government agencies came in third, with an average of 2,512 attacks per week, marking a 6% reduction from the previous year.
These trends demonstrate that industries holding vast amounts of data and requiring persistent service provision remain primary targets for cybercriminals. With environments now integrating hybrid work, cloud solutions, and legacy systems, continuous attacks exploit the heavy reliance on digital infrastructure and the flow of sensitive data.
Regional Insights on Cyber Threats
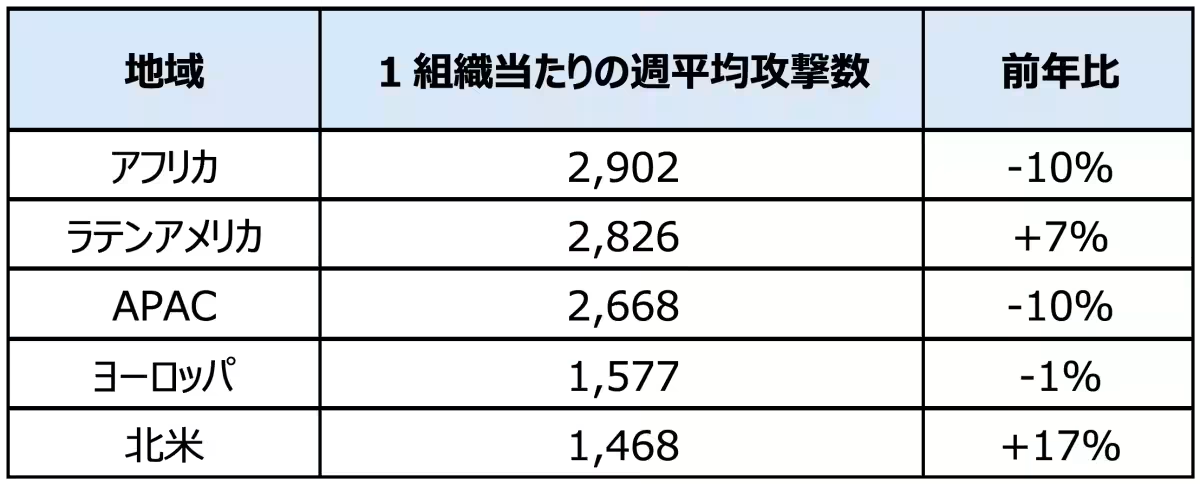
Regionally, Africa persisted in hosting the highest average attack numbers but noted a 10% year-on-year decrease, with organizations experiencing an average of 2,902 attacks weekly. Latin America closely followed with an average of 2,826 attacks (up 7% year-over-year), while the Asia-Pacific region saw a 10% drop, down to 2,668 attacks.
Europe recorded an average of 1,577 weekly attacks (down 1% year-on-year), whereas North America exhibited the most significant increase, with a total of 1,468 attacks (up 17% from the previous year). This data indicates a growing regional polarization; while some areas experienced temporary decreases, others, particularly North America, faced a resurgence of sophisticated ransomware attacks and data extortion.
Increasing Data Risks Linked to Generative AI
With the growing incorporation of generative AI into corporate workflows, new attack vectors related to data breaches have emerged. In September, 1 in 54 prompts from company networks posed a high risk of leaking sensitive data, affecting 91% of organizations that frequently use generative AI tools. Furthermore, 15% of all prompts contained potentially sensitive information, including customer data and internal communications.
This situation underscores the urgent need for governance and security management concerning generative AI adoption. Insufficient protective measures could lead to major increases in data security risks, undermining productivity gains.
Escalation of Ransomware Activity
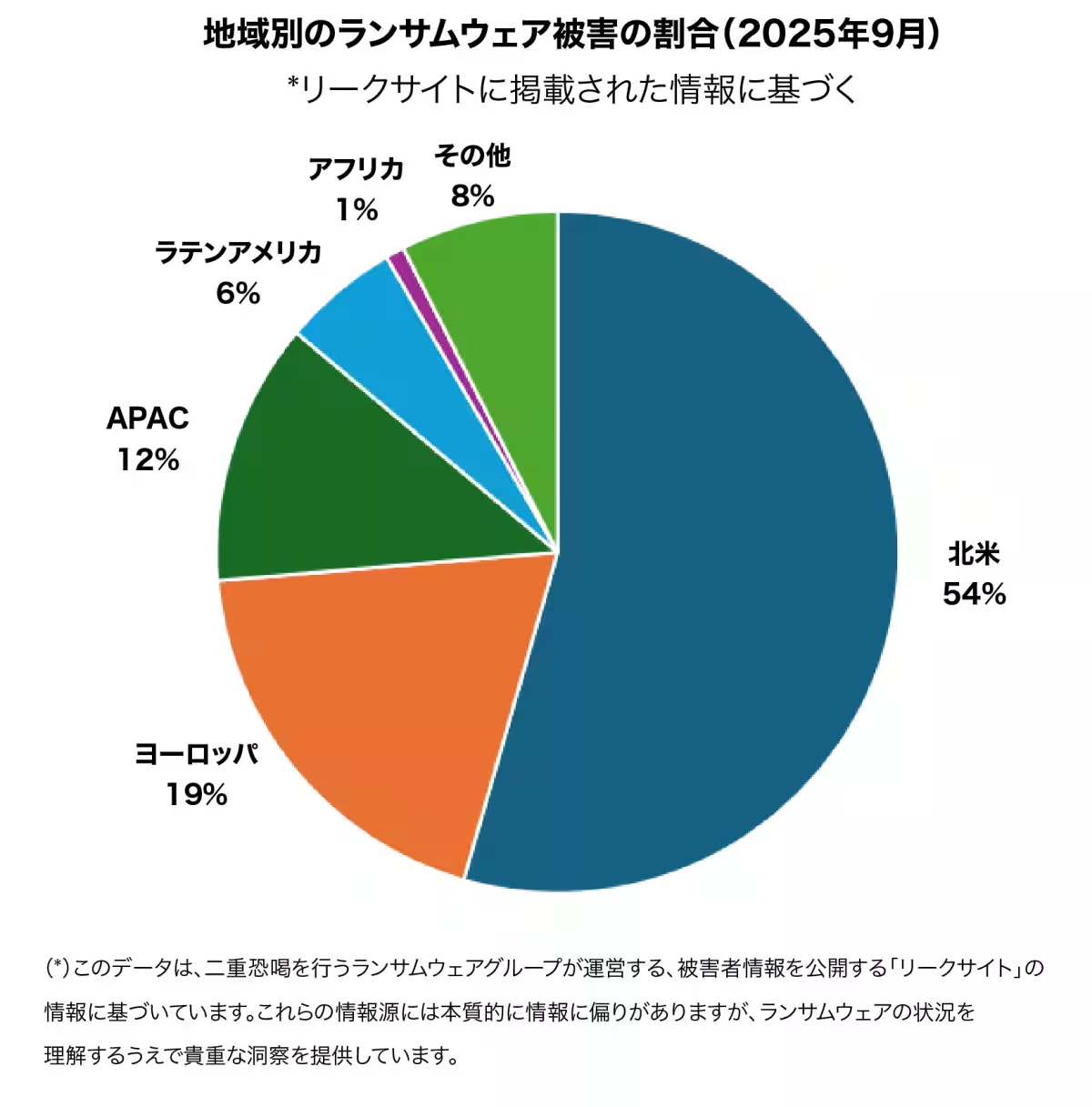
September witnessed a significant surge in ransomware activity, with a reported 562 incidents, marking a staggering 46% increase year-on-year. North America was the most affected region, accounting for 54% of reported incidents, followed by Europe at 19%. The United States alone represented 52% of total incidents, with South Korea, the United Kingdom, and Germany trailing at 5%, 4%, and 4%, respectively.
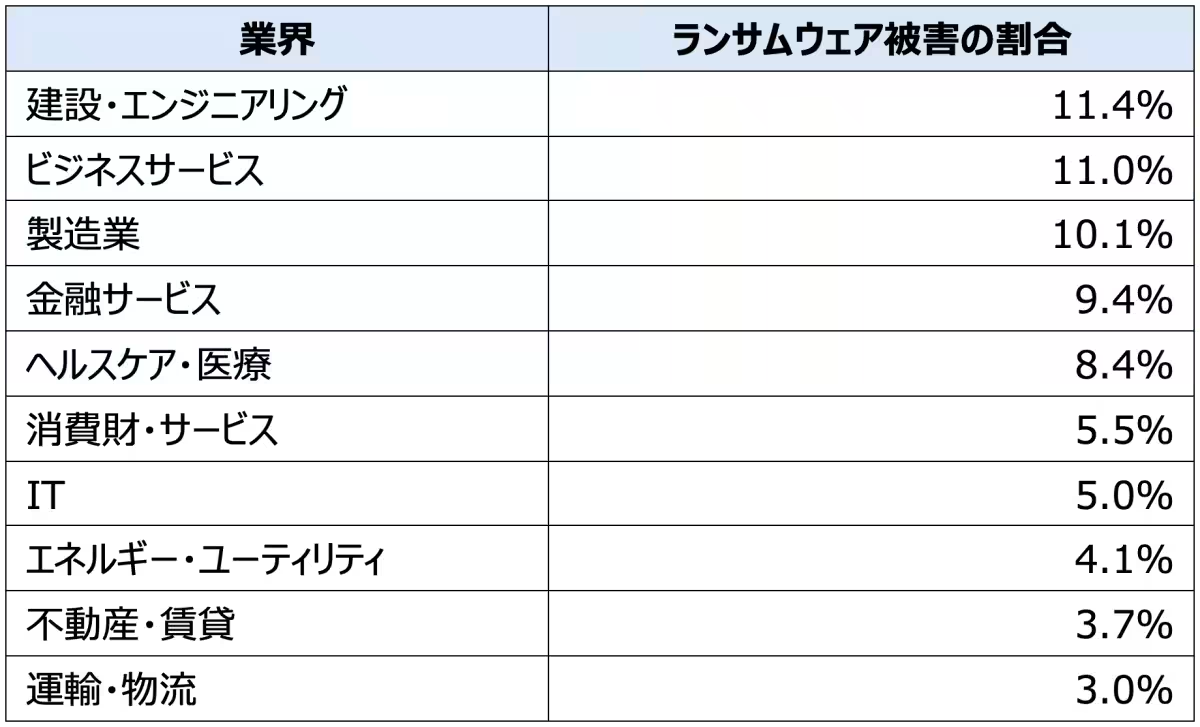
In terms of industries affected by ransomware, construction and engineering led, comprising 11.4% of reported cases. Business services followed closely with 11% and manufacturing represented 10.1%. Other crucial sectors such as financial services (9.4%), healthcare (8.4%), and consumer goods (5.5%) remained significant targets, reflecting continued diversification in ransomware activities.
Notable Ransomware Groups
Recent insights from threat actor leak sites highlight several prominent ransomware groups:
1. Qilin (14.1%) - One of the leading RaaS groups, constantly publishing victim data since 2022. After the cessation of RansomHub, Qilin expanded its network by utilizing Rust-based encryption tools and advanced RaaS panels for affiliated organizations.
2. Play (9.3%) - Also known as PlayCrypt, this group targets organizations in North and South America and Europe, exploiting unpatched vulnerabilities, particularly in Fortinet’s SSL VPN, while evading detection using LOLBin techniques.
3. Akira (7.3%) - Active since early 2023, Akira’s Rust-based variant now targets Windows, Linux, and ESXi systems, focusing on business services and manufacturing and using runtime control to obscure detection and analysis.
These groups illustrate a professionalized RaaS model, showcasing a rapid expansion of operations spurred by quick tool development.
Conclusion
The insights from this report highlight that while total attack incidents appear relatively stable, enhancements in attack techniques and a widening array of targeted sectors and regions are evident. The 46% surge in ransomware activity, along with increasing risks associated with generative AI, particularly against educational, manufacturing, and critical infrastructure sectors, emphasizes the urgent need for organizations to fortify their defenses.
Check Point’s research continues to illustrate the complexities and rapid pace of today’s cyber threats, necessitating multilevel defenses. Conventional detection methods are inadequate; real-time and proactive security measures that can thwart attacks before they occur are crucial.
Looking forward, it is imperative for all organizations to adopt a prevention-first posture, leveraging advanced threat intelligence to ensure robust defenses across their environments, from on-premises to the cloud and endpoints. Only by staying ahead of attackers can effective risk mitigation and long-term cyber resilience be achieved.
Topics Other)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.