
Revolutionary Dye-Sensitized Optoelectronic Synapses for Next-Gen Machine Vision
Revolutionary Dye-Sensitized Optoelectronic Synapses for Next-Gen Machine Vision
In a significant breakthrough in machine vision systems, researchers from the Faculty of Advanced Engineering at Tokyo University of Science, led by Associate Professor Takashi Ikuno, have developed cutting-edge dye-sensitized optoelectronic synapses. This transformative device operates without the need for an external power source, marking a leap towards low-power, self-sustaining vision technologies.
Overview of the Development
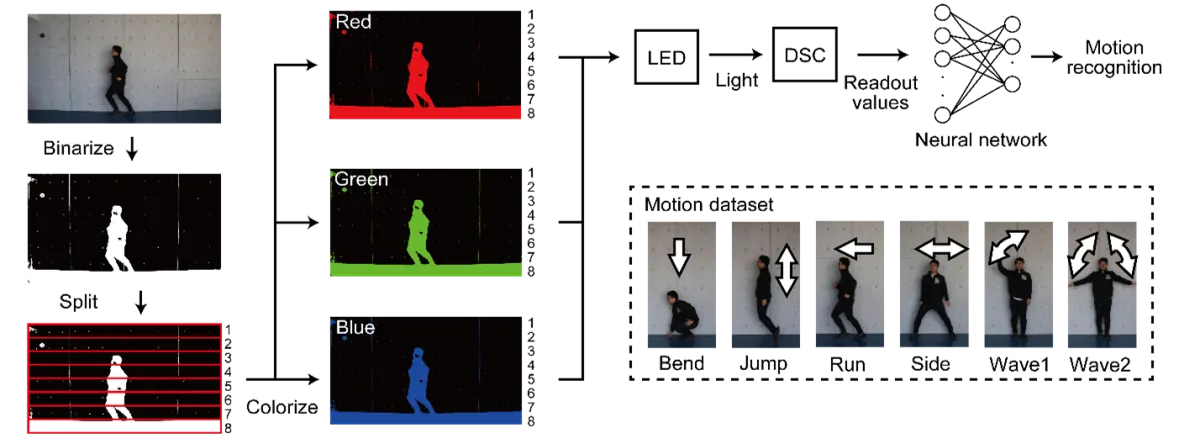
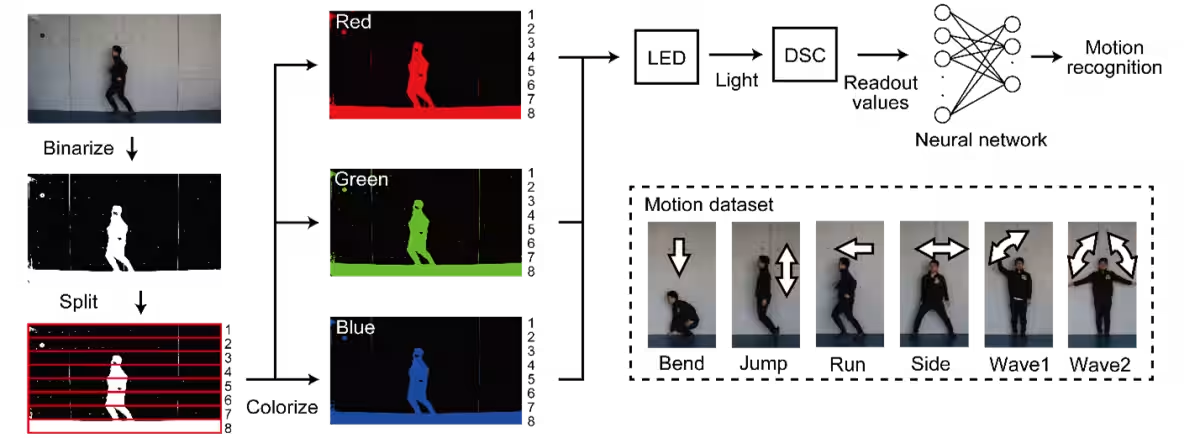
The innovative synapse mimics the functional characteristics of biological synapses in the human brain. This allows it to respond sensitively to light stimuli, with output properties that change gently while retaining past information. By combining two types of dye-sensitized solar cells, the researchers have demonstrated the ability of the device to differentiate color responses based on the wavelength of visible light.
Moreover, by incorporating this device as a reservoir layer in a physical reservoir computing model, the team validated its capability for high-precision visual processing tasks, such as color identification and pattern recognition. These advancements are anticipated to propel the evolution of next-gen machine vision technologies, which are essential for driving innovations in autonomous vehicles, surveillance systems, and smart agriculture.
Addressing Traditional Machine Vision Limitations
Traditional machine vision systems face challenges such as high power consumption and substantial processing speed limitations due to the need for real-time handling of massive visual data. The newly developed synapse operates independently of external power by harnessing the energy from light itself, allowing it to process visual information efficiently without the burden of extensive energy requirements. It possesses the unique ability to identify multiple colors with varying response characteristics from a single element.
This breakthrough opens up avenues for the development of ultra-low power AI vision devices that can support next-generation electric vehicle autonomous driving features and the construction of edge AI systems that integrate sensing and processing capabilities.
The research was published online on May 12, 2025, in the esteemed journal Scientific Reports.
Background of the Research
The demand for sophisticated machine vision technology in areas like autonomous driving, smart agriculture, and surveillance has notably increased. Conventional systems process large amounts of image data by collecting them into memory before undergoing complicated processing and analysis, resulting in high energy consumption and data transfer burdens.
To address this, there has been a rising interest in
Topics Consumer Technology)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.