

Exploring the 2025 Survey Results on Nurses' Work Conditions and Satisfaction
Overview of the Survey
The 2025 Nurses' Work Conditions Survey, conducted by SMS Co., Ltd., examined the opinions of 9,304 nurses across Japan regarding their work environments and satisfaction levels. This survey marks the fourth iteration since its inception in 2021, aiming to provide valuable insights into the evolving landscape of nursing.
Key Findings
1. Job Satisfaction
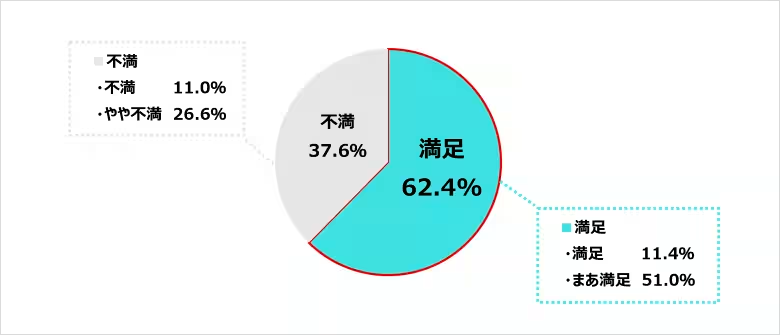
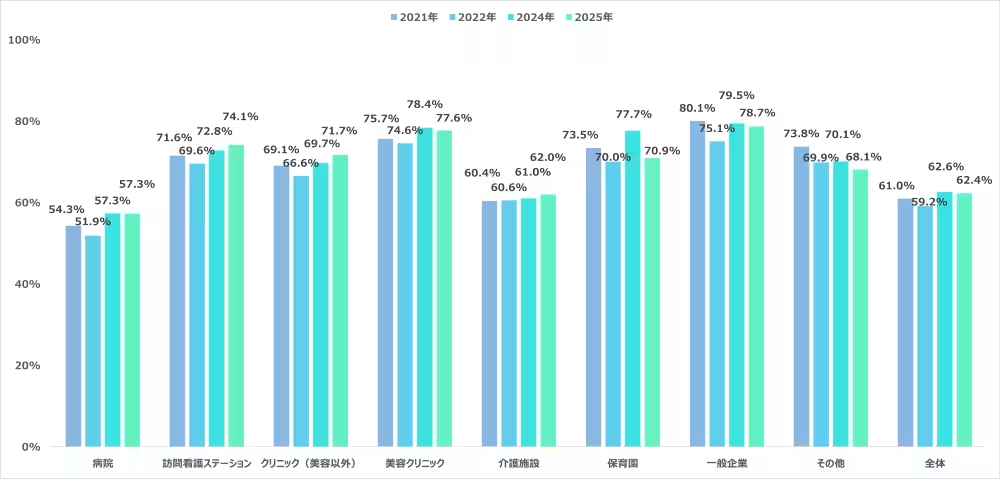
An encouraging 62.4% of nurses expressed satisfaction with their workplaces. Although overall satisfaction levels remained consistent over the years, there are notable improvements in satisfaction rates among nurses in clinics, home-visit nursing stations, and care facilities.
2. Factors Contributing to Satisfaction and Dissatisfaction
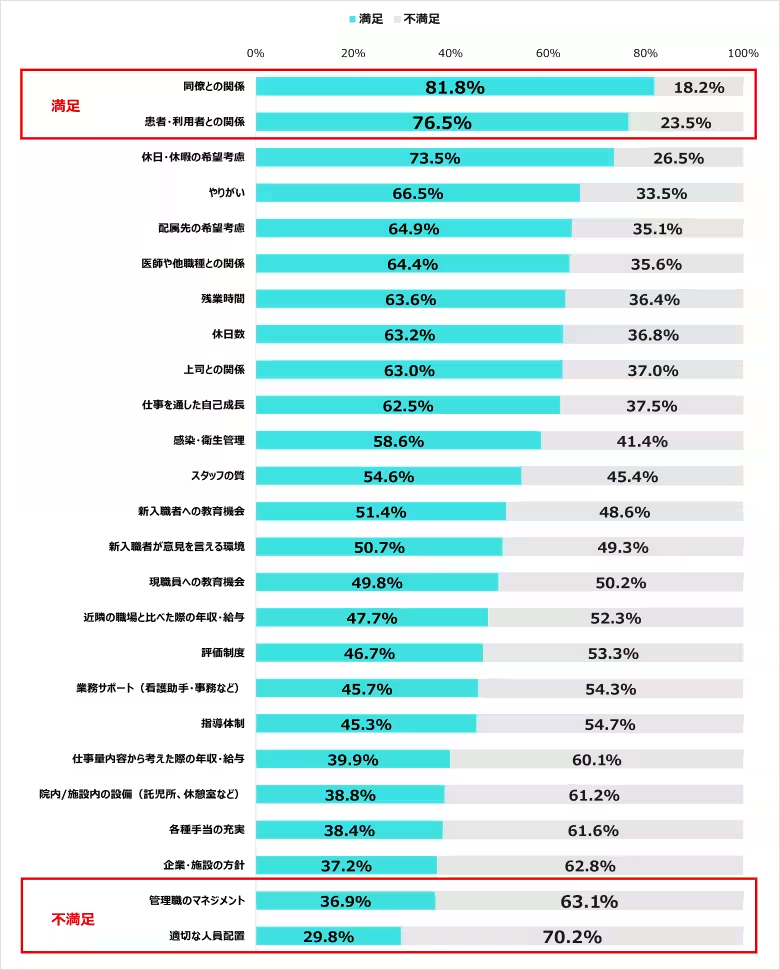
The top positive aspects of current roles included relationships with colleagues (81.8%) and patients (76.5%). Conversely, significant dissatisfaction stemmed from issues like appropriate staff allocation (70.2%) and management practices (63.1%). These findings echoed results from previous surveys, highlighting ongoing issues within organizational structures.
3. Reasons for Leaving Previous Jobs
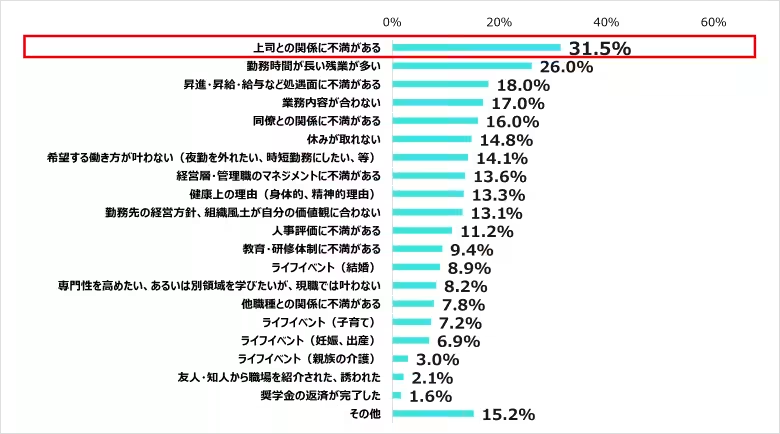
One prominent reason leading to past resignations was dissatisfaction with relationships with supervisors, reported by 31.5% of former nurses. This number has risen slightly compared to earlier surveys, indicating a growing concern over management relationships in nursing.
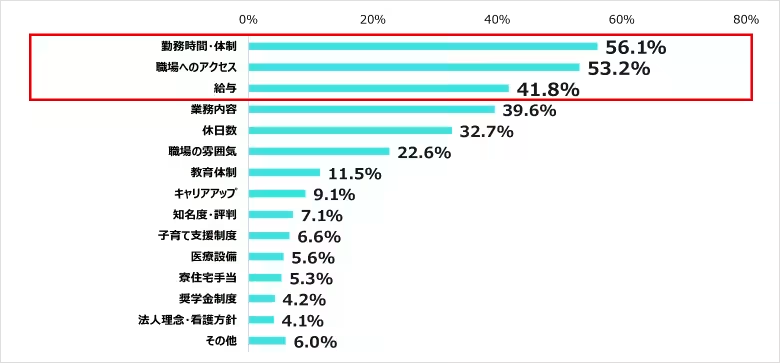
4. Key Considerations in Job Selection
When selecting workplaces, nurses prioritized factors such as work hours (56.1%), workplace accessibility (53.2%), and salary (41.8%). These rankings have remained consistent across all four surveys, indicating their importance in workplace decision-making.
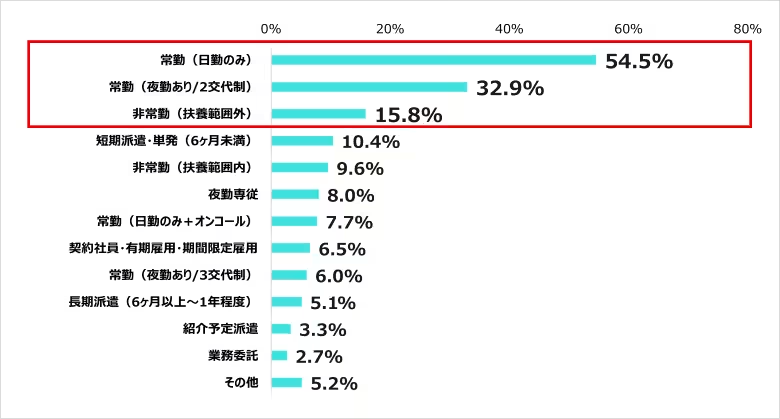
5. Preferred Employment Types Post-Transition
Among those contemplating career changes, most preferred full-time positions with only daytime shifts (54.5%), followed by full-time roles that included night shifts (32.9%). Compared to last year's data, there was a slight uptick in interest for full-time night shift positions, likely influenced by rising living costs.
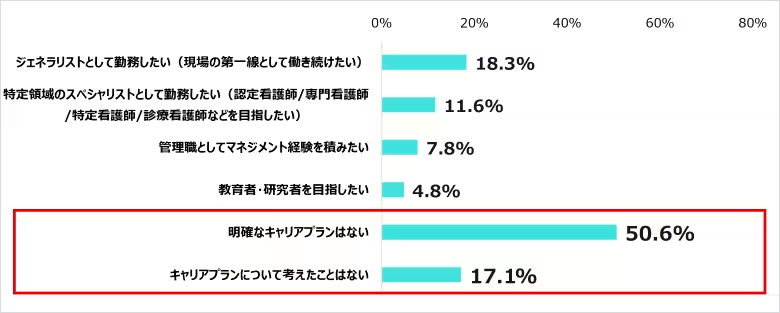
6. Career Planning Perspectives
A significant portion of respondents (50.6%) indicated they do not have a clear career plan. However, the desire to remain a generalist and work actively in nursing saw a modest increase. This suggests a trend towards maintaining the status quo, despite the absence of structured planning.
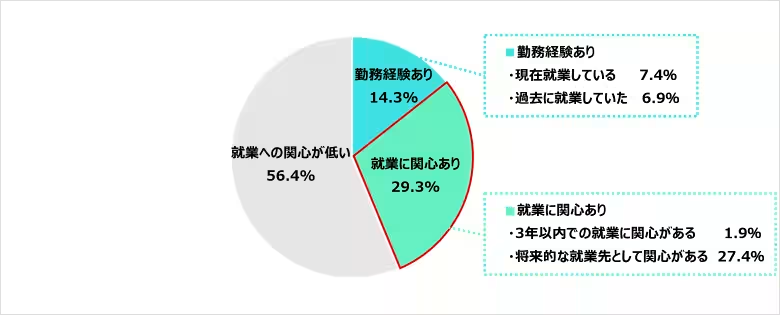
7. Interest in Home-Visit Nursing
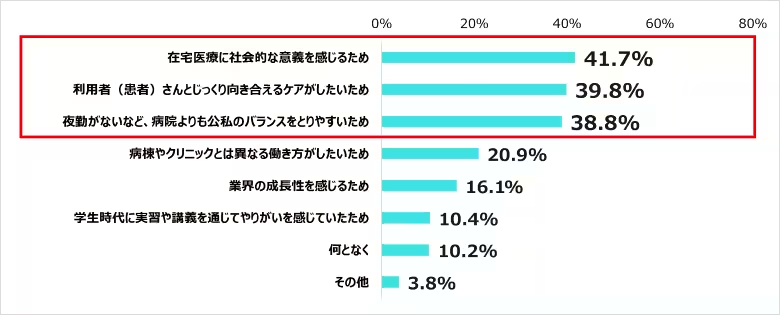
About 29.3% of surveyed nurses expressed interest in future employment at home-visit nursing stations. The primary reasons include recognizing the societal value of home care (41.7%), the opportunity to provide more individualized care (39.8%), and a better work-life balance compared to hospital settings (38.8%).
8. ICT Adoption in Nursing
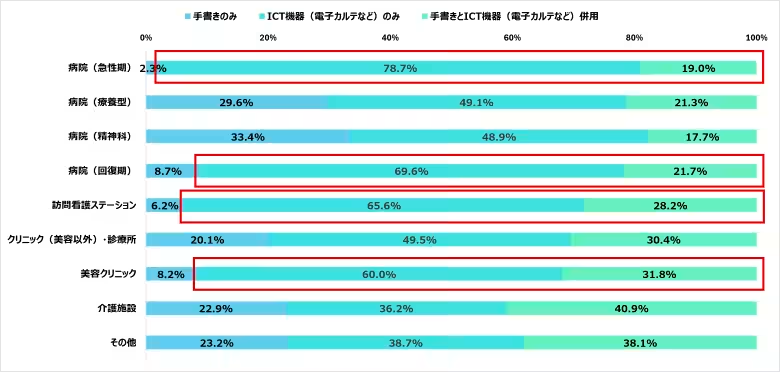
ICT integration is on the rise, with 97.7% of acute care hospitals adapting electronic nursing record systems, while figures remain high in home-visit nursing stations (93.8%) and cosmetic clinics (91.8%).
9. Positive Aspects of ICT Implementation
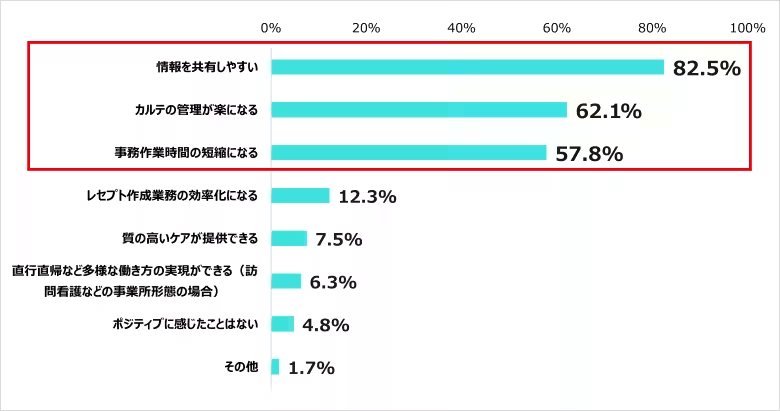
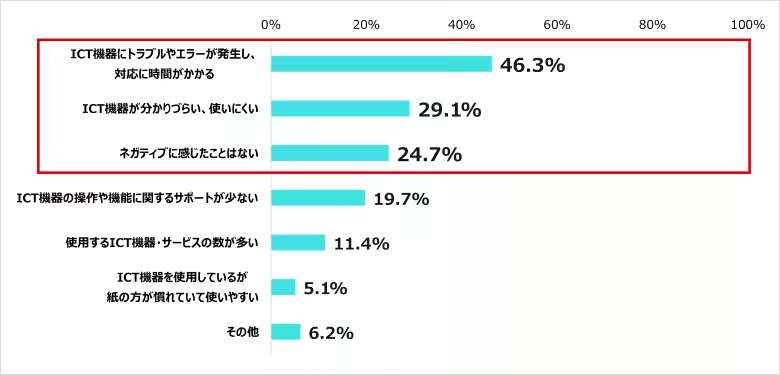
Nurses reported several benefits of ICT in their work, with ease of information sharing (82.5%), simplified management of patient records (62.1%), and decreased administrative workload (57.8%) being the most cited advantages. However, 46.3% of nurses expressed concerns regarding technical issues with ICT equipment causing delays.
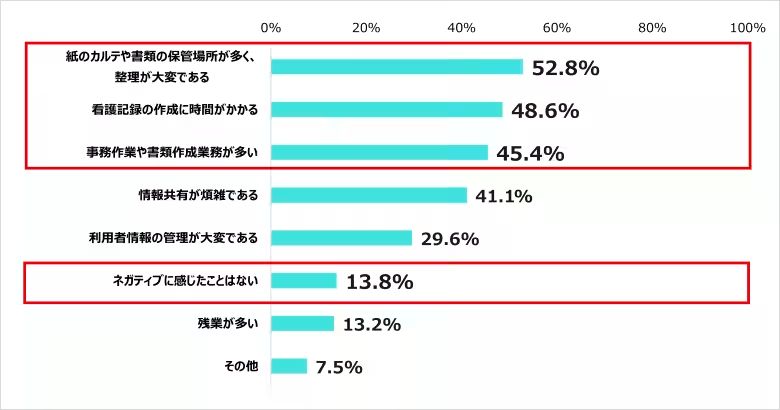
10. Challenges with Handwritten Records
Despite technology advancements, a significant portion of nurses still manage handwritten records, citing issues like organizing various documents (52.8%) and lengthy record creation times (48.6%). Only a small percentage (13.8%) felt there were no drawbacks to maintaining paper records.
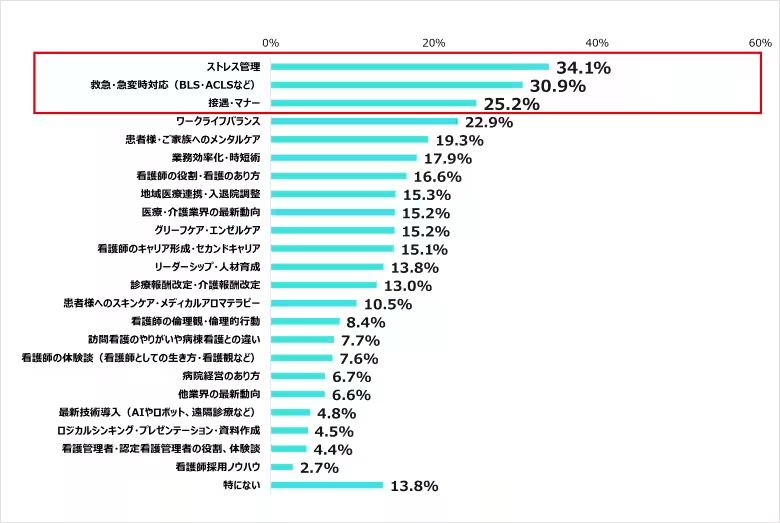
11. Desired Training Opportunities
Nurses expressed a strong interest in training focused on stress management (34.1%), followed by emergency response training (30.9%), and enhancing interpersonal skills (25.2%). This highlights a need for ongoing professional development to support their mental health and relationship management within teams.
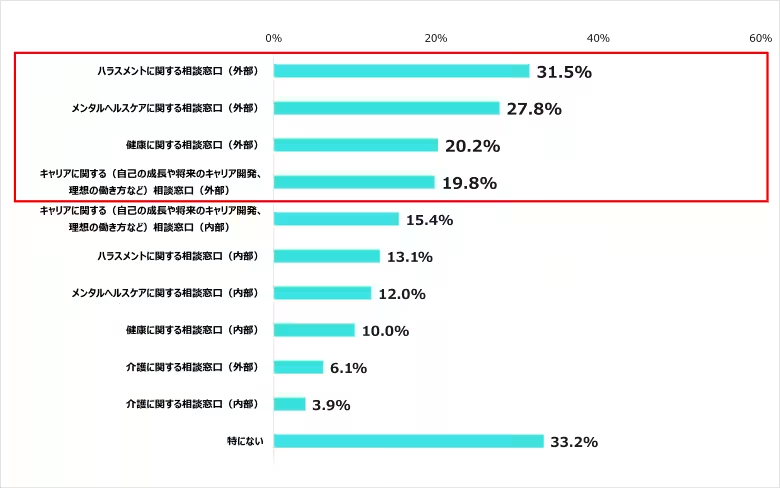
12. Support Services Needed
External support services were also emphasized, with a demand for harassment advisory services (31.5%), mental health support (27.8%), and health consultation services (20.2%). The majority of nurses prefer external support, suggesting limitations in existing internal resources.
Conclusion
The 2025 Nurses' Work Conditions Survey sheds light on several critical areas in nursing, including job satisfaction, desired support, and emerging trends. Regular monitoring of these metrics will be essential to addressing challenges within the workforce and improving the overall experience of nurses in Japan. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, understanding these dynamics will provide valuable resources for optimizing nursing practices and ensuring the well-being of staff as they contribute vital services to the community.

Topics Health)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.