
Check Point Research Reveals Key Cybersecurity Trends for 2026
Overview of Cyber Security Report 2026
Check Point Research (CPR), the threat intelligence division of Check Point Software Technologies, has unveiled its latest findings in the "Cyber Security Report 2026". This report reviews the cyber environment of 2025, indicating significant changes in how adversaries operate. Through a comprehensive analysis of cyberattacks over the past year, it illustrates how attackers have collaborated and expanded their reach in enterprise environments.
Key Findings
The report highlights the emergence of several prominent trends, including the adoption of AI-driven attacks, ransomware evolvement, and advanced hybrid environments. Notably, these attacks have transcended isolated incidents and evolved into organized campaigns that leverage a mix of AI, identity exploitation, and human factors at speeds that outpace many existing security programs.
Japan's Cyber Threat Landscape
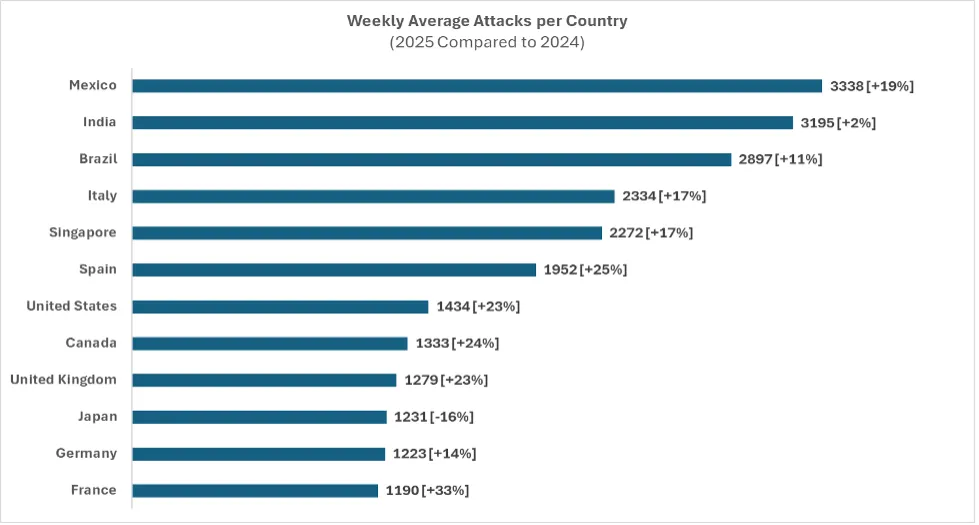
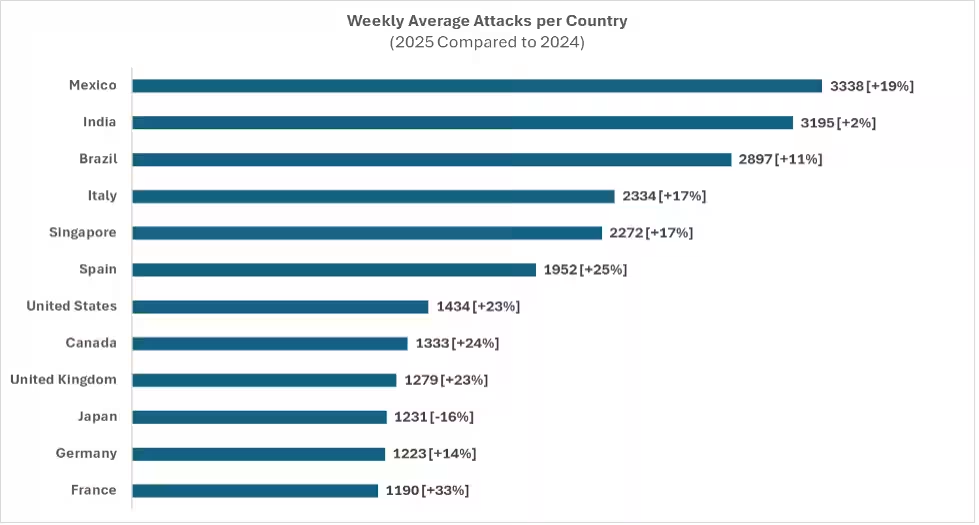
In 2025, Japan faced an average of 1,231 attacks per organization weekly, marking a 16% decrease from 2024’s figures, placing it 10th among the top 12 countries. Manufacturing emerged as the most targeted industry with an average of 1,038 attacks, followed by financial services and consumer goods.
| Country | Average Attacks per Week | Change from 2024 |
|---|---|---|
| ---- | ------ | ------ |
| Japan | 1231 | -16% |
AI Integration in Cyberattacks
The integration of AI into companies has advanced faster than many security measures could keep pace with. Black hats have promptly adopted AI, embedding it throughout their attack chains. Recent data suggests that:
- - 90% of organizations detected high-risk AI prompts in the past three months.
- - 1 in 48 prompts sent to enterprise AI tools were classified as high-risk.
- - Over 16% of prompts displayed indicators of data leaks or privilege misuse.
The infrastructure supporting AI systems is also under direct attack; a study by Lakera, a Check Point subsidiary, found security vulnerabilities in 40% of analyzed servers.
Ransomware’s Evolution
Ransomware attacks are increasing in frequency, now being marked by fragmentation and automation. The year 2025 saw the emergence of smaller, quicker, and more specialized ransomware units, driven by AI automation. This shift has resulted in heightened operational strain on security teams, leading to more frequent and unpredictable attacks.
- - Victims of ransomware attacks increased by 48% year-on-year.
- - The number of Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) groups has grown by 50%.
These attacks do not rely heavily on new vulnerabilities but instead exploit existing access points post-infiltration, utilizing AI to refine targeting and negotiation strategies. Notably, more than half of ransomware victims are based in the United States.
The Hybrid Environment Challenge
Across various industries, the most consistent risk factor has been the uncontrolled expansion of operational environments. As companies employ hybrid infrastructures, the resultant increased exposure is exploited by attackers. There has been a notable rise in using edge devices as entry points for initial access and leveraging unattended devices.
Modern Warfare and Cyber Operations
In 2025, cyber operations have become clearly embedded within broader conflicts, utilizing civilian systems and cloud services. The prevalence of AI in influencing public opinion and executing tactical disruptions in everyday operations poses a significant threat. Unmonitored exposures identified during reconnaissance can quickly become operational assets for adversaries.
Expanding Attack Vectors in Social Engineering
While email remains a primary channel for distributing malicious files, it is increasingly used in conjunction with web, phone, and collaboration tools to bypass technical security measures. Recent statistics indicate that:
- - 1.46% of emails with attachments were malicious.
- - Emails account for 82% of all malicious file delivery methods, while web-based attacks make up 18%.
- - Phone impersonation scams targeting corporations have evolved significantly.
Conclusion
The findings laid out in the Cyber Security Report 2026 illustrate how attackers are merging speed, automation, and trust to launch large-scale attacks. In 2025, there was an 18% increase in cyber incidents compared to the previous year, with organizations facing an average of 1,968 weekly attack attempts. The education/research sector was the most impacted, but considerable increases were also observed in healthcare, government, energy, automotive, hospitality, and agriculture.
As security leaders prepare their strategies for the upcoming year, the message is clear: attacks are working in concert, with measurable impacts. Leveraging insights from Check Point's "Cyber Security Report 2026" is crucial for planning effective responses.
Topics Other)









【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.