
Demonstrating 6G Connectivity Performance with Quantum Computing Innovations
Revolutionizing 6G Connectivity with Quantum Technology
The National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT) has made a significant leap in the field of wireless telecommunications by successfully demonstrating a groundbreaking method that enhances 6G connectivity using quantum computing technology. This innovative technique combines quantum annealing machines with traditional computing systems, enabling simultaneous communication with up to ten devices in outdoor environments, a crucial requirement for the 6G era.
The 6G Landscape
With the anticipated surge in diverse devices such as drones, robots, and XR (extended reality) devices, the demand for massive connection performance is rapidly increasing. Experts predict that the density of connected devices in 6G networks could exceed that of 5G by more than tenfold. To address this burgeoning demand, NICT has developed a hybrid signal processing method that significantly improves multi-device connectivity through quantum computing.
Combining Quantum and Classical Computing
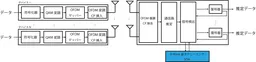
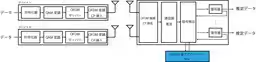
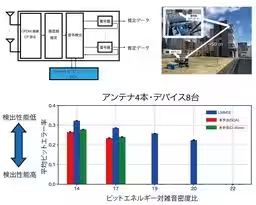
This new approach developed by NICT effectively utilizes a quantum annealing machine, a type of quantum computer, to perform combinatorial optimization required for simultaneous communications at base stations. The traditional challenge in 5G systems limited a single device's ability to communicate over the same frequency and time slot, but the new method facilitates multiple devices transmitting data concurrently. This was made possible by solving complex computational problems related to the signals transmitted by these devices, which follow a rapidly exponential growth pattern with increased device numbers.
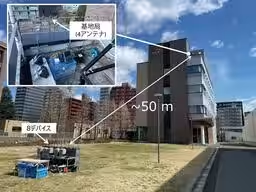
Successful Outdoor Experiments
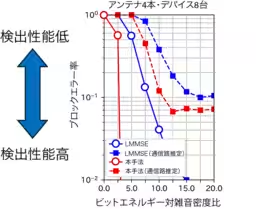
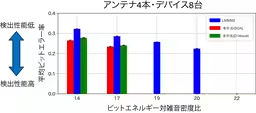
NICT's initial experiments involved sophisticated computer simulations with multiple antenna arrays and varying signal conditions, leading to the successful demonstration of the new signal processing method in real-world outdoor environments. The results revealed an unprecedented ability to achieve zero error rates in signal detection across different methodologies, including using both simulated quantum annealing and D-Wave quantum computing technology. The team confirmed that the technique effectively manages the simultaneous communication demands of up to ten devices.
Addressing Existing Challenges
One significant hurdle addressed in this innovation is the computational heat generated by multiple overlapping signals at base stations, which traditionally complicates the accurate detection of individual device transmissions. The hybridized signal processing method not only mitigates these issues but also incorporates essential techniques for communication environment estimation, which are vital for modern telecommunications.
Future Implications of the Findings
The implications of NICT's research extend beyond merely improving communication efficiency; they represent a pivotal stride towards actualizing a fully connected 6G world. This technology is anticipated to revolutionize the way machines communicate, leading to smarter and more integrated systems capable of managing extensive device networks efficiently and effectively. Future research will aim to handle even larger connection scenarios, further pushing the boundaries of quantum computing's role in telecommunications.
Upcoming Presentation and Acknowledgments
This groundbreaking work will be presented at the forthcoming International Conference on Consumer Communications & Networking (CCNC) 2026, where NICT hopes to engage with leading minds in the field to explore the limitless possibilities that these advances present. This study was partially funded through a grant from the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, showcasing a commitment to advancing innovative technologies in Japan's telecommunications industry.
As the world gears up for 6G, developments like these are critical for enabling the next phase of global connectivity, ensuring our devices can communicate seamlessly and efficiently, thus highlighting the vital intersection of quantum computing and practical telecommunications solutions.
Topics Telecommunications)









【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.