

The Trends in Food Delivery App Usage Across Different Age Groups
Trends in Food Delivery App Usage
Introduction
In recent years, the proliferation of smartphones and changing lifestyles have made food delivery services increasingly popular. A survey conducted by For-IT Co., Ltd., which runs the affiliate platform "afb," examined the usage patterns of food delivery apps among the Japanese population aged 20 to 69. This article delves into the results of the survey, shedding light on various demographics and their interactions with food delivery services.
Survey Overview
The survey involved a sample of 500 individuals across Japan, encompassing multiple age groups. It was conducted through an online research method on February 14, 2025. Participants were asked whether they utilize food delivery apps and to what extent. The options included frequent users, occasional users, those who have previously used them but do not currently do so, as well as those with no intention to use them.
Key Findings
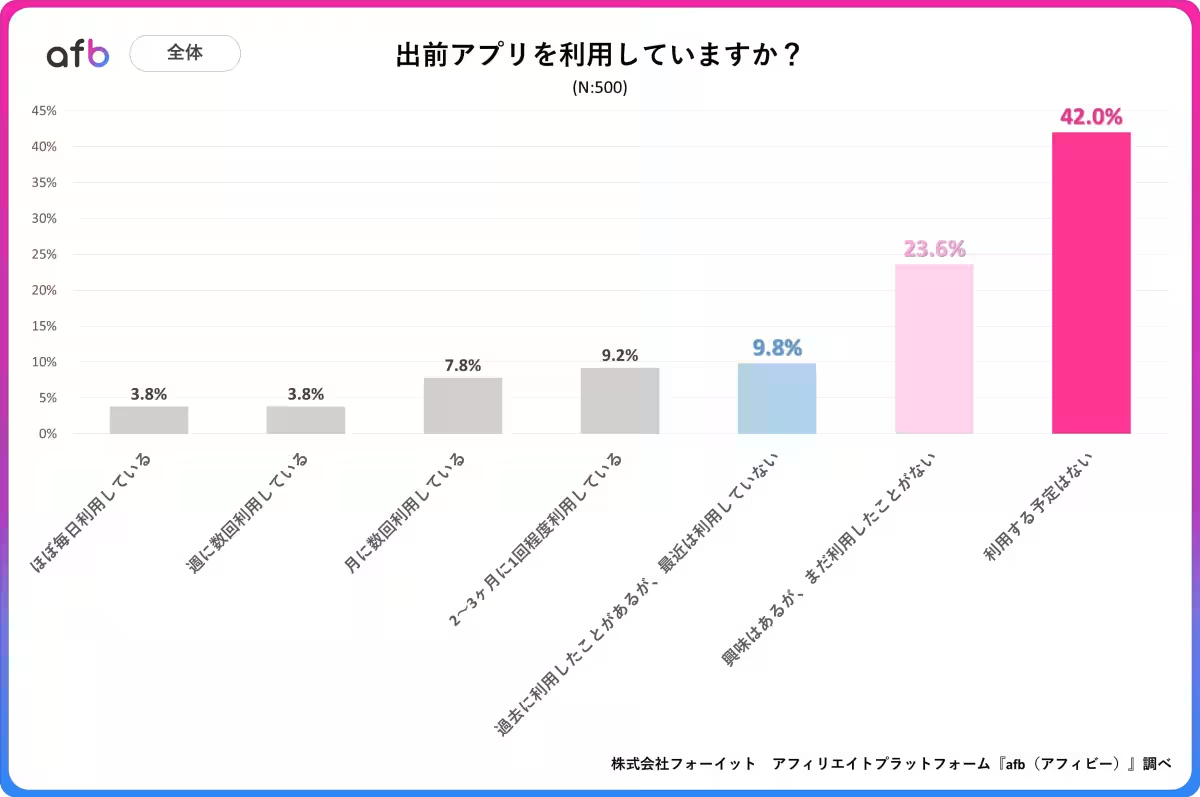
1. High Interest in Food Delivery Apps
The survey revealed that 42% of respondents indicated they had no plans to use food delivery apps. Those expressing interest but who have never used them accounted for 23.6%, suggesting a curiosity that has not yet translated into usage. In contrast, only 15% reported they use food delivery apps on a regular basis.
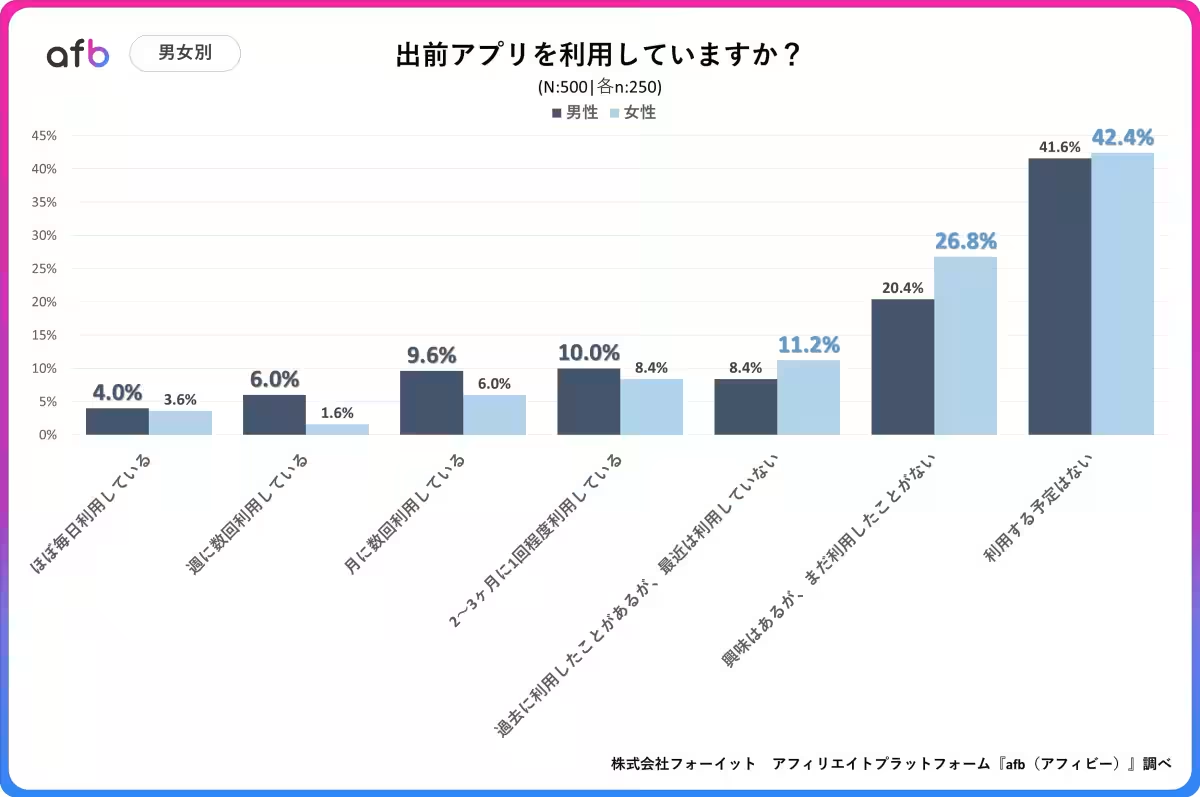
2. Gender Disparities in App Usage
When breaking down the results by gender, it was evident that male respondents showed higher rates of app utilization. Based on family dynamics outlined by the Gender Equality Bureau, men generally spend less time on household chores. Consequently, those returning home late due to longer work hours may prefer food delivery to save time on meal preparation.
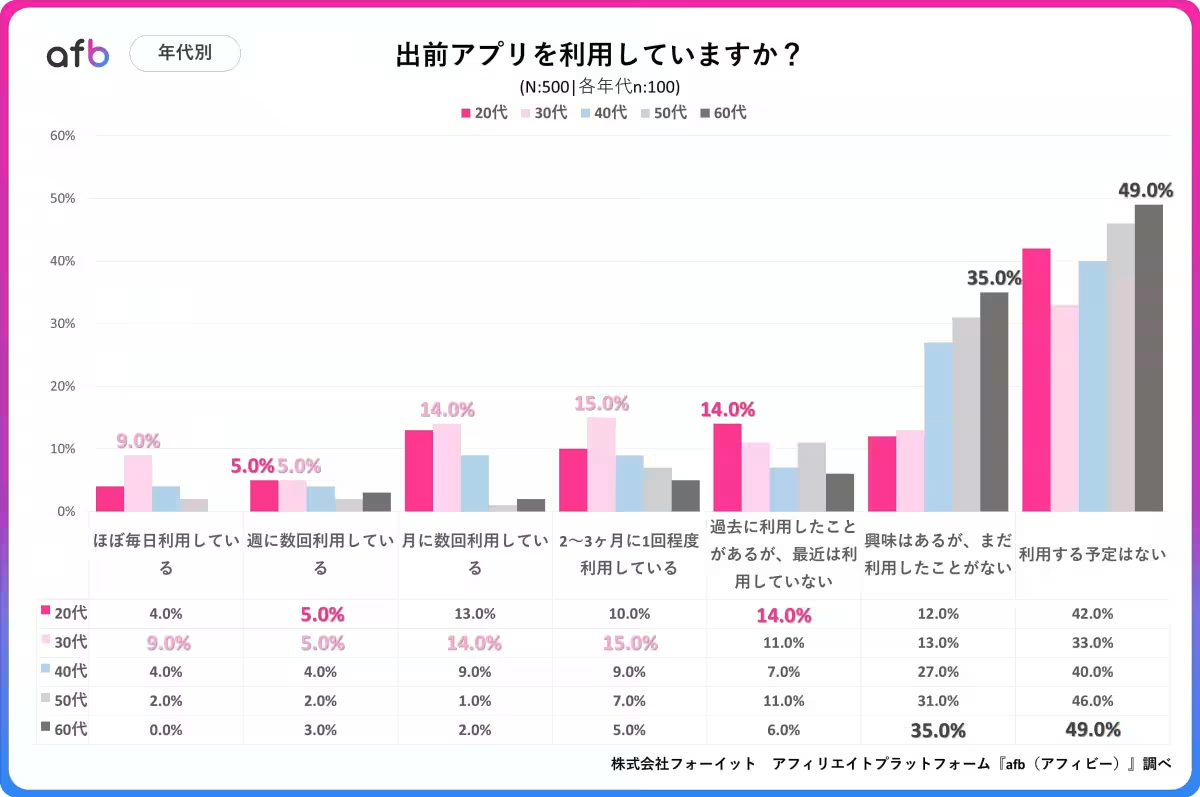
3. Younger Generations Are More Engaged
Looking at age demographics, the survey indicated that among those in their 20s and 30s, over 50-60% have used food delivery apps. This contrasts sharply with those aged 40 and above, particularly those in their 60s, where usage fell to a mere 16%. It's likely that younger, tech-savvy generations show a higher adoption of these services, while older individuals may have reservations about using new technology.
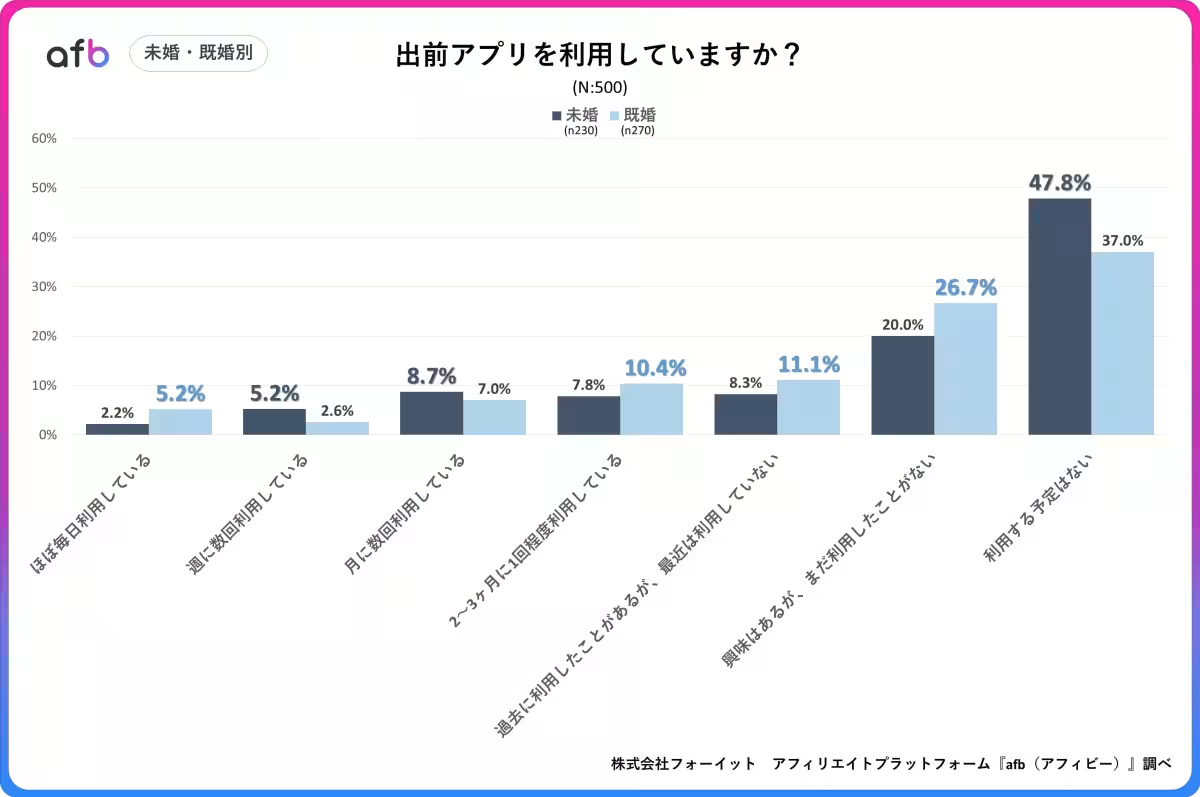
4. Preferences Among Married Individuals
The results also suggested that married individuals are slightly more likely to have used food delivery services compared to singles. One explanation may be that married people are often tasked with preparing meals for the entire family, making the convenience of a delivery app more appealing. Ordering meals for several people can also reduce the individual cost, making these services more attractive.
Competitive Landscape
As food delivery services mature, competition has intensified. Numerous companies, including those traditionally focused on dine-in experiences, are now launching their delivery applications. Amid rising prices, a trend towards saving could contribute to decreased consumption of delivery services. Companies may need to adjust their pricing strategies in response, instigating a new phase of competitive pricing.
Conclusion
The findings from this survey illustrate varying engagement levels with food delivery apps across different age groups and genders. While interest remains substantial, barriers to usage persist, particularly among older generations. Understanding these trends can better inform the strategies that food delivery companies adopt to capture and retain a broader demographic of customers. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, staying abreast of consumer preferences will be essential for the ongoing success of these platforms.
For those interested in the broader implications of this survey and future marketing strategies, insights can be found via the For-IT's AFB.


Topics Consumer Products & Retail)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.