

Exploring the Current Utilization Trends of Generative AI in Japanese Enterprises
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of digital technology, the integration of generative AI tools among businesses is becoming increasingly prevalent. A recent survey conducted by SmartCamp, which runs the SaaS comparison site BOXIL, has shed light on the current state of generative AI adoption across Japanese enterprises. Spanning over a thousand employees across various sectors, this survey investigates usage patterns, organizational adoption rates, and the real-world impact of these technologies on business operations.
Key Findings
The survey, targeting 1,365 employees working in organizations utilizing generative AI tools like ChatGPT and Gemini, reveals key insights:
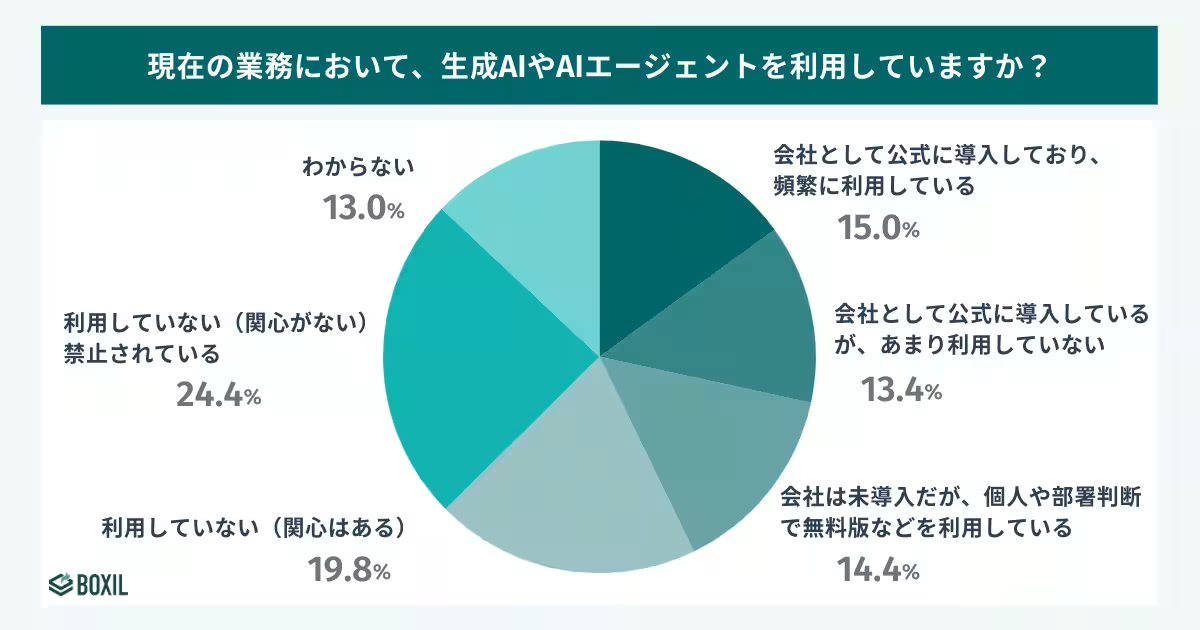
- - While only 28.4% of businesses have officially adopted generative AI, a substantial 42.8% of employees reported using it in their daily operations.
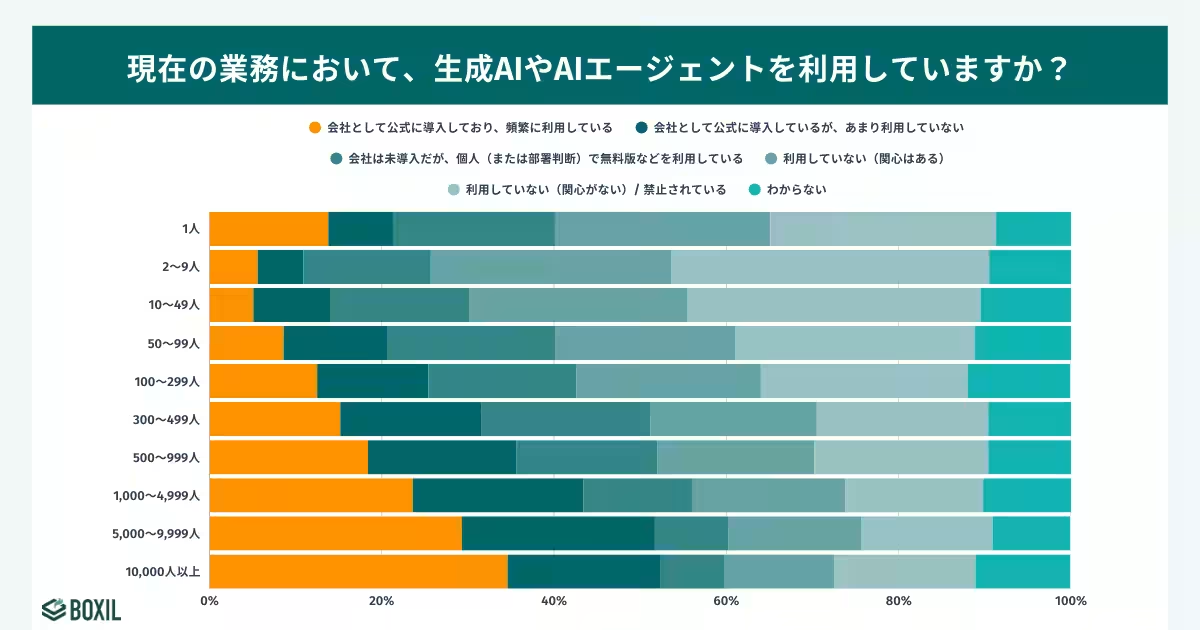
- - Large corporations with over 10,000 employees show a robust adoption rate of 52.3%, indicating that larger organizations are more likely to implement these technologies formally.
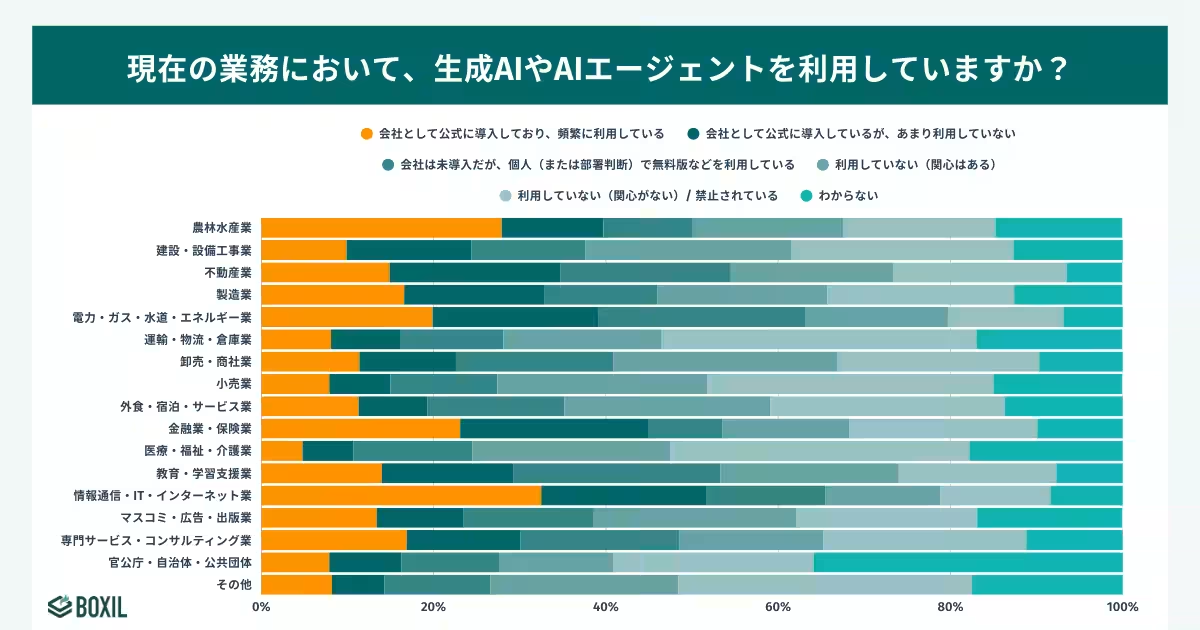
- - The IT and financial sectors also lead the adoption race, with nearly half of the organizations in these fields embracing generative AI solutions.
Utilization Patterns
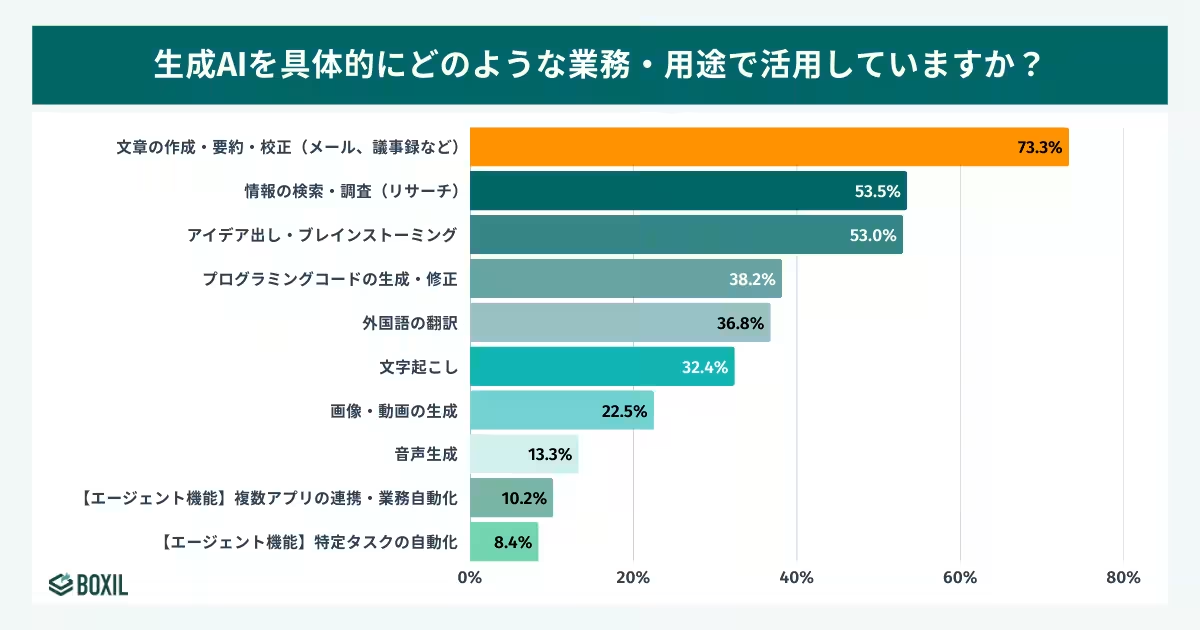
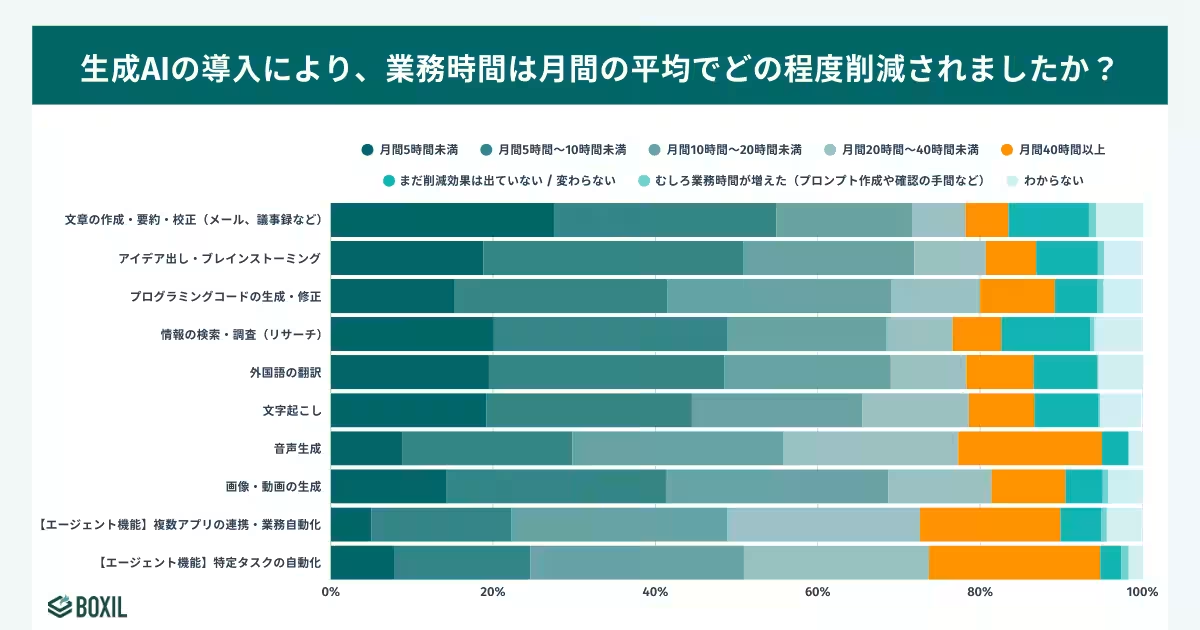
The survey highlights that businesses are primarily utilizing generative AI for content creation and summarization, with 73.3% indicating this as their primary application. However, achieving significant time savings—such as reducing work hours by 40 hours a month—through generative AI remains challenging, particularly for those relying on free versions of these tools. Interestingly, only 5.3% of businesses using generative AI for content tasks have succeeded in achieving such extensive time reductions.
Conversely, an important distinction arises with those leveraging AI as 'agents' for specific tasks. This group represents 21.1% of respondents who reported significant efficiency gains, highlighting the nuanced capabilities of AI when utilized strategically.
Sectorial Insights
Breaking down the data by industry, the findings reflect a stark contrast between various sectors. The information technology and communication sector leads with an impressive 51.7% adoption rate, followed closely by the finance and insurance sectors at 44.9%. Conversely, the healthcare and welfare sectors lag behind, with only 10.7% of organizations officially adopting generative AI.
This gap indicates an interesting phenomenon where personal use surpasses official adoption in certain fields, especially in healthcare, where 13.8% of employees use generative AI informally.
Barriers to Effective Use
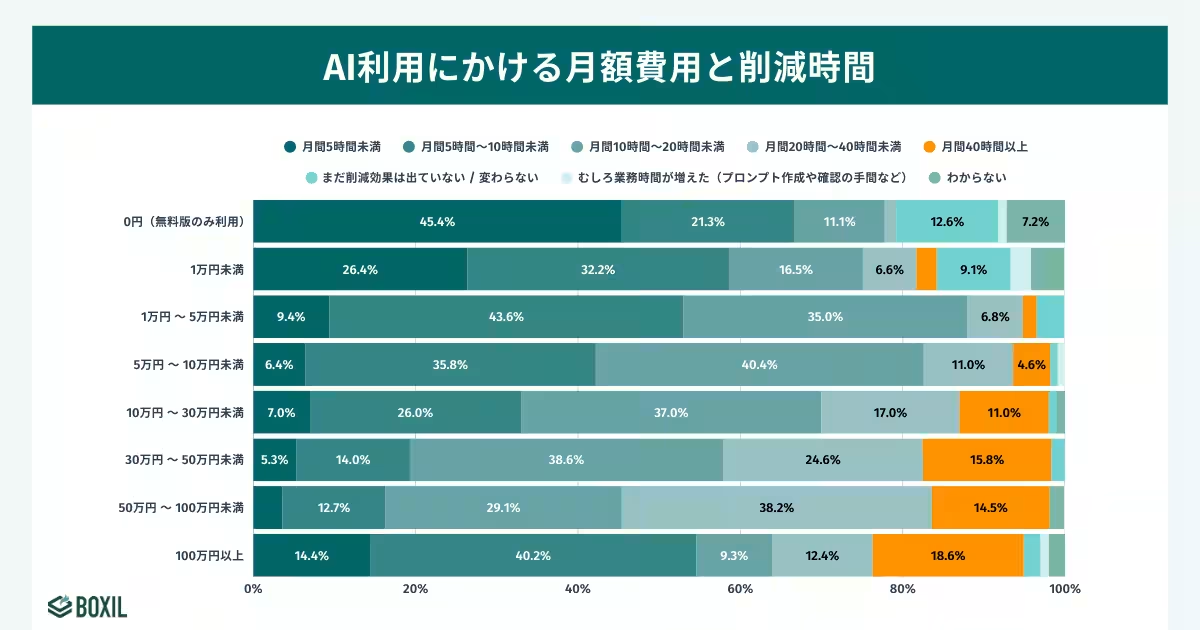
Despite the potential of generative AI to drastically cut down work hours, much of its success hinges on the investment level. Analysis reveals that among companies investing over 1 million yen per month, 18.6% have achieved significant time savings. In contrast, those relying solely on free versions find it exceedingly difficult to yield measurable benefits, with 0.0% seeing reductions exceeding 40 hours.
Conclusion
The survey results from SmartCamp provide a comprehensive look into how generative AI is reshaping organizational practices in Japan. While the official adoption rates may appear modest, the actual utilization rates reflect a significant engagement with these technologies, particularly in larger organizations and specific sectors like IT and finance. As businesses look to the future, the strategic incorporation of generative AI, particularly as specialized agents, could offer unprecedented efficiency and productivity gains in the workplace. These insights not only highlight current trends but also pave the way for discussions on how enterprises can better leverage AI to enhance their operational frameworks.
For further details about the survey, visit BOXIL.

Topics Business Technology)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.